Choose A Reliable Biological Sequence Database for Large Molecule Drug's FTO
Research and development (R&D) efforts in biopharmaceuticals are high, cycles are long, and risks are significant. Companies in this industry heavily rely on core technologies, specialized talents, and intellectual property protection. Drug patents' freedom to operate (FTO) is crucial for determining whether drug candidates can be further commercialized. Therefore, for biopharmaceutical R&D companies, FTO analysis should be integrated throughout product development and company growth.
Biological large molecule patents typically protect amino acid or nucleic acid sequences. Hence, any new drug involving sequences carries potential risks of patent infringement. The lengthy and capital-intensive nature of developing new large-molecule drugs necessitates FTO analysis to guide R&D decision-making and for investors to assess the risks associated with substantial investments.
To perform FTO analysis on large molecule sequences, three mainstream databases are commonly used: STN Biosequences, GenomeQuest (GQ), and Patsnap Bio. However, I recommend utilizing the Patsnap Bio Sequence Database, the world's largest sequence search platform currently offering free trial registrations. Recently, the Bio database launched a groundbreaking "Degenerate Sequence" search database to reduce further the risk of overlooking relevant information during FTO analysis and patent searching. To address the challenges of generic sequences, the Patsnap algorithm engineering team has developed deep learning models using their in-house expertise in Natural Language Processing (NLP), Computer Vision (CV), entity recognition, and coreference resolution technologies. These models identify and parse generic sequence information and substitution details in sequence listings and full patent texts, establishing a comprehensive Degenerate Sequence Search database.
The Patsnap Bio Sequence Database offers comprehensive and feature-rich data, providing multiple scenario-based sequence retrieval options. These include antibody CDR retrieval, multi-sequence combined retrieval, pattern-based sequence search, structural and functional domain search, and drug-gene indexing, catering to the work scenarios of researchers. The database comprehensively collects and processes protein and nucleic acid sequence data from global patents, biological journals, and public biological databases.
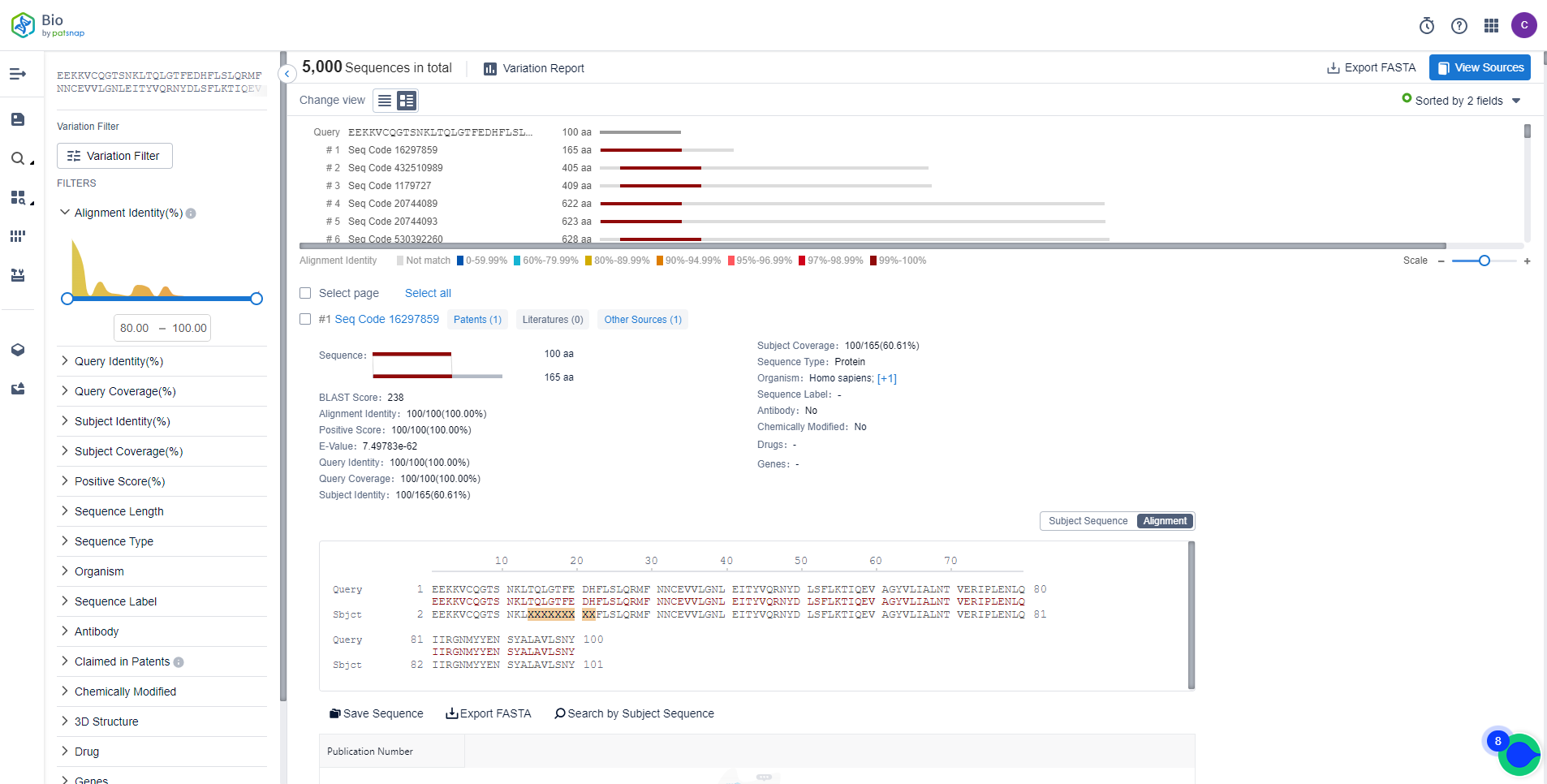
With multiple advanced sequence alignment algorithms, it enables rapid retrieval and analysis of globally known similar sequences, allowing users to assess risks and gather competitive intelligence effectively. The database allows for one-click filtering of core patent sequences, highlights sequence information within patent texts, and provides fast online sequence alignment and analysis for a convenient and user-friendly experience.
Free registration is available for the Bio biological sequence database: https://bio.patsnap.com. Act now to expedite your sequence search tasks.