Deep Scientific Insights on Triazolam's R&D Progress, Mechanism of Action, and Drug Target
Triazolam's R&D Progress
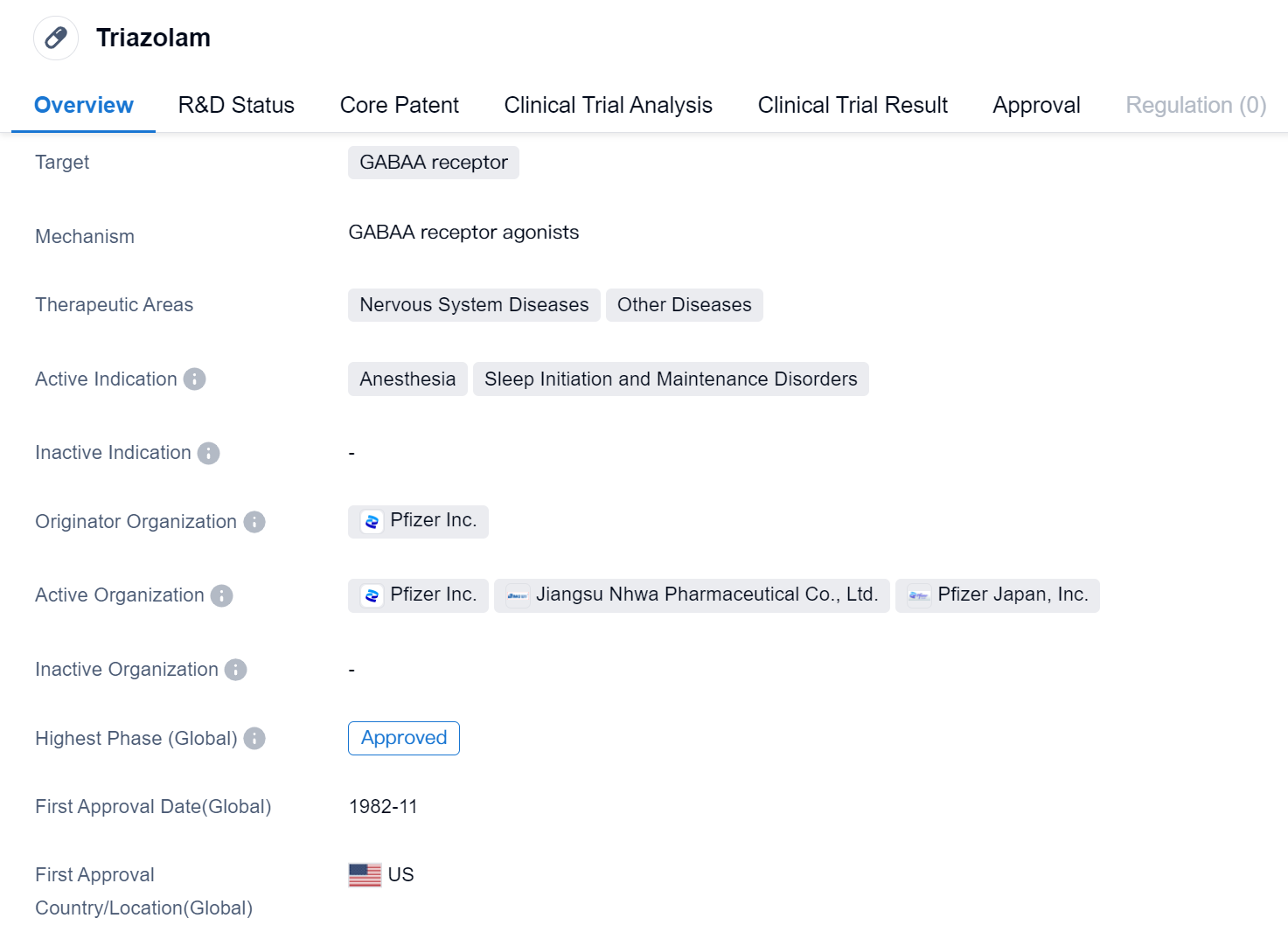
Triazolam is a small molecule drug that targets the GABAA receptor. It is primarily used in the treatment of nervous system diseases and other diseases. The drug is specifically indicated for anesthesia and sleep initiation and maintenance disorders.
Triazolam was developed by Pfizer Inc., a renowned pharmaceutical company. It has received approval for use in multiple countries, including the United States. The drug was first approved in November 1982 in the United States, making it a well-established medication in the market.
As a small molecule drug, Triazolam is designed to interact with the GABAA receptor, which is involved in the regulation of inhibitory neurotransmission in the central nervous system. By targeting this receptor, Triazolam enhances the effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a neurotransmitter that inhibits brain activity. This mechanism of action allows Triazolam to induce sedation and promote sleep, making it effective in treating sleep initiation and maintenance disorders.
In addition to its use in sleep disorders, Triazolam is also utilized as an anesthetic. Its sedative properties make it suitable for inducing and maintaining anesthesia during surgical procedures. This versatility in therapeutic applications contributes to the drug's significance in the field of biomedicine.
Triazolam's approval in the global markets indicates its widespread recognition and acceptance as a safe and effective medication. Its long history of use since 1982 further supports its established position in the pharmaceutical industry.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Triazolam: GABAA receptor agonists
From a biomedical perspective, GABAA receptor agonists are a type of drugs that bind to and activate the GABAA receptors in the brain. GABAA receptors are a type of neurotransmitter receptor that respond to the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). When GABAA receptors are activated, they enhance the inhibitory actions of GABA in the brain, leading to a decrease in neuronal excitability.
By acting as agonists, these drugs enhance the effects of GABA on GABAA receptors, resulting in various pharmacological effects. GABAA receptor agonists are commonly used in the treatment of conditions such as anxiety disorders, insomnia, epilepsy, and muscle spasms. They can help promote relaxation, sedation, and reduce seizure activity by increasing the inhibitory actions of GABA in the brain.
It's important to note that GABAA receptor agonists should be used under medical supervision, as they can have sedative and hypnotic effects, and may cause side effects such as drowsiness, dizziness, and impaired coordination. The specific GABAA receptor agonists used in clinical practice may vary, and their selection depends on the specific medical condition being treated.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Triazolam
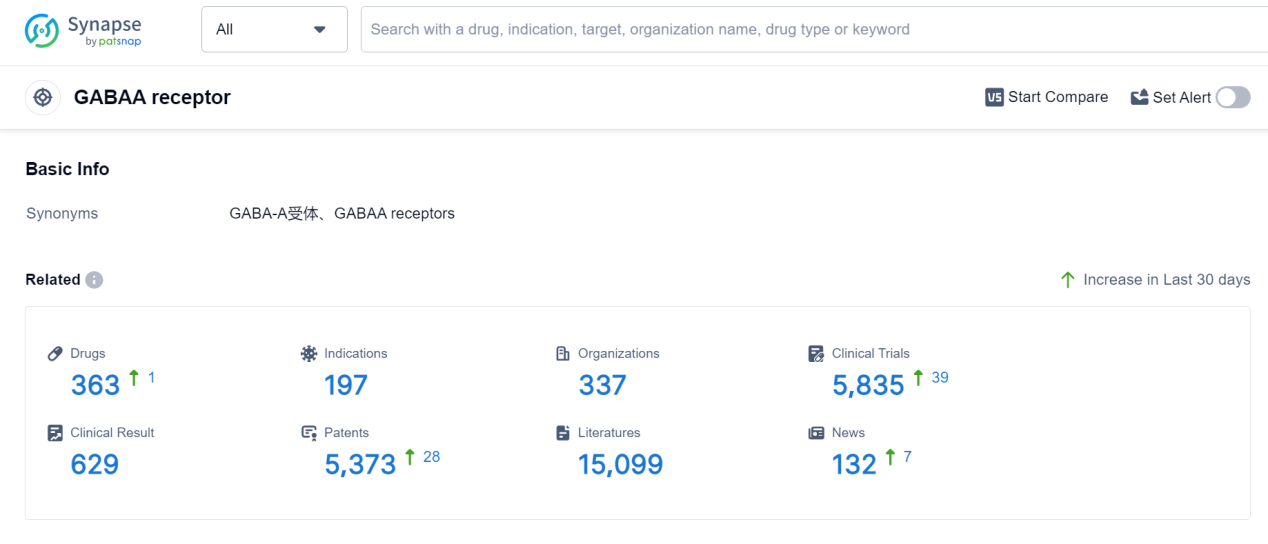
GABAA receptor is a crucial component of the human body's central nervous system. It is a type of neurotransmitter receptor that binds to the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Activation of the GABAA receptor leads to the inhibition of neuronal activity, resulting in a calming and sedative effect. This receptor plays a vital role in regulating anxiety, sleep, muscle relaxation, and the prevention of seizures. Additionally, it is the target of various pharmaceutical drugs, such as benzodiazepines, which enhance the receptor's activity to treat conditions like anxiety disorders, insomnia, and epilepsy. Understanding the function of the GABAA receptor is essential for developing effective medications in the pharmaceutical industry.
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 7 Sep 2023, there are a total of 363 GABAA receptor drugs worldwide, from 337 organizations, covering 197 indications, and conducting 5835 clinical trials.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
Overall, Triazolam is a small molecule drug developed by Pfizer Inc. that targets the GABAA receptor. It is primarily used for the treatment of anesthesia and sleep initiation and maintenance disorders. With its approval in multiple countries, including the United States, Triazolam has proven to be a valuable medication in the field of biomedicine.