Similar Sequence Search for Adeno-associated virus (AAV)
Adeno-associated virus (AAV) is reckoned as one of the most propitious vectors for gene research and therapy. This perception is due to an amalgamation of characteristics such as its variant types, minimal immunogenicity, extensive safety considerations, the extensive range of host cells it can infect (including both dividing and non-dividing cells), its potent dissemination capabilities, and its ability to facilitate prolonged gene expression.
In the context of the Patsnap Bio Sequence Database, it's possible to extract sequences analogous to definite AAV sequences and examine new AAV data from sources accessible to the public, thereby providing a catalyst for advanced AAV research. An illustration of this can be seen in the use of AAV9 mutants:
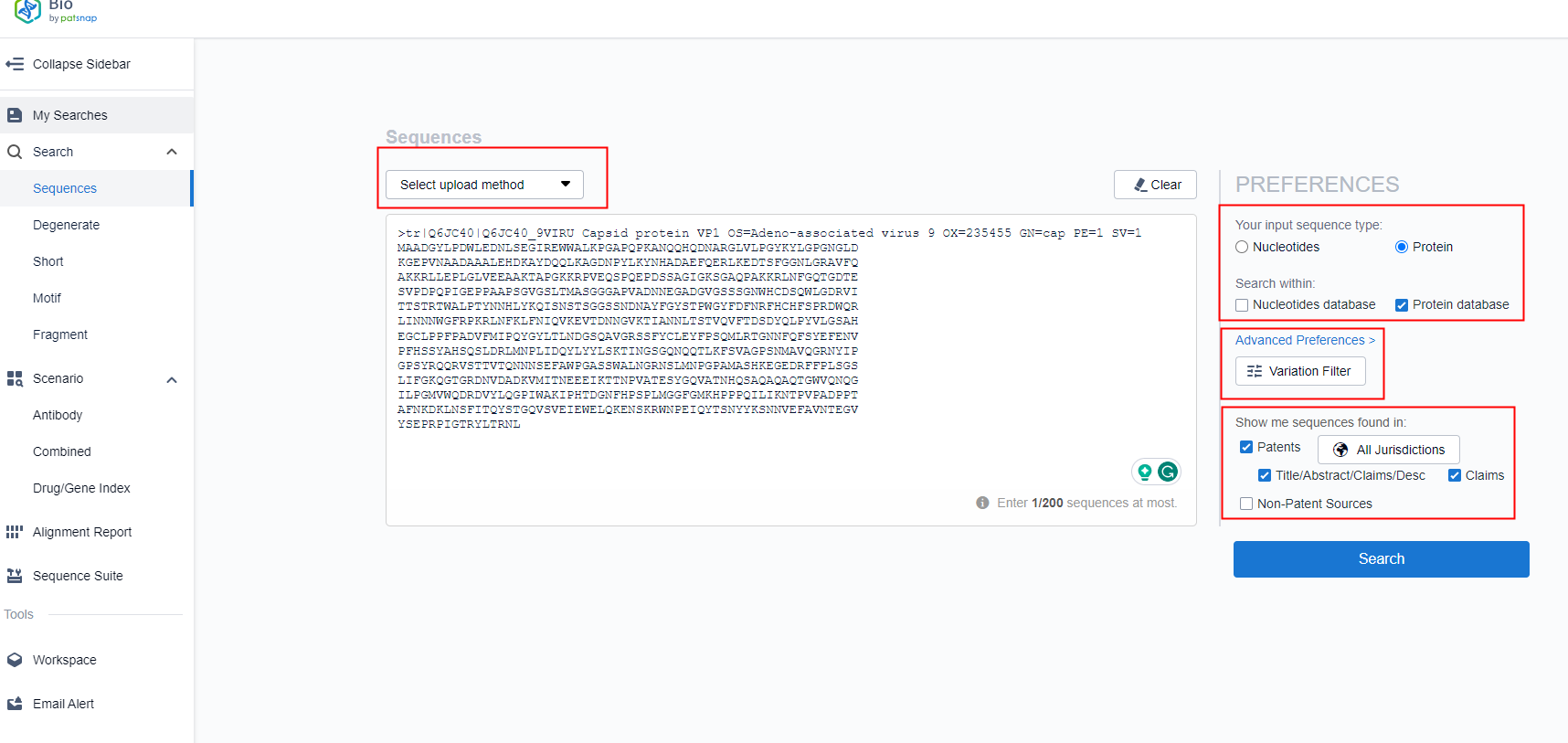
Researchers may initiate by entering the wild-type AAV9 sequence in the regular search section of the Bio database and initiating a filtered hunt for corresponding sequences (Figure 1). Depending on the precise requirements of the search, scholars can engage the "Advanced Settings" feature to tweak the Blast parameters. Upon activating the search button, an array of sequence results replete with comprehensive and precise data is produced. One can utilize the mutation report to gain a broad overview of publicly accessible mutation sequences.
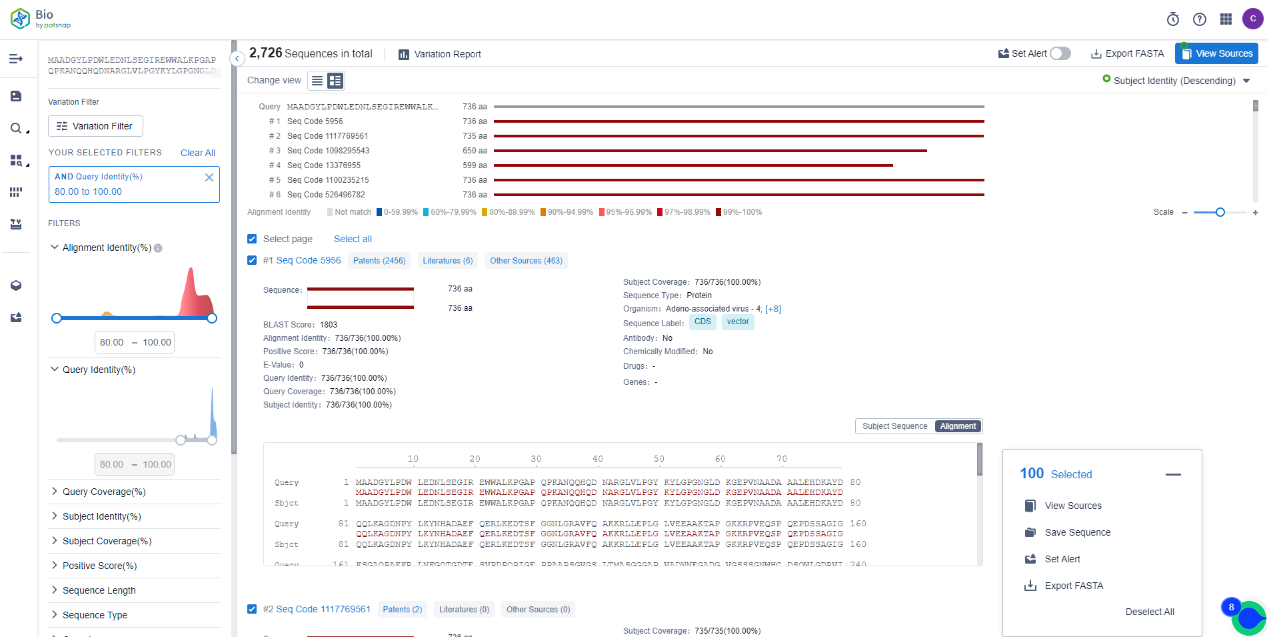
One may delve into the particulars of the matched sequences by clicking the "View Sources" function. Quickly exporting the FASTA file and public data table is also an option.
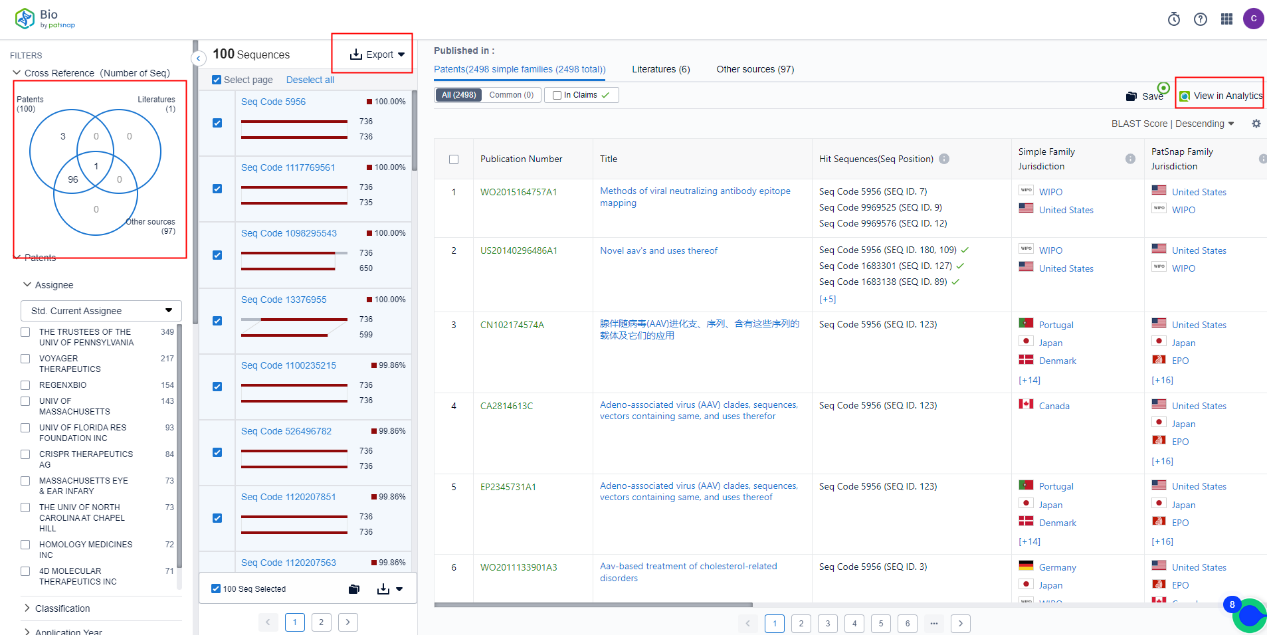
The patent database can be harnessed to conduct a search on research patents associated with AAV9 mutants from the preceding two years, amalgamating target tissues and keywords. In the complete patent texts, the sequence assistant can be employed to locate the sequences and instigate a comparative analysis.
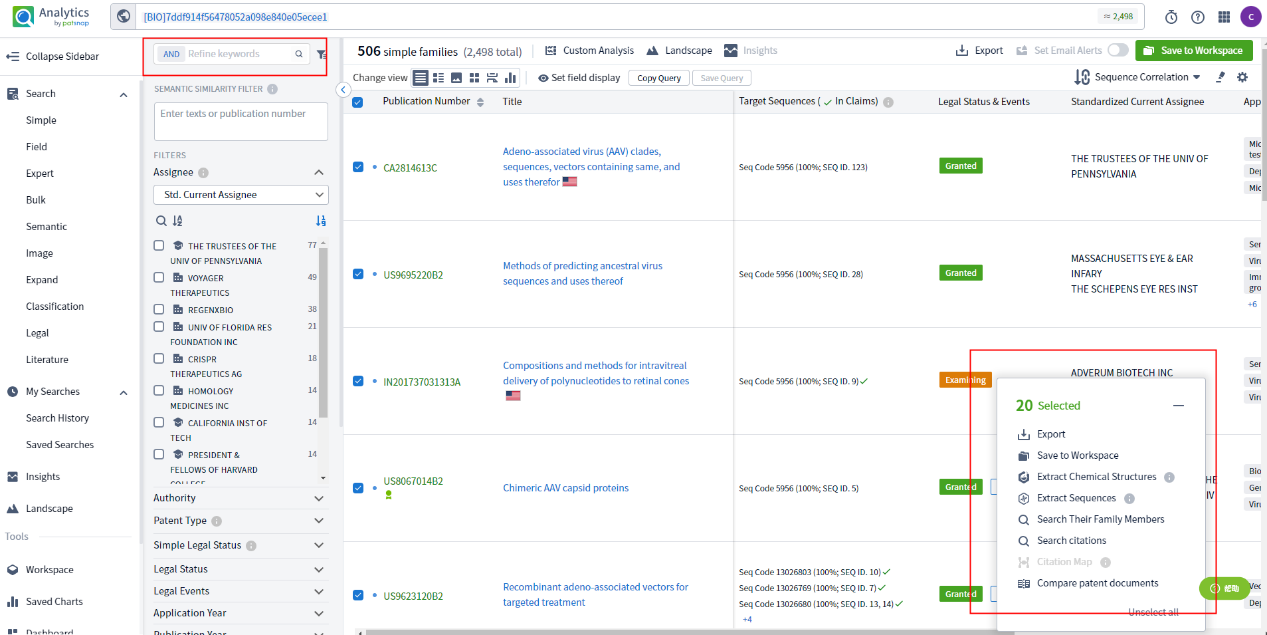
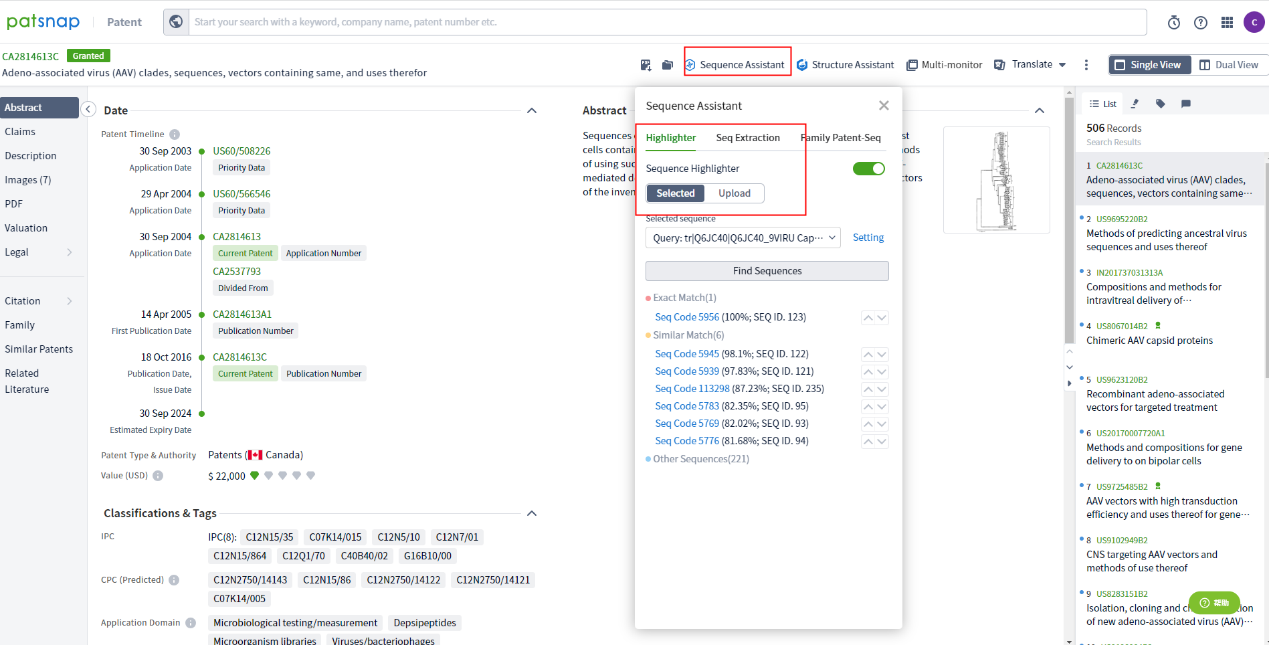
Patsnap Bio represents the most extensive sequence search platform within the Patsnap database framework. The platform incorporates Artificial Intelligence (AI) and human-curated data for comprehensive protein and nucleotide sequence data processing from worldwide patents, biological periodicals, and public repositories. Crucial biological sequences receive manual annotation, and overlooked structural modifications are highlighted for enhanced sequence retrieval efficiency.
Free registration is currently available to utilize the Bio biological sequence database: https://bio.patsnap.com. Act now to expedite your antibody sequence alignment tasks.




