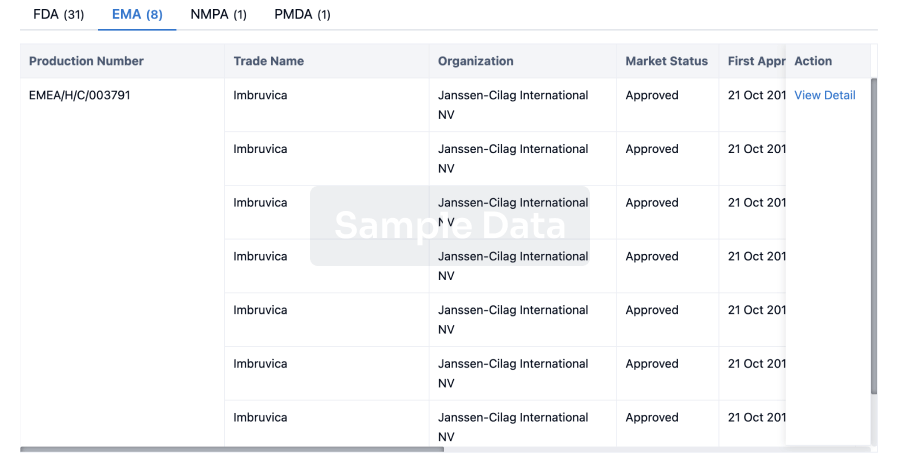
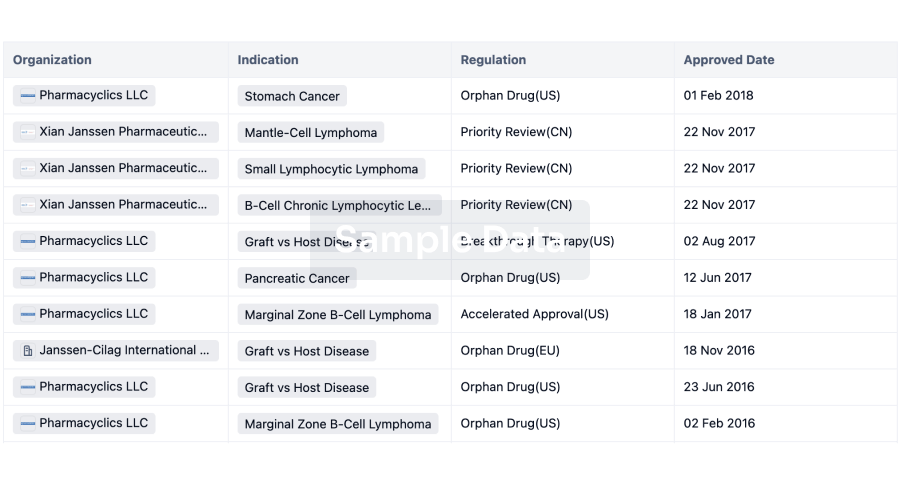
Artemisinin, which contains a sesquiterpene trioxane skeleton, was originally isolated from Artemisia annua L., a traditional Chinese medicine with antimalarial activity.The 2015 Nobel Prize in Physiol. or Medicine was awarded to Youyou Tu for her discoveries concerning a novel therapy against malaria.Over the past several decades, a series of novel artemisinin derivatives have been synthesized and evaluated for antimalarial and immunosuppressive activities.1 Artesunate, artemether and dihydroartemisinin have expanded the clin. applications of artemisinin, which has indeed become a gift from traditional Chinese medicine to the world.Our groups have identified several water-soluble artemisinin derivatives that exhibit strong immunosuppressive activity, among which SM905 and SM934 exert notable anti-inflammatory effects in vitro and in vivo.2, 3, 4.SM905 and SM934 significantly inhibit the proliferation of splenocytes induced by various mitogens and IFN-γ production triggered by anti-CD3/CD28 in vitro, as well as the immune response against ovalbumin in vivo.4, 5.These artemisinin derivatives have been investigated for potential therapeutic effects and underlying mechanisms in models of autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), exptl. autoimmune encephalomyelitis, membranous nephropathy, collagen-induced arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease (Yan, 2017, unpublished data), as listed in Figure 1.SLE is a refractory chronic autoimmune disease that is characterized by the loss of tolerance to and sustained autoantibody production against self-antigen, which results in the development of immune complex-mediated renal and skin injuries.6.The etiol. of SLE is multifactorial and includes genetic susceptibility, epigenetic regulation and environment factors.Administration of SM934 to MRL/lpr mice greatly ameliorates proteinuria and renal lesion and results in decreased levels of serum biochem. indexes, inflammatory cytokines and autoantibodies.7 SM934 inhibits both Th1 and Th17 cell responses ex vivo.Furthermore, SM934 significantly restores the B cell compartment in the spleens of MRL/lpr mice; this compound increases the number of quiescent B cells and maintains germinal center B cells, while decreasing the number of activated B cells and plasma cells.8.Consistent with the results obtained in MRL/lpr mice, SM934 inhibits Toll-like receptor ligand-associatedB cell activation and plasma cell differentiation in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells.In addition, SM934 treatment for 3 or 6 mo dramatically slows the progression of glomerulonephritis and increases the survival rate of lupus-prone female NZB/W F1 mice via inhibiting pathogenic helper T cell development.Increasing evidence has revealed the essential role of the initiation of innate inflammatory responses in the development of lupus, in which macrophages are generally regarded as a bridge between innate and adaptive immunity.9.SM934 promotes IL-10 secretion by macrophages obtained from NZB/W F1 mice and ovalbumin-immunized C57BL/6 mice, as well as by IFN-γ-primed peritoneal macrophages.10.The kidney is often a target of pathogenic renal autoantigen or systemic autoimmune responses.11 Membranous nephropathy, a common manifestation of nephrotic syndromes in adults, is an immune-mediated disease that is distinguished by the deposition of immune complexes in the glomerular basement membrane and podocytes.12.SM934 treatment attenuates kidney injury and renal fibrosis by reducing proteinuria and circulating antibodies, as well as decreasing immune complex deposition in the kidney in a rat model of membrane nephropathy induced by anti-Fx1A serum.13 Furthermore, SM934 can modulate the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway and can block tubular epithelial mesenchymal transition.13.This study provides evidence that SM934 may be a treatment option for proteinuric renal diseases.Multiple sclerosis is a demyelinating disease in which autoreactive myelin-specific T cells enter the central nervous system and disrupt the insulating covers of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord, resulting in a chronic inflammatory response.14.Exptl. autoimmune encephalomyelitis symptoms resulting from immunization with MOG35-55 provide a classical animal model of multiple sclerosis.SM934 treatment can reverse the clin. and histol. signs of exptl. autoimmune encephalomyelitis, both prophylactically and therapeutically.15.Furthermore, SM934 enlarges the population of Tregs in both the peripheral immune system and in the lesioned region of the central nervous system, indicating the prominent role of Tregs in regulating immune responses in exptl. autoimmune encephalomyelitis mice.Rheumatoid arthritis is a heterogeneous chronic systemic autoimmune disease that is characterized by bone destruction, synovial inflammation and joint deformity.16.Multiple studies have demonstrated that circulating autoantibodies, inflammatory cytokines and disturbances in the proportion and activation of lymphocytes are closely associated with rheumatoid arthritis pathogenesis.16, 17.SM934 treatment greatly attenuates arthritis severity, joint swelling and bone erosion and destruction, and similar effects have been observed following SM905 treatment.2, 18.Moreover, SM905- and SM934-treated arthritic mice manifest with suppressed bovine type II collagen-specific immune responses and inflammatory and pathogenic Th17 responses.Administration of SM934 also reduces the polarization of naive CD4+ T cells into T follicular helper cells by dampening IL-21 downstream signaling through STAT3.After years of effort, SM934 was approved in 2015 by the Chinese Food and Drug Administration for phase I/II/III clin. trials for SLE treatment.A phase I study at the Clin. Trials Research Center of Shanghai Xuhui District Central Hospital is ongoing, and a preclin. study for inflammatory bowel disease is being performed to expand the second indications of SM934.Altogether, the potential uses of SM934, a paragon of immunosuppressant discovery based on artemisinin derivatives, should encourage pharmacists to pay more attention to traditional Chinese medicine, a treasure trove for new drug discovery.