Request Demo
Last update 08 May 2025
LT-ZP001
Last update 08 May 2025
Overview
Basic Info
Drug Type Synthetic peptide |
Synonyms oligopeptide (Logical) |
Target- |
Action- |
Mechanism- |
Therapeutic Areas |
Active Indication- |
Inactive Indication |
Originator Organization |
Active Organization- |
Inactive Organization |
License Organization- |
Drug Highest PhaseDiscontinuedDiscovery |
First Approval Date- |
Regulation- |
Related
100 Clinical Results associated with LT-ZP001
Login to view more data
100 Translational Medicine associated with LT-ZP001
Login to view more data
100 Patents (Medical) associated with LT-ZP001
Login to view more data
6
Literatures (Medical) associated with LT-ZP00101 Mar 2024·Journal of Advanced Research
Potential nutritional strategies to prevent and reverse sarcopenia in aging process: Role of fish oil-derived ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, wheat oligopeptide and their combined intervention
Article
Author: Yang, Chao ; Yang, Xian ; Wang, Yuanyuan ; Yang, Ligang ; Liu, Hechun ; Xia, Hui ; Xu, Dengfeng ; Sun, Jihan ; Pan, Da ; Gao, Han ; Sun, Guiju ; Wang, Shaokang ; Lu, Yifei
01 Dec 2019·Journal of Food BiochemistryQ3 · AGRICULTURAL & FORESTRY SCIENCE
Hypoglycemic effects and biochemical mechanisms of Pea oligopeptide on high‐fat diet and streptozotocin‐induced diabetic mice
Q3 · AGRICULTURAL & FORESTRY SCIENCE
Article
Author: Cai, Muyi ; Fang, Lei ; Gu, Ruizeng ; Wei, Ying ; Lu, Jun ; Qin, Xiuyuan ; Wang, Yuqing ; Zhang, Ruixue
01 May 1996·StrokeQ1 · MEDICINE
Treatment of Focal Cerebral Ischemia With Synthetic Oligopeptide Corresponding to Lectin Domain of Selectin
Q1 · MEDICINE
Article
Author: Toyoda, Tomikatsu ; Zhang, Shi-Ming ; Kirino, Takaaki ; Morikawa, Eiharu ; Seko, Yoshinori
8
News (Medical) associated with LT-ZP00124 Oct 2022
A deal with Myovant will give Sumitomo control of a pipeline prospect, MVT-602.
Sumitomo has landed its takeover target. After seeing Myovant turn down its original offer, the Japanese drugmaker has added almost 20% to its price to get the deal done and snag a phase 2 in vitro fertilization asset.
Osaka-based Sumitomo became a major shareholder in Myovant in 2019 and, having seen its partner’s share price fall from above $20 to briefly below $10, made a move to buy the remaining 48% of the drug developer earlier this month. Myovant promptly knocked back the $22.75-a-share offer but left the door open to negotiations. Sumitomo returned with an offer of $27 a share and persuaded Myovant to sign.
The deal centers on two commercial products, Orgovyx and Myfembree, but will also give Sumitomo control of a pipeline prospect, MVT-602. Takeda tried and failed to develop the oligopeptide kisspeptin-1 receptor agonist as a treatment for low levels of testosterone and other sex hormones.
After missing the endpoints in phase 2 trials, Takeda offloaded the rights to the drug candidate as part of the deal with Roivant Sciences that birthed Myovant. While Takeda studied the molecule, then known as TAK-448, in men with sex hormone disorders, the new partners pitched it for use in female infertility at the time of their deal in 2016.
Since then, Myovant has published phase 1 and phase 2a data on the candidate, linking it to a surge in luteinizing hormone associated with high and dose-dependent rates of ovulation. The company framed the data as evidence that MVT-602 could become a safe alternative egg-maturation trigger.
Yet the progress of, and investment in, MVT-602 has stalled. In its 2021-22 financial year, Myovant racked up $318,000 in R&D costs specific to the candidate, down from $4.9 million in 2018-19. In theory, Sumitomo, a larger company, has the resources to kick-start development, but it made no mention of the molecule in its statement to disclose the Myovant merger.
Acquisition
06 Aug 2022
Data from the Phase 3 SPIRIT program showed MYFEMBREE reduced menstrual pain and non-menstrual pelvic pain in premenopausal women with endometriosis, and a loss of mean bone mineral density of less than 1% from baseline through one year of treatment Myovant and Pfizer will continue to jointly commercialize MYFEMBREE, with product available immediatelyMyovant to host conference call and webcast on Monday, August 8, 2022, at 8:30 a.m. Eastern Time / 5:30 a.m. Pacific Time BASEL, Switzerland and NEW YORK, Aug. 05, 2022 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Myovant Sciences (NYSE: MYOV) and Pfizer Inc. (NYSE: PFE) today announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved MYFEMBREE® (relugolix 40 mg, estradiol 1 mg, and norethindrone acetate 0.5 mg) as a one-pill, once-a-day therapy for the management of moderate to severe pain associated with endometriosis in pre-menopausal women, with a treatment duration of up to 24 months. The approval is supported by one-year efficacy and safety data, including 24-week data from the Phase 3 SPIRIT 1 and SPIRIT 2 trials, which were published in The Lancet, and the first 28 weeks of an open-label extension study for eligible women who completed either SPIRIT 1 or SPIRIT 2. MYFEMBREE also is approved for heavy menstrual bleeding associated with uterine fibroids in pre-menopausal women. Myovant and Pfizer will continue to jointly commercialize MYFEMBREE in the U.S. and product is available immediately. “Endometriosis is a painful, chronic disease with limited therapies to manage symptoms,” said Juan Camilo Arjona Ferreira, M.D., Chief Medical Officer of Myovant Sciences, Inc. “The new MYFEMBREE indication helps advance our mission to redefine care for women by helping address a disease with high unmet need, giving women and physicians a new meaningful treatment option to manage moderate to severe pain associated with endometriosis.” “This approval is an important milestone reflecting Pfizer and Myovant’s commitment to women’s health in areas of significant unmet need,” said James Rusnak, M.D., Ph.D., Senior Vice President, Chief Development Officer, Internal Medicine and Hospital, Global Product Development at Pfizer. “We look forward to making MYFEMBREE available to women with endometriosis and broadening their options in managing this complex disorder.” MYFEMBREE offers an effective, once-daily treatment option for the management of moderate to severe pain associated with endometriosis, with a treatment duration of up to 24 months. Endometriosis is a serious chronic condition that requires long-term interventions. Optimization of medical therapies is the recommended treatment paradigm.1,2,3 MYFEMBREE introduces an option for up to two years of pharmacological management of moderate to severe pain associated with endometriosis in pre-menopausal women. “The data from the SPIRIT studies showed the clinical benefit that relugolix combination therapy can have on moderate to severe pain associated with endometriosis and how it can impact patients,” said Linda Giudice, M.D., Ph.D., Distinguished Professor at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), and Chair, SPIRIT Program Steering Committee. “This newly approved option for patients with pain from endometriosis offers the convenience of one pill taken once daily with a mean change in bone mineral density of <1% that did not appear to worsen at 12 months of treatment; however, monitoring is recommended.” This approval is supported by one-year data from the Phase 3 SPIRIT program, which included two 24-week multi-national clinical studies (SPIRIT 1 and SPIRIT 2) in more than 1,200 women with pain associated with endometriosis, as well as the first 28 weeks of an open-label extension study to assess its longer-term use. Overall, these studies showed MYFEMBREE reduced menstrual pain and non-menstrual pelvic pain with a loss of mean bone mineral density of less than 1% from baseline through one year of treatment.4 SPIRIT 1 and 2 each met their co-primary endpoints with 75% of women in the MYFEMBREE group in both studies achieving a clinically meaningful reduction in dysmenorrhea compared with 27% and 30% of women in the placebo groups at Week 24, respectively (both p <0.0001). For non-menstrual pelvic pain, treatment with MYFEMBREE demonstrated a clinically meaningful reduction in pain in 59% and 66% of women, compared with 40% and 43% of women in the placebo groups (p < 0.0001). Adverse reactions occurring in at least 3% of women treated with MYFEMBREE and greater than placebo were: headache, vasomotor symptoms, mood disorders, abnormal uterine bleeding, nausea, toothache, back pain, decreased sexual desire and arousal, arthralgia, fatigue, and dizziness. The open-label extension study for eligible women who completed either SPIRIT 1 or SPIRIT 2 showed mean bone mineral density loss of less than 1% from baseline through one year of treatment; some patients (19.7%) had losses >3%. Annual bone density measurement is recommended while treating women for endometriosis. MYFEMBREE is available immediately to patients with moderate to severe pain associated with endometriosis with a prescription from their healthcare provider. Myovant and Pfizer also are committed to supporting women in the U.S. who are prescribed MYFEMBREE throughout their treatment journeys. The MYFEMBREE Support Program provides access support services, including insurance benefits checks, prior authorization support, co-pay support for commercially insured patients, and patient assistance for qualifying uninsured patients. Program terms and conditions apply. For more information and additional resources, please contact 833-MYFEMBREE (833-693-3627), 8 a.m. – 8 p.m. Eastern Time, Monday – Friday. Myovant Conference CallMyovant will hold a conference call on Monday, August 8, 2022, at 8:30 a.m. Eastern Time / 5:30 a.m. Pacific Time to discuss the FDA approval of MYFEMBREE for the management of moderate to severe pain associated with endometriosis. Investors and the general public may access the live webcast here. The live webcast can also be accessed by visiting the company’s investor relations page of Myovant’s website at: https://investors.myovant.com/. About EndometriosisEndometriosis is a condition in which tissue similar to the uterine lining is found outside of the uterine cavity, which often causes disruptive symptoms like painful periods, fatigue, pain in the lower back and abdomen, heavy menstrual bleeding, and even painful or difficult sexual intercourse. For endometriosis-associated pain, current treatment options include prescription and over-the-counter pain medications, combined oral contraceptives, progestins, danazol, GnRH agonists and antagonists, and surgical interventions. Endometriosis can also impact general physical, mental, and social well-being, requiring a multi-disciplinary approach to care. Approximately 190 million women suffer from symptoms of endometriosis globally.5 In the U.S., there are approximately 7.5 million premenopausal women with endometriosis and approximately 75-80 percent of them are symptomatic.6,7,8,9 Many women with pain associated with endometriosis are not able to manage their pain symptoms with current treatment options, underscoring the high unmet need for this disease.10 It can take between four and eleven years to get an endometriosis diagnosis11,12,13 and for some women, current treatment options do not provide relief.14 About MYFEMBREE®MYFEMBREE (relugolix, estradiol, and norethindrone acetate) is a once-daily oral treatment approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for the management of moderate to severe pain associated with endometriosis, with a treatment duration of up to 24 months. It is also currently available in the U.S. for the management of heavy menstrual bleeding associated with uterine fibroids in premenopausal women, with a treatment duration of up to 24 months. MYFEMBREE contains relugolix, which reduces the amount of estrogen (and other hormones) produced by ovaries, estradiol (an estrogen) which may reduce the risk of bone loss, and norethindrone acetate (a progestin) which is necessary when women with a uterus (womb) take estrogen. For full prescribing information including Boxed Warning and patient information, please click here. Indications and UsageMYFEMBREE is indicated in premenopausal women for the management of: Heavy menstrual bleeding associated with uterine leiomyomas (fibroids)Moderate to severe pain associated with endometriosis Limitations of Use: Use of MYFEMBREE should be limited to 24 months due to the risk of continued bone loss which may not be reversible. IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION BOXED WARNING: THROMBOEMBOLIC DISORDERS AND VASCULAR EVENTS Estrogen and progestin combination products, including MYFEMBREE, increase the risk of thrombotic or thromboembolic disorders including pulmonary embolism, deep vein thrombosis, stroke and myocardial infarction, especially in women at increased risk for these events.MYFEMBREE is contraindicated in women with current or a history of thrombotic or thromboembolic disorders and in women at increased risk for these events, including women over 35 years of age who smoke or women with uncontrolled hypertension. CONTRAINDICATIONSMYFEMBREE is contraindicated in women with any of the following: high risk of arterial, venous thrombotic, or thromboembolic disorder; pregnancy; known osteoporosis; current or history of breast cancer or other hormone-sensitive malignancies; known hepatic impairment or disease; undiagnosed abnormal uterine bleeding; known hypersensitivity to components of MYFEMBREE. WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONSThromboembolic Disorders: Discontinue immediately if an arterial or venous thrombotic, cardiovascular, or cerebrovascular event occurs or is suspected. Discontinue at least 4 to 6 weeks before surgery associated with an increased risk of thromboembolism, or during periods of prolonged immobilization, if feasible. Discontinue immediately if there is sudden unexplained partial or complete loss of vision, proptosis, diplopia, papilledema, or retinal vascular lesions and evaluate for retinal vein thrombosis as these have been reported with estrogens and progestins. Bone Loss: MYFEMBREE may cause a decrease in bone mineral density (BMD) in some patients, which may be greater with increasing duration of use and may not be completely reversible after stopping treatment. Consider the benefits and risks in patients with a history of low trauma fracture or risk factors for osteoporosis or bone loss, including medications that may decrease BMD. Assessment of BMD by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) is recommended at baseline in all women. During treatment, periodic DXA is recommended for women with heavy menstrual bleeding due to uterine fibroids; in those with moderate to severe endometriosis pain, annual DXA is recommended. Consider discontinuing MYFEMBREE if the risk of bone loss exceeds the potential benefit. Hormone-Sensitive Malignancies: Discontinue MYFEMBREE if a hormone-sensitive malignancy is diagnosed. Surveillance measures in accordance with standard of care, such as breast examinations and mammography are recommended. Use of estrogen alone or estrogen plus progestin has resulted in abnormal mammograms requiring further evaluation. Suicidal Ideation and Mood Disorders (Including Depression): Evaluate patients with a history of suicidal ideation, depression, and mood disorders prior to initiating treatment. Monitor patients for mood changes and depressive symptoms including shortly after initiating treatment, to determine whether the risks of continuing therapy with MYFEMBREE outweigh the benefits. Patients with new or worsening depression, anxiety, or other mood changes should be referred to a mental health professional, as appropriate. Advise patients to seek immediate medical attention for suicidal ideation and behavior and reevaluate the benefits and risks of continuing MYFEMBREE. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor antagonists, including MYFEMBREE, have been associated with mood disorders (including depression) and suicidal ideation. Hepatic Impairment and Transaminase Elevations: Steroid hormones may be poorly metabolized in these patients. Instruct women to promptly seek medical attention for symptoms or signs that may reflect liver injury, such as jaundice or right upper abdominal pain. Acute liver test abnormalities may necessitate the discontinuation of MYFEMBREE use until the liver tests return to normal and MYFEMBREE causation has been excluded. Gallbladder Disease or History of Cholestatic Jaundice: Discontinue MYFEMBREE if signs or symptoms of gallbladder disease or jaundice occur. For women with a history of cholestatic jaundice associated with past estrogen use or with pregnancy, assess the risk-benefit of continuing therapy. Studies among estrogen users suggest a small increased relative risk of developing gallbladder disease. Elevated Blood Pressure: For women with well-controlled hypertension, monitor blood pressure and stop MYFEMBREE if blood pressure rises significantly. Change in Menstrual Bleeding Pattern and Reduced Ability to Recognize Pregnancy: Advise women to use non-hormonal contraception during treatment and for one week after discontinuing MYFEMBREE. Avoid concomitant use of hormonal contraceptives. MYFEMBREE may delay the ability to recognize pregnancy because it alters menstrual bleeding. Perform testing if pregnancy is suspected and discontinue MYFEMBREE if pregnancy is confirmed. Risk of Early Pregnancy Loss: MYFEMBREE can cause early pregnancy loss. Exclude pregnancy before initiating and advise women to use effective non-hormonal contraception. Uterine Fibroid Prolapse or Expulsion: Advise women with known or suspected submucosal uterine fibroids about the possibility of uterine fibroid prolapse or expulsion and instruct them to contact their physician if severe bleeding and/or cramping occurs. Alopecia: Alopecia, hair loss, and hair thinning were reported in phase 3 trials with MYFEMBREE. Consider discontinuing MYFEMBREE if hair loss becomes a concern. Whether the hair loss is reversible is unknown. Effects on Carbohydrate and Lipid Metabolism: More frequent monitoring in MYFEMBREE-treated women with prediabetes and diabetes may be necessary. MYFEMBREE may decrease glucose tolerance and result in increased blood glucose concentrations. Monitor lipid levels and consider discontinuing if hypercholesterolemia or hypertriglyceridemia worsens. In women with pre-existing hypertriglyceridemia, estrogen therapy may be associated with elevations in triglycerides levels leading to pancreatitis. Use of MYFEMBREE is associated with increases in total cholesterol and LDL-C. Effect on Other Laboratory Results: Patients with hypothyroidism and hypoadrenalism may require higher doses of thyroid hormone or cortisol replacement therapy. Use of estrogen and progestin combinations may raise serum concentrations of binding proteins (e.g., thyroid-binding globulin, corticosteroid-binding globulin), which may reduce free thyroid or corticosteroid hormone levels. Use of estrogen and progestin may also affect the levels of sex hormone-binding globulin, and coagulation factors. Hypersensitivity Reactions: Immediately discontinue MYFEMBREE if a hypersensitivity reaction occurs. ADVERSE REACTIONS: Most common adverse reactions for MYFEMBREE (incidence ≥3% and greater than placebo) were: Heavy menstrual bleeding associated with uterine fibroids: vasomotor symptoms, abnormal uterine bleeding, alopecia, and decreased libido.Moderate to severe pain associated with endometriosis: headache, vasomotor symptoms, mood disorders, abnormal uterine bleeding, nausea, toothache, back pain, decreased sexual desire and arousal, arthralgia, fatigue, and dizziness. These are not all the possible side effects of MYFEMBREE. DRUG INTERACTIONS: P-gp Inhibitors: Avoid use of MYFEMBREE with oral P-gp inhibitors. If use is unavoidable, take MYFEMBREE first, separate dosing by at least 6 hours, and monitor patients for adverse reactions. Combined P-gp and Strong CYP3A Inducers: Avoid use of MYFEMBREE with combined P-gp and strong CYP3A inducers. LACTATION: Advise women not to breastfeed while taking MYFEMBREE. About Myovant Sciences Myovant Sciences aspires to redefine care for women and for men through purpose-driven science, empowering medicines, and transformative advocacy. Founded in 2016, Myovant has executed five successful Phase 3 clinical trials across oncology and women’s health leading to three regulatory approvals by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for men with advanced prostate cancer, women with heavy menstrual bleeding associated with uterine fibroids, and pre-menopausal women with moderate to severe pain associated with endometriosis, respectively. Myovant also has received regulatory approvals by the European Commission (EC) and the United Kingdom Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) for women with symptomatic uterine fibroids and for men with advanced hormone-sensitive prostate cancer. Myovant has a supplemental New Drug Application under review with the FDA for updates to the United States Prescribing Information (USPI) based on safety and efficacy data from the Phase 3 LIBERTY randomized withdrawal study (RWS) of MYFEMBREE in premenopausal women with heavy menstrual bleeding due to uterine fibroids for up to two years. Myovant also is conducting a Phase 3 study to evaluate the prevention of pregnancy in women with uterine fibroids or endometriosis. Myovant also is developing MVT-602, an investigational oligopeptide kisspeptin-1 receptor agonist, which has completed a Phase 2a study for female infertility as part of assisted reproduction. Sumitovant Biopharma, Ltd., a wholly owned subsidiary of Sumitomo Pharma Co., Ltd., is Myovant’s majority shareholder. For more information, please visit www.myovant.com. Follow @Myovant on Twitter and LinkedIn. About Pfizer: Breakthroughs That Change Patients’ Lives At Pfizer, we apply science and our global resources to bring therapies to people that extend and significantly improve their lives. We strive to set the standard for quality, safety and value in the discovery, development and manufacture of health care products, including innovative medicines and vaccines. Every day, Pfizer colleagues work across developed and emerging markets to advance wellness, prevention, treatments and cures that challenge the most feared diseases of our time. Consistent with our responsibility as one of the world's premier innovative biopharmaceutical companies, we collaborate with health care providers, governments and local communities to support and expand access to reliable, affordable health care around the world. For more than 170 years, we have worked to make a difference for all who rely on us. We routinely post information that may be important to investors on our website at www.Pfizer.com. In addition, to learn more, please visit us on www.Pfizer.com and follow us on Twitter at @Pfizer and @PfizerNews, LinkedIn, YouTube and like us on Facebook at Facebook.com/Pfizer. Myovant Sciences Forward-Looking StatementsThis press release contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. In this press release, forward-looking statements include, but are not limited to, all statements reflecting Myovant Sciences’ expectations, including: statements regarding Myovant’s aspiration to redefine care for women and for men; the expectations regarding the continued commercialization of MYFEMBREE by Myovant and Pfizer jointly in the U.S. and the timeline of product availability; the expectations that MYFEMBREE’s indication helps advance Myovant’s mission to redefine care for women by helping address a disease with high unmet need, giving women and physicians a new meaningful treatment option to manage moderate to severe pain associated with endometriosis in Dr. Arjona Ferreira’s quote; the expectation of making MYFEMBREE available to women with endometriosis and broadening their options in managing this complex disorder in Dr. Rusnak’s quote; and the expectations of the MYFEMBREE Support Program for patients and the features of such program. Myovant Sciences’ forward-looking statements are based on management’s current expectations and beliefs and are subject to a number of risks, uncertainties, assumptions, and other factors known and unknown that could cause actual results and the timing of certain events to differ materially from future results expressed or implied by the forward-looking statements, including unforeseen circumstances or other disruptions to normal business operations arising from or related to the COVID-19 pandemic and the conflict in Ukraine. Myovant Sciences cannot assure you that the events and circumstances reflected in the forward-looking statements will be achieved or occur, and actual results could differ materially from those expressed or implied by these forward-looking statements. Factors that could materially affect Myovant Sciences’ operations and future prospects or which could cause actual results to differ materially from expectations include, but are not limited to, the risks and uncertainties listed in Myovant Sciences’ filings with the United States Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), including under the heading “Risk Factors” in Myovant Sciences’ Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed on July 27, 2022, as such risk factors may be amended, supplemented, or superseded from time to time. These risks are not exhaustive. New risk factors emerge from time to time, and it is not possible for Myovant Sciences’ management to predict all risk factors, nor can Myovant Sciences assess the impact of all factors on its business or the extent to which any factor, or combination of factors, may cause actual results to differ materially from those contained in any forward-looking statements. You should not place undue reliance on the forward- looking statements in this press release, which speak only as of the date hereof, and, except as required by law, Myovant Sciences undertakes no obligation to update these forward-looking statements to reflect events or circumstances after the date of such statements. Pfizer Disclosure NoticeThe information contained in this release is as of August 5, 2022. Pfizer assumes no obligation to update forward-looking statements contained in this release as the result of new information or future events or developments. This release contains forward-looking information about MYFEMBREE® (relugolix 40 mg, estradiol 1 mg, and norethindrone acetate 0.5 mg), a new indication in the U.S. for the management of moderate to severe pain associated with endometriosis in pre-menopausal women, and a collaboration between Pfizer and Myovant Sciences to develop and commercialize relugolix in advanced prostate cancer and women’s health, including their potential benefits, that involves substantial risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ materially from those expressed or implied by such statements. Risks and uncertainties include, among other things, uncertainties regarding the commercial success of MYFEMBREE; the uncertainties inherent in research and development, including the ability to meet anticipated clinical endpoints, commencement and/or completion dates for clinical trials, regulatory submission dates, regulatory approval dates and/or launch dates, as well as the possibility of unfavorable new clinical data and further analyses of existing clinical data; the risk that clinical trial data are subject to differing interpretations and assessments by regulatory authorities; whether regulatory authorities will be satisfied with the design of and results from the clinical studies; whether and when applications may be filed for any other potential indications for MYFEMBREE; whether and when regulatory authorities may approve any such applications for MYFEMBREE that may be pending or filed, which will depend on myriad factors, including making a determination as to whether the product’s benefits outweigh its known risks and determination of the product’s efficacy and, if approved, whether MYFEMBREE will be commercially successful; decisions by regulatory authorities impacting labeling, manufacturing processes, safety and/or other matters that could affect the availability or commercial potential of MYFEMBREE; whether our collaboration with Myovant Sciences will be successful; uncertainties regarding the impact of COVID-19 on Pfizer’s business, operations and financial results; and competitive developments. A further description of risks and uncertainties can be found in Pfizer’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2021 and in its subsequent reports on Form 10-Q, including in the sections thereof captioned “Risk Factors” and “Forward-Looking Information and Factors That May Affect Future Results”, as well as in its subsequent reports on Form 8-K, all of which are filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission and available at www.sec.gov and www.pfizer.com. Myovant Sciences ContactsInvestor Contact: Uneek MehraChief Financial and Business OfficerMyovant Sciences, Inc.investors@myovant.com Media Contact:Noelle Cloud DuganVice President, Corporate CommunicationsMyovant Sciences, Inc.media@myovant.com Pfizer Contacts:Media RelationsPfizerMediaRelations@Pfizer.com+1 (212) 733-1226 Investor RelationsIR@Pfizer.com+1 (212) 733-4848 1 American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM), Treatment of pelvic pain associated with endometriosis: a committee opinion. Fertil Steril. 2014;101(4):927-35.2 Becker CM et al. ESHRE guideline: endometriosis, Human Reproduction Open. 2022 Feb 26;2022(2): hoac009.3 Taylor HS et al. Endometriosis is a chronic systemic disease: clinical challenges and novel innovations. Lancet 2021;397(10276):839-52 4 Giudice LC, et al. Lancet. 2022 Jun; 399(10343): 2267-2279.5 Adamson, G. et al. Journal Endometriosis. 2010; 2:3-66 US census 2019 (table 1; approx. 75 million women in the US ages 15-49). Available online at https://data.census.gov/cedsci/table?q=United%20States&t=Age%20and%20Sex7 Shafrir. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2018 Aug; 51:1-158 Fuldeore Gynecol Obstet Invest. 2017;82:453-4619 Bulletti J Asist Reprod Genet 201010 Becker CM, et al. Fertil Steril. 2017 Jul;108(1):125-136.11 Zondervan KT, et al. NEJM. 2020;382(13):1244–125612 Nnoaham KE et al. Fertil Steril. 2011;96(2):366.e8–373.e813 Ballard K et al. Fertil Steril. 2006;86:1296–30114 Soliman et al. J Women’s Health. 2017. 26(7): 788-797
CollaborateFinancial StatementVaccine
27 Jul 2022
First fiscal quarter 2022 total revenue of $116.5 million, including net product revenue of $41.4 million Net product revenue from U.S. sales of ORGOVYX® of $36.0 million in first fiscal quarter 2022, with sequential quarterly demand volume growth of 26% and cumulative patients estimated at 18,000 through June 2022Net product revenue from U.S. sales of MYFEMBREE® of $4.0 million in first fiscal quarter 2022, with sequential quarterly demand volume growth of 54%MYFEMBREE remains the number one prescribed FDA-approved gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) antagonist therapy for the treatment of uterine fibroids for new patients and is now the market leader in total prescriptions (TRx) with 51% TRx share in June 2022FDA provided labeling comments with respect to the MYFEMBREE supplemental New Drug Application (sNDA) for the management of moderate to severe pain associated with endometriosis; on track for a decision by its August 6, 2022 target action dateFDA accepted sNDA proposing updates to MYFEMBREE’s U.S. Prescribing Information based on 2-year data from the Phase 3 LIBERTY randomized withdrawal study; set target action date of January 29, 2023Myovant remains well-capitalized with cash, cash equivalents, marketable securities, and committed financing of $400.0 million as of June 30, 2022 BASEL, Switzerland, July 27, 2022 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Myovant Sciences (NYSE: MYOV), a biopharmaceutical company that aspires to redefine care for women and for men through purpose-driven science, empowering medicines, and transformative advocacy, today announced financial results for the first quarter of fiscal year 2022 and provided other corporate updates. “We’re excited to start fiscal year 2022 with solid performance across both brands,” said David Marek, Chief Executive Officer of Myovant Sciences, Inc. “ORGOVYX delivered double digit volume growth across treatment settings and MYFEMBREE is now the market leader in new and total prescriptions while continuing to grow the class.” Mr. Marek added, “despite the challenging macro-economic environment, we remain well capitalized to build on our commercial momentum and advance our pipeline in women’s health and hormone-sensitive oncology.” First Fiscal Quarter 2022 and Recent Corporate Updates ORGOVYX (relugolix 120 mg) First fiscal quarter 2022 net product revenues for ORGOVYX in the U.S. were $36.0 million, reflecting 22% sequential growth compared to fourth fiscal quarter 2021. ORGOVYX commercial demand volume grew 26% quarter-over-quarter driven by broad adoption and strong growth across all treatment settings.Approximately 3,500 new patients started treatment on ORGOVYX in the first fiscal quarter of 2022, reaching approximately 18,000 cumulative patients since launch.A $50.0 million upfront payment was received from Accord Healthcare, Ltd. (Accord), pursuant to the exclusive license agreement Myovant entered into with Accord in May 2022 to commercialize ORGOVYX for the treatment of advanced hormone-sensitive prostate cancer in Europe.On April 29, 2022, the European Commission (EC), and on June 17, 2022, the United Kingdom (U.K.) Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA), approved ORGOVYX as the first and only oral androgen deprivation therapy for advanced hormone-sensitive prostate cancer in the European Union (EU) and U.K., respectively. We expect our commercialization partner, Accord, to commence the launch of ORGOVYX for the treatment of advanced hormone-sensitive prostate cancer in Europe in the second half of calendar year 2022. MYFEMBREE (relugolix 40 mg, estradiol 1.0 mg, and norethindrone acetate 0.5 mg) First fiscal quarter 2022 net product revenues for MYFEMBREE in the U.S. were $4.0 million.MYFEMBREE maintains market leadership in new-to-brand prescription (NBRx) share among GnRH antagonist therapies approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of uterine fibroids and is now the number one prescribed GnRH antagonist therapy for uterine fibroids with 51% total prescription (TRx) share in June 2022. Data provided by Symphony Health.Approximately 2,400 new patients started treatment on MYFEMBREE in first fiscal quarter 2022, resulting in 71% sequential quarterly growth in the number of patients treated since launch.MYFEMBREE continues to drive total prescription growth of the GnRH antagonist for uterine fibroids class, which has grown 180% since its launch in June 2021, with 61% of MYFEMBREE prescribers being first time prescribers of a GnRH antagonist FDA-approved for the treatment of uterine fibroids.FDA provided labeling comments with respect to the MYFEMBREE sNDA for the management of moderate to severe pain associated with endometriosis. FDA’s decision is expected by the extended Prescription Drug User Fee Act (PDUFA) goal date of August 6, 2022. An approval would trigger a $100.0 million milestone payment from Pfizer. If approved by the PDUFA goal date, Myovant and Pfizer expect to launch MYFEMBREE in the U.S. for this indication in August 2022.In June 2022, the FDA accepted for review an sNDA that proposes updates to MYFEMBREE’s U.S. Prescribing Information (USPI) based on 2-year safety and efficacy data from the Phase 3 LIBERTY randomized withdrawal study (RWS) of MYFEMBREE in premenopausal women with heavy menstrual bleeding associated with uterine fibroids. The FDA set a target action date of January 29, 2023 for this sNDA.In June 2022, Myovant and Pfizer announced that the results of the Phase 3 SPIRIT 1 and SPIRIT 2 studies of once-daily relugolix combination therapy (relugolix 40 mg, estradiol 1.0 mg, and norethindrone acetate 0.5 mg) in women with endometriosis-associated pain were published in The Lancet.Additional data from the SPIRIT 2-year extension study in women with endometriosis were presented at the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE) 2022 Annual Meeting in July 2022. The Society recognized the presentation as the best oral presentation of a clinical topic at the ESHRE 2022 Annual Meeting. Expected Upcoming Milestones Myovant expects the FDA decision for the MYFEMBREE sNDA seeking approval for the management of moderate to severe pain associated with endometriosis by its extended PDUFA goal date of August 6, 2022. Approval would trigger a $100.0 million milestone payment from Pfizer. If approved by the PDUFA goal date, Myovant and Pfizer expect to launch MYFEMBREE in the U.S. for this indication in August 2022.European Medicines Agency regulatory submission for RYEQO® for the treatment of women with endometriosis-associated pain is expected in the second half of calendar year 2022. Gedeon Richter Plc. (Richter) will be the sponsor.Myovant expects to submit New Drug Submissions to Health Canada seeking marketing approval for ORGOVYX for advanced prostate cancer, MYFEMBREE for heavy menstrual bleeding associated with uterine fibroids, and MYFEMBREE for the treatment of endometriosis-associated pain in Canada in the second half of calendar year 2022.Accord is expected to commence the launch of ORGOVYX for the treatment of advanced hormone-sensitive prostate cancer in Europe in the second half of calendar year 2022.Myovant expects the FDA decision for the MYFEMBREE sNDA proposing updates to MYFEMBREE’s USPI based on the safety and efficacy data from the Phase 3 LIBERTY RWS of MYFEMBREE in premenopausal women with heavy menstrual bleeding associated with uterine fibroids for up to two years by the January 29, 2023 PDUFA goal date. First Fiscal Quarter 2022 Financial Summary Total revenues for the three months ended June 30, 2022, and 2021 were $116.5 million and $41.1 million, respectively. Product revenue, net for the three months ended June 30, 2022 and 2021 were $41.4 million and $11.6 million, respectively. Product revenue, net consisted of the following: Product revenue, net from sales of ORGOVYX in the U.S. for the three months ended June 30, 2022 was $36.0 million compared to $10.5 million for the three months ended June 30, 2021.Product revenue, net from sales of MYFEMBREE in the U.S. for the three months ended June 30, 2022 was $4.0 million compared to $1.1 million for the three months ended June 30, 2021. MYFEMBREE was launched in the U.S in June 2021.Product revenue, net related to product supply to Richter for the three months ended June 30, 2022 was $1.1 million. Product revenue, net related to royalties on net sales of RYEQO in Richter’s Territory for the three months ended June 30, 2022 was $0.2 million. There were no such revenues in the year ago period. Pfizer collaboration revenue for the three months ended June 30, 2022 and 2021 was $25.1 million and $29.5 million, respectively, reflecting the partial recognition of the upfront payment Myovant received from Pfizer upon entering into the Pfizer Collaboration and License Agreement in December 2020 and of the regulatory milestone payment from Pfizer that was triggered upon the FDA approval of MYFEMBREE for the management of heavy menstrual bleeding associated with uterine fibroids in May 2021.Accord license revenue for the three months ended June 30, 2022 was $50.0 million, reflecting the recognition of the upfront payment received from Accord in May 2022 pursuant to the Accord License Agreement. There was no Accord license revenue in the year ago period. Cost of product revenue for the three months ended June 30, 2022 was $4.9 million, compared to $1.0 million for the three months ended June 30, 2021 related to the cost of goods sold and royalty expense payable to Takeda pursuant to the Takeda License Agreement. The increase in cost of product revenue in the three months ended June 30, 2022 was primarily due to an increase in cost of goods sold and royalty expense payable to Takeda as a result of higher sales of ORGOVYX and MYFEMBREE in the U.S., as compared to the year ago period. Collaboration expense to Pfizer for the three months ended June 30, 2022, was $18.0 million, compared to $5.3 million for the three months ended June 30, 2021, reflecting Pfizer’s 50% share of net profits from sales of ORGOVYX and MYFEMBREE in the U.S., pursuant to the Pfizer Collaboration and License Agreement. The increase in collaboration expense to Pfizer in the three months ended June 30, 2022 was due to an increase in net profits generated from sales of ORGOVYX and MYFEMBREE in the U.S., as compared to the year ago period. Selling, general and administrative (SG&A) expenses for the three months ended June 30, 2022, and 2021 were $79.0 million and $61.2 million, respectively. The increase in SG&A expenses primarily reflects higher expenses to support the ORGOVYX and MYFEMBREE commercialization activities in the U.S, including higher personnel-related costs, patient activation costs particularly for MYFEMBREE, as well as a banker fee associated with the Accord License Agreement. Research and development (R&D) expenses for the three months ended June 30, 2022, and 2021 were $23.9 million and $30.9 million, respectively. The decrease in R&D expenses primarily reflects a reduction in clinical study costs due to the completion and wind down of Myovant’s Phase 3 LIBERTY, HERO, and SPIRIT studies. Interest expense for the three months ended June 30, 2022, and 2021 was $4.2 million and $3.5 million, respectively, and was primarily related to the Sumitomo Pharma Loan Agreement. Interest expense related to the Sumitomo Pharma Loan Agreement increased $0.7 million, as a result of an increase in 3-month LIBOR as compared to the year ago period. Interest expense includes $0.6 million of accretion of the financing component of the cost share advance from Pfizer for both the three months ended June 30, 2022, and 2021. Income tax expense for the three months ended June 30, 2022, and 2021 was $8.2 million and $0.9 million, respectively. The increase in income tax expense was driven principally by the changed requirement under Internal Revenue Code Section 174, effective for years beginning after December 31, 2021, to capitalize and subsequently amortize R&D expenditures, pursuant to changes enacted in the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act 2017. For periods beginning prior to December 31, 2021, R&D expenses were allowed to be expensed as incurred. Net loss for the three months ended June 30, 2022 was $21.2 million compared to $61.7 million for the year ago period. On a per common share basis, net loss was $0.22 and $0.67 for the three months ended June 30, 2022 and 2021, respectively. Capital resources: Cash, cash equivalents, marketable securities, and amounts available under the Sumitomo Pharma Loan Agreement totaled $400.0 million as of June 30, 2022, and consisted of $358.7 million of cash, cash equivalents, and marketable securities and $41.3 million of available borrowing capacity under the Sumitomo Pharma Loan Agreement. Conference CallAs previously announced, Myovant will hold a webcast and conference call to discuss corporate updates and financial results for its first fiscal quarter, ended June 30, 2022. The webcast and conference call will be held at 5:00 p.m. Eastern Time / 2:00 p.m. Pacific Time on July 27, 2022. Investors and the general public may access the live webcast: https://edge.media-server.com/mmc/p/oi3u5djb. The live webcast can also be accessed by visiting the investor relations page of Myovant’s website at: https://investors.myovant.com/. A replay of the webcast, along with the earnings press release and presentation materials, can be found on Myovant’s investor relations website for a period of one year. About Relugolix Relugolix is a once-daily, oral gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) receptor antagonist that reduces testicular testosterone, a hormone known to stimulate the growth of prostate cancer, and ovarian estradiol, a hormone known to stimulate the growth of uterine fibroids and endometriosis. ORGOVYX® (relugolix, 120 mg) was approved in the U.S. by the FDA in December 2020 as the first and only oral GnRH receptor antagonist for the treatment of adult patients with advanced prostate cancer. In April and June 2022, respectively, the European Commission and the United Kingdom (U.K.) Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) approved ORGOVYX® (relugolix, 120 mg) as the first and only oral GnRH receptor antagonist for the treatment of adult patients with advanced hormone-sensitive prostate cancer in Europe and the U.K. MYFEMBREE® (relugolix 40 mg, estradiol 1.0 mg, and norethindrone acetate 0.5 mg) was approved in the U.S. by the FDA in May 2021 as the first and only once-daily oral treatment for the management of heavy menstrual bleeding associated with uterine fibroids in premenopausal women, with a treatment duration of up to 24 months. In July 2021, the European Commission, and in August 2021, the U.K. MHRA, approved RYEQO® (relugolix 40 mg, estradiol 1.0 mg, and norethindrone acetate 0.5 mg) for the treatment of moderate to severe symptoms of uterine fibroids in adult women of reproductive age, with no limitation for duration of use. In September 2021, the FDA accepted to review Myovant’s supplemental New Drug Application (sNDA) for MYFEMBREE for the management of moderate to severe pain associated with endometriosis. On May 6, 2022, Myovant and Pfizer announced that the FDA extended the Prescription Drug User Fee Act (PDUFA) goal date for this sNDA to August 6, 2022. In June 2022, the FDA accepted to review Myovant’s sNDA for updates to the United States Prescribing Information (USPI) based on safety and efficacy data from the Phase 3 LIBERTY randomized withdrawal study (RWS) of MYFEMBREE in premenopausal women with heavy menstrual bleeding due to uterine fibroids for up to two years. The FDA set a PDUFA goal date of January 29, 2023 for this sNDA. MYFEMBREE is also being assessed for contraceptive efficacy in women with endometriosis or uterine fibroids who are 18 to 50 years of age and at risk for pregnancy. About Myovant Sciences Myovant Sciences aspires to redefine care for women and for men through purpose-driven science, empowering medicines, and transformative advocacy. Founded in 2016, Myovant has executed five successful Phase 3 clinical trials across oncology and women’s health leading to two regulatory approvals by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for men with advanced prostate cancer and women with heavy menstrual bleeding associated with uterine fibroids, respectively. Myovant also has received regulatory approvals by the European Commission (EC) and the United Kingdom Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) for women with symptomatic uterine fibroids and for men with advanced hormone-sensitive prostate cancer. Myovant has supplemental New Drug Applications under review with the FDA for endometriosis-associated pain, and for updates to the United States Prescribing Information (USPI) based on safety and efficacy data from the Phase 3 LIBERTY randomized withdrawal study (RWS) of MYFEMBREE in premenopausal women with heavy menstrual bleeding due to uterine fibroids for up to two years. Myovant also is conducting a Phase 3 study to evaluate the prevention of pregnancy in women with uterine fibroids or endometriosis. Myovant also is developing MVT-602, an investigational oligopeptide kisspeptin-1 receptor agonist, which has completed a Phase 2a study for female infertility as part of assisted reproduction. Sumitovant Biopharma, Ltd., a wholly owned subsidiary of Sumitomo Pharma Co., Ltd., is Myovant’s majority shareholder. For more information, please visit www.myovant.com. Follow @Myovant on Twitter and LinkedIn. About Sumitovant Biopharma Ltd. Sumitovant is a global biopharmaceutical company leveraging data-driven insights to rapidly accelerate development of new potential therapies for unmet patient conditions. Through its unique portfolio of wholly-owned “Vant” subsidiaries—Urovant, Enzyvant, Spirovant, Altavant—and use of embedded computational technology platforms to generate business and scientific insights, Sumitovant has supported the development of FDA-approved products and advanced a promising pipeline of early through late-stage investigational assets for other serious conditions. Sumitovant, a wholly-owned subsidiary of Sumitomo Pharma, is also the majority-shareholder of Myovant (NYSE: MYOV). For more information, please visit Sumitovant’s website at https://www.sumitovant.com. About Sumitomo Pharma Co., Ltd. Sumitomo Pharma is among the top-ten listed pharmaceutical companies in Japan, operating globally in major pharmaceutical markets, including Japan, the U.S., China, and other Asian countries with more than 7,000 employees worldwide. Sumitomo Pharma defines its corporate mission as “To broadly contribute to society through value creation based on innovative research and development activities for the betterment of healthcare and fuller lives of people worldwide.” Additional information about Sumitomo Pharma is available through its corporate website at https://www.sumitomo-pharma.com. Forward-Looking Statements This press release contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. In this press release, forward-looking statements include, but are not limited to, all statements reflecting Myovant Sciences’ expectations, including: statements regarding Myovant’s aspiration to redefine care for women and for men; Myovant’s expectations of the success of commercialization of its approved drug products; statements with respect to Myovant’s expectations to remain well capitalized to build on its commercial momentum and advance its pipeline in women’s health and hormone-sensitive oncology in Mr. Marek’s quote; statements regarding the timing of Myovant’s regulatory submissions, anticipated regulatory review results, as well as Myovant’s and its collaboration and commercialization partners’ expected commercial launches of Myovant’s products, including, with no limitations, the timeline and potential outcome of the FDA’s review of the MYFEMBREE sNDA for the management of moderate to severe pain associated with endometriosis and if approved by the FDA, the potential milestone payment from Pfizer and the timing and expected launch of MYFEMBREE for this indication; the timeline and potential outcome of the FDA’s review of the MYFEMBREE sNDA proposing updates to MYFEMBREE’s USPI based on 2-year safety and efficacy data from the Phase 3 LIBERTY RWS of MYFEMBREE in premenopausal women with heavy menstrual bleeding associated with uterine fibroids; the timeline and expectation of launching ORGOVYX for the treatment of advanced hormone-sensitive prostate cancer in Europe by Accord; the timeline and expectation of submitting New Drug Submissions to Health Canada seeking marketing approval for ORGOVYX for advanced prostate cancer, MYFEMBREE for heavy menstrual bleeding associated with uterine fibroids, and MYFEMBREE for the treatment of endometriosis-associated pain in Canada; and other statements under the caption “Expected Upcoming Milestones.” Myovant Sciences’ forward-looking statements are based on management’s current expectations and beliefs and are subject to a number of risks, uncertainties, assumptions, and other factors known and unknown that could cause actual results and the timing of certain events to differ materially from future results expressed or implied by the forward-looking statements, including unforeseen circumstances or other disruptions to normal business operations arising from or related to the COVID-19 pandemic and the conflict in Ukraine. Myovant Sciences cannot assure you that the events and circumstances reflected in the forward-looking statements will be achieved or occur, and actual results could differ materially from those expressed or implied by these forward-looking statements. Factors that could materially affect Myovant Sciences’ operations and future prospects or which could cause actual results to differ materially from expectations include, but are not limited to, the risks and uncertainties listed in Myovant Sciences’ filings with the United States Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), including under the heading “Risk Factors” in Myovant Sciences’ Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q to be filed on July 27, 2022, as such risk factors may be amended, supplemented, or superseded from time to time. These risks are not exhaustive. New risk factors emerge from time to time and it is not possible for Myovant Sciences’ management to predict all risk factors, nor can Myovant Sciences assess the impact of all factors on its business or the extent to which any factor, or combination of factors, may cause actual results to differ materially from those contained in any forward-looking statements. You should not place undue reliance on the forward-looking statements in this press release, which speak only as of the date hereof, and, except as required by law, Myovant Sciences undertakes no obligation to update these forward-looking statements to reflect events or circumstances after the date of such statements. MYOVANT SCIENCES LTD.Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Loss(Unaudited, in thousands, except share and per share data) Three Months Ended June 30, 2022 2021 Revenues: Product revenue, net$41,351 $11,554 Pfizer collaboration revenue 25,141 29,509 Accord license revenue 50,000 — Total revenues 116,492 41,063 Operating costs and expenses: Cost of product revenue(1) 4,915 1,032 Collaboration expense to Pfizer 18,016 5,261 Selling, general and administrative(1) 79,032 61,212 Research and development(1) 23,890 30,880 Total operating costs and expenses 125,853 98,385 Loss from operations (9,361) (57,322)Interest expense 4,200 3,505 Interest income (486) (78)Loss before income taxes (13,075) (60,749)Income tax expense 8,164 911 Net loss and comprehensive loss$(21,239) $(61,660) Net loss per common share — basic and diluted$(0.22) $(0.67) Weighted average common shares outstanding — basic and diluted 95,388,294 91,637,151 (1)Includes the following share-based compensation: Selling, general and administrative$5,972 $7,155Research and development 3,666 3,957Cost of product revenue 68 3Total share-based compensation$9,706 $11,115 Revenue components are as follows: Product revenue, net: ORGOVYX$36,034 $10,479MYFEMBREE 3,999 1,075Richter product supply and royalties 1,318 —Total product revenue, net 41,351 11,554Pfizer collaboration revenue: Amortization of upfront payment 20,974 20,974Amortization of regulatory milestone 4,167 8,535Total Pfizer collaboration revenue 25,141 29,509Accord license revenue 50,000 —Total revenues$116,492 $41,063 MYOVANT SCIENCES LTD.Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets(Unaudited, in thousands) June 30, 2022 March 31, 2022Assets Current assets: Cash and cash equivalents$325,535 $406,704 Accounts receivable, net 29,648 23,296 Marketable securities 31,216 27,483 Inventories 21,222 7,584 Prepaid expenses and other current assets 18,750 22,498 Amount due from related party 458 580 Total current assets 426,829 488,145 Property and equipment, net 2,681 2,944 Operating lease right-of-use asset 7,501 7,961 Marketable securities, non-current 1,938 — Other assets 21,181 20,961 Total assets$460,130 $520,011 Liabilities and Shareholders’ Deficit Current liabilities: Accounts payable$9,552 $12,250 Accrued expenses and other current liabilities 65,688 68,594 Deferred revenue 100,564 100,564 Amounts due to Pfizer 39,244 32,563 Cost share advance from Pfizer 8,555 33,818 Operating lease liability 2,256 2,148 Amounts due to related parties 382 393 Total current liabilities 226,241 250,330 Deferred revenue, non-current 350,565 375,706 Long-term operating lease liability 6,431 7,041 Long-term debt, less current maturities (related party) 358,700 358,700 Other liabilities 1,717 1,711 Total liabilities 943,654 993,488 Total shareholders’ deficit (483,524) (473,477)Total liabilities and shareholders’ deficit$460,130 $520,011 Investor Contact:Uneek MehraChief Financial OfficerMyovant Sciences, Inc.investors@myovant.com Media Contact:Noelle Cloud DuganVice President, Corporate CommunicationsMyovant Sciences, Inc.media@myovant.com
Financial Statement
100 Deals associated with LT-ZP001
Login to view more data
R&D Status
10 top R&D records. to view more data
Login
| Indication | Highest Phase | Country/Location | Organization | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2 | Discovery | United States | - | |
| Obesity | Discovery | United States | - |
Login to view more data
Clinical Result
Clinical Result
Indication
Phase
Evaluation
View All Results
| Study | Phase | Population | Analyzed Enrollment | Group | Results | Evaluation | Publication Date |
|---|
No Data | |||||||
Login to view more data
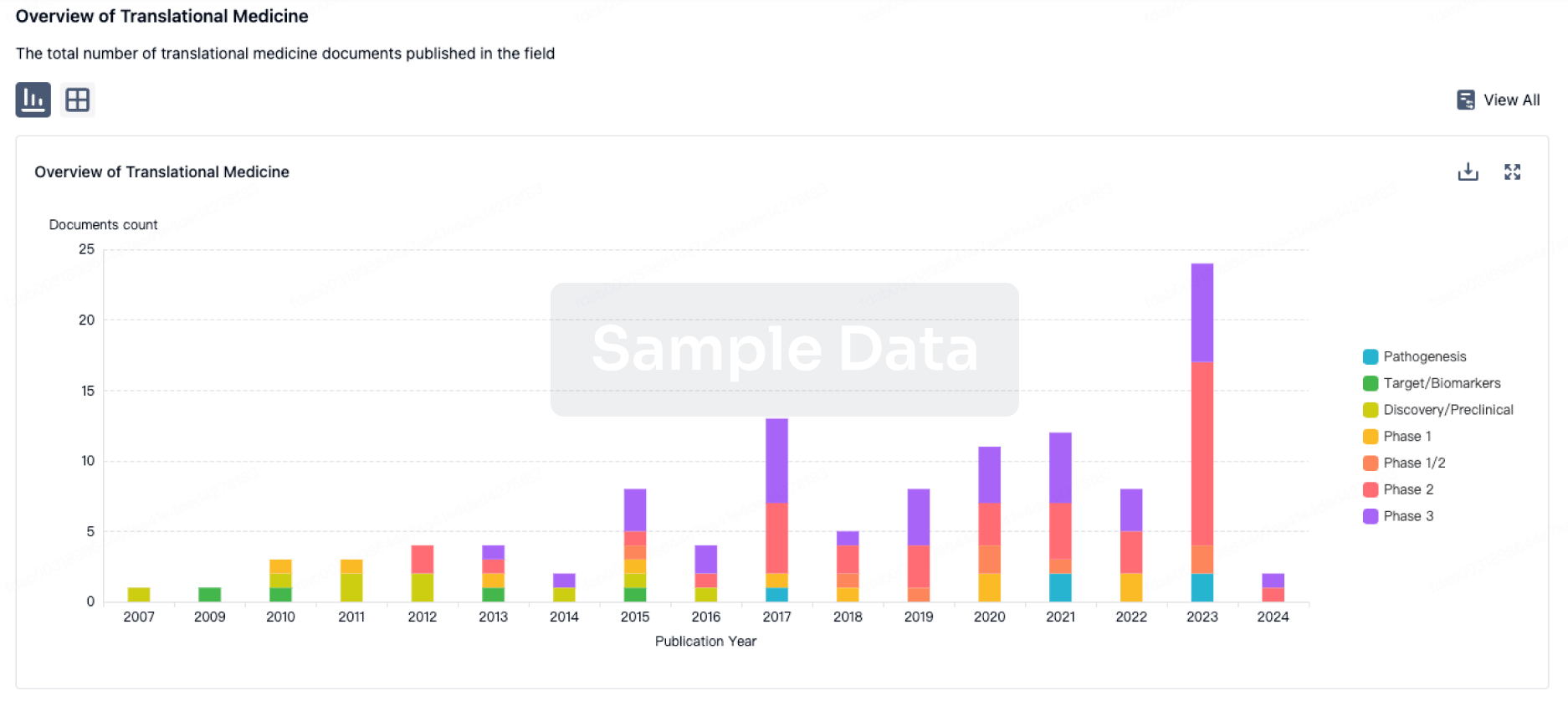
Translational Medicine
Boost your research with our translational medicine data.
login
or
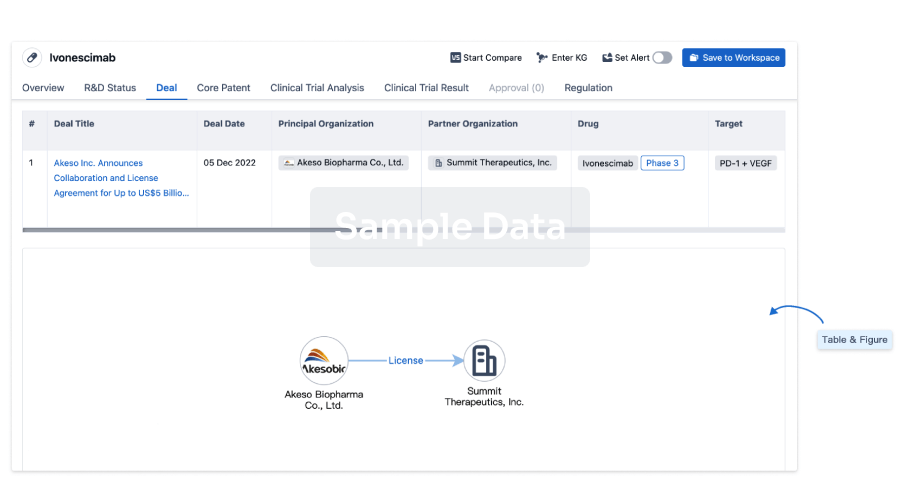
Deal
Boost your decision using our deal data.
login
or
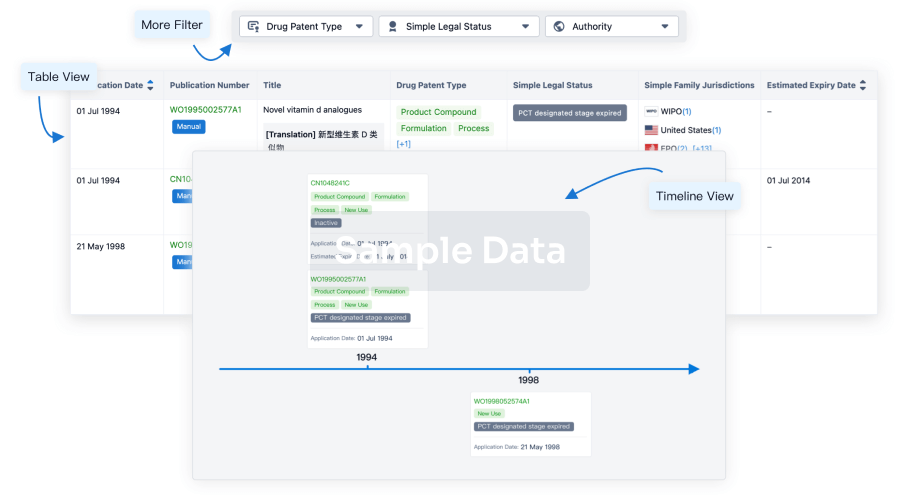
Core Patent
Boost your research with our Core Patent data.
login
or
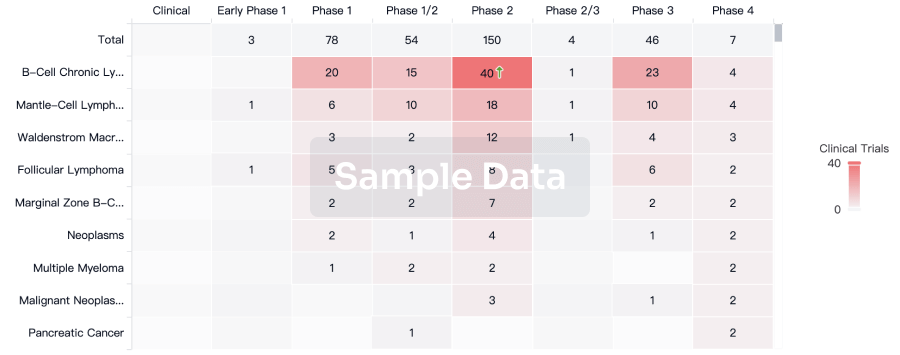
Clinical Trial
Identify the latest clinical trials across global registries.
login
or
Approval
Accelerate your research with the latest regulatory approval information.
login
or
Biosimilar
Competitive landscape of biosimilars in different countries/locations. Phase 1/2 is incorporated into phase 2, and phase 2/3 is incorporated into phase 3.
login
or
Regulation
Understand key drug designations in just a few clicks with Synapse.
login
or
AI Agents Built for Biopharma Breakthroughs
Accelerate discovery. Empower decisions. Transform outcomes.
Get started for free today!
Accelerate Strategic R&D decision making with Synapse, PatSnap’s AI-powered Connected Innovation Intelligence Platform Built for Life Sciences Professionals.
Start your data trial now!
Synapse data is also accessible to external entities via APIs or data packages. Empower better decisions with the latest in pharmaceutical intelligence.
Bio
Bio Sequences Search & Analysis
Sign up for free
Chemical
Chemical Structures Search & Analysis
Sign up for free
