Request Demo
Last update 13 Sep 2025
Haloxazolam
Last update 13 Sep 2025
Overview
Basic Info
Drug Type Small molecule drug |
Synonyms Haloxazolam (JP17/INN), CS-430, Somelin + [1] |
Target |
Action agonists |
Mechanism GABAA receptor agonists(Gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptor agonists) |
Therapeutic Areas |
Active Indication |
Inactive Indication- |
Originator Organization |
Active Organization |
Inactive Organization- |
License Organization- |
Drug Highest PhaseApproved |
First Approval Date Japan (10 Jun 1980), |
Regulation- |
Login to view timeline
Structure/Sequence
Molecular FormulaC17H14BrFN2O2 |
InChIKeyXDKCGKQHVBOOHC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
CAS Registry59128-97-1 |
Related
100 Clinical Results associated with Haloxazolam
Login to view more data
100 Translational Medicine associated with Haloxazolam
Login to view more data
100 Patents (Medical) associated with Haloxazolam
Login to view more data
66
Literatures (Medical) associated with Haloxazolam03 Apr 2024·International Journal of Biosciences
Bioactive potential of Distimake dissectus leaf: GC–MS analysis and in-vitro bioassays for antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory properties
Author: Prabhakar, G. ; Kamalakar, P. ; Nagaraju, R.
Distimake dissectus (Jacq.) A.R.Simões & Staples. is belonging to the family Convolvulaceae.It is commonly called as ''alamo vine'' is a perennial herb.The current study investigates the GC-MS characterization, antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory properties of D. dissectus.The methanolic leaf extract included 53 different phytochems., as determined by the GC-MS anal.The DPPH radical scavenging assay revealed the IC50 values of methanol extract 160.03±0.857, hexane extract 145.61±0.62, and ascorbic acid 24.12±0.313 resp.The anti-bacterial activity was studied by the Agar well-diffusion method with four concentrations (25μl, 50μl, 75μl and 100μl).The leaf extracts showed remarkable antibacterial activities, the maximum zone of inhibition observed in methanol extract compared to hexane extract for each bacterium was as follows., S. aureus (100μg/18mm), E. coli (100μg/18mm), S. pneumonia, (100μg/13mm), P. aeruginosa (100μg/14mm), the MIC was recorded its active at concentration of 200μg/mL in S. aureus and E. coli.The anti fungal activity was tested by well diffusion method, the methanol extract showed C. albicans (100μg/16mm) and hexane (100μg/14mm).The Griess test, which measures the anti-inflammatory response, was employed to assess the substances that inhibit the production of NO, at a concentration of 100μg/mL, the methanol extract exhibited a NO inhibition of 49.04±0.457.The current study's findings will pave the way for the creation of herbal remedies using.The findings of the current study on D. dissectus may pave the way for the development of herbal remedies for a variety of illnesses, potentially resulting in the creation of innovative therapeutics.
01 Apr 2024·Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry
Development of a rapid-fire drug screening method by probe electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry for human urine (RaDPi-U)
Article
Author: Iguchi, Akira ; Hisatsune, Kazuaki ; Ogata, Koretsugu ; Zaitsu, Kei ; Asano, Tomomi ; Taniguchi, Masaru ; Murata, Tasuku
Drug screening tests are mandatory in the search for drugs in forensic biological samples, and immunological methods and mass spectrometry (e.g., gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry) are commonly used for that purpose. However, these methods have some drawbacks, and developing new screening methods is required. In this study, we develop a rapid-fire drug screening method by probe electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry (PESI-MS/MS), which is an ambient ionization mass spectrometry method, for human urine, named RaDPi-U. RaDPi-U is carried out in three steps: (1) mixing urine with internal standard (IS) solution and ethanol, followed by vortexing; (2) pipetting the mixture onto a sample plate for PESI; and (3) rapid-fire analysis by PESI-MS/MS. RaDPi-U targets 40 forensically important drugs, which include illegal drugs, hypnotics, and psychoactive substances. The analytical results were obtained within 3 min because of the above-mentioned simple workflow of RaDPi-U. The calibration curves of each analyte were constructed using the IS method, and they were quantitatively valid, resulting in good linearity (0.972-0.999) with a satisfactory lower limit of detection and lower limit of quantitation (0.01-7.1 ng/mL and 0.02-21 ng/mL, respectively). Further, both trueness and precisions were 28% or less, demonstrating the high reliability and repeatability of the method. Finally, we applied RaDPi-U to three postmortem urine specimens and successfully detected different drugs in each urine sample. The practicality of the method is proven, and RaDPi-U will be a strong tool as a rapid-fire drug screening method not only in forensic toxicology but also in clinical toxicology.
01 Feb 2023·CNS & Neurological Disorders-Drug Targets
Benzodiazepines and Sleep Architecture: A Systematic Review
Review
Author: Maurício Castaldelli-Maia, João ; Souza, Laura Costa ; de Mendonça, Felipe Maraucci Ribeiro ; Galvão, Lucas Pequeno ; Paiva, Henrique Soares ; Ventriglio, Antonio ; Torales, Julio ; de Azevedo Marques Périco, Cintia ; Sousa Martins Silva, Anderson ; de Mendonça, Giulia Paulo Rossi Ribeiro
Background::
Insomnia, defined as a difficulty in initiating or maintaining sleep, is a relevant
medical issue. Benzodiazepines (BZDs) are commonly prescribed to treat insomnia. Two
phases characterize human sleep structure: sleep with Non-Rapid Eye Movement (NREM) and
sleep with Rapid Eye Movement (REM). Physiological sleep includes NREM and REM phases in
a continuous cycle known as “Sleep Architecture.”
Objective::
This systematic review summarizes the studies that have investigated effects of BZDs
on Sleep Architecture.
Methods::
The articles selection included human clinical trials (in English, Portuguese, or Spanish)
only, specifically focused on BZDs effects on sleep architecture. PubMed, BVS, and Google Scholar
databases were searched.
Results::
Findings on BZDs effects on sleep architecture confirm an increase in stage 2 of NREM
sleep and a decrease in time of stages 3 and 4 of NREM sleep with a reduction in time of REM
sleep during the nocturnal sleep.
Conclusion::
Variations in NREM and REM sleep may lead to deficits in concentration and working
memory and weight gain. The increase in stage 2 of NREM sleep may lead to a subjective improvement
of sleep quality with no awakenings. BZDz should be prescribed with zeal and professional
judgment. These patients should be closely monitored for possible long-term side effects.
1
News (Medical) associated with Haloxazolam31 Jul 2018
PDF (205KB)PDF
For Immediate Release
Company name: DAIICHI SANKYO COMPANY, LIMITED Representative: Sunao Manabe, Representative Director, President and COO (Code no.: 4568, First Section, Tokyo Stock Exchange) Please address inquiries to Koji Ogawa, Corporate Officer, Vice President, Corporate Communications Department Telephone: +81-3-6225-1126 https://www.daiichisankyo.com
Tokyo, Japan (July 31, 2018) – Daiichi Sankyo Company, Limited (hereafter, Daiichi Sankyo) announces that at a Board of Directors meeting held today a resolution was passed to transfer the domestic manufacturing and sales approvals for 41 long-listed products that Daiichi Sankyo and Daiichi Sankyo’s subsidiary, Daiichi Sankyo Espha Co., Ltd. (hereafter, Daiichi Sankyo Espha), manufacture and sell in Japan to Alfresa Holdings Corporation’s subsidiary, Alfresa Pharma Corporation (hereafter, Alfresa Pharma).
Daiichi Sankyo has been working for many years to create innovative pharmaceuticals and continuously deliver top-quality pharmaceutical products, and is now giving priority to the investment of resources in the oncology field toward its 2025 Vision of becoming “a global pharma innovator with competitive advantage in oncology. In addition, Daiichi Sankyo Espha, as a generic drug company, contributes to the medical treatment of people in Japan against the backdrop of a rapidly aging society.
Under these circumstances, Daiichi Sankyo has examined the business optimization of domestic long-listed products and judged that the responsibility for their stable provision can continue to be fulfilled by transferring some of Daiichi Sankyo and Daiichi Sankyo Espha’s long-listed products to Alfresa Pharma.
In accordance with the resolution, the inventories of a total of 41 products, which comprise 35 of Daiichi Sankyo’s long-listed products and six of Daiichi Sankyo Espha’s long-listed products (book value of ¥3.08 billion as of the end of March 2018), and the rights and obligations pertaining to their domestic manufacturing and sales, will be transferred to Alfresa Pharma from March 2019, for which Daiichi Sankyo and Daiichi Sankyo Espha are expected to receive payment of ¥8.42 billion (excluding the value of the inventories) from Alfresa Pharma. The revenues of the 41 long-listed products being transferred were ¥9.16 billion in the fiscal year ending March 31, 2018.
The assets and the manufacturing and sales rights and obligations for 30 of Daiichi Sankyo’s 35 long-listed products will transferred to Alfresa Pharma through a company split effective March 1, 2019, and those for the other products will individually transferred to Alfresa Pharma in order starting from March 2, 2019.
The assets and the manufacturing and sales rights and obligations for five of Daiichi Sankyo Espha’s six long-listed products will be transferred to Alfresa Pharma through a company split scheme effective March 1, 2019, and those for the other product will individually be transferred to Alfresa Pharma after March 2, 2019.
The 41 long-listed products that Daiichi Sankyo and Daiichi Sankyo Espha are transferring to Alfresa Pharma are as follows.
Table: List of 41 Long-listed Products
Brand Name Drug Classification by Efficacy Manufacturing & Marketing Reference 1 ATP Agents affecting metabolism, not otherwise categorized Daiichi Sankyo 〇 2 Actosin® Cardiac stimulant Daiichi Sankyo 〇 3 Adsorbin® Antacid Daiichi Sankyo 〇 4 Amisaline® Antiarrhythmic agent Daiichi Sankyo 〇 5 Allergin® Antihistamine Daiichi Sankyo 〇 6 Iscotin® Antituberculous agent Daiichi Sankyo 〇 7 Indigocarmine Function test reagent Daiichi Sankyo 〇 8 Gammalon® Other circulatory organ agent Daiichi Sankyo 〇 9 Chlomy® Antibiotic Daiichi Sankyo 〇 10 Chloromycetin® Antibiotic Daiichi Sankyo 〇 11 Cefmetazon® Antibiotic Daiichi Sankyo 〇 12 Serenal® Sedative, anxiolytic Daiichi Sankyo 〇 13 Somelin® Sedative, anxiolytic Daiichi Sankyo 〇 14 Daipin® Antispasmodic Daiichi Sankyo 〇 15 Tarivid® tablets Synthetic antibacterial Daiichi Sankyo 〇 Tarivid® ear drops Daiichi Sankyo 16 Dopasol® Antiparkinson agent Daiichi Sankyo 〇 17 Tolopelon® Psychoneurosis agent Daiichi Sankyo 〇 18 Droleptan® General anesthetic Daiichi Sankyo 〇 19 Neoiscotin® Antituberculous agent Daiichi Sankyo 〇 20 Neodopasol® Antiparkinson agent Daiichi Sankyo 〇 21 Nelbon® Sedative, anxiolytic Daiichi Sankyo 〇 22 Nor-Adrenalin® Adrenal hormone preparation Daiichi Sankyo 〇 23 Sodium para-aminohippurate Function test reagent Daiichi Sankyo 〇 24 Bal® Antidote Daiichi Sankyo 〇 25 Pyramide® Antituberculous agent Daiichi Sankyo 〇 26 Phenolsulfonphthalein Function test reagent Daiichi Sankyo 〇 27 Forit® Psychoneurosis agent Daiichi Sankyo 〇 28 Liverall® Liver disease agent Daiichi Sankyo 〇 29 Amyl nitrite Vasodilator, antidote Daiichi Sankyo 〇 30 Glucose Saccharide preparation Daiichi Sankyo 〇 31 Gabalon® Antispasmodic Daiichi Sankyo 32 Cortrosyn® Pituitary hormone preparation Daiichi Sankyo 33 Sedrena® Antiparkinson agent Daiichi Sankyo 34 Sepazon® Sedative, anxiolytic Daiichi Sankyo 35 Vitamedin® Mixed vitamin preparation Daiichi Sankyo 36 S・M Digestant Daiichi Sankyo Espha △ 37 Sinlestal® Hyperlipidemia agent Daiichi Sankyo Espha △ 38 Neuer® Peptic ulcer agent Daiichi Sankyo Espha △ 39 Hyamine® External disinfectant Daiichi Sankyo Espha △ 40 Pantosin® Vitamin B preparation Daiichi Sankyo Espha △ 41 Captoril® Hypotensive agent Daiichi Sankyo Espha
Brand Name
Drug Classification by Efficacy
Manufacturing & Marketing
Reference
1
ATP
Agents affecting metabolism, not otherwise categorized
Daiichi Sankyo
〇
2
Actosin®
Cardiac stimulant
Daiichi Sankyo
〇
3
Adsorbin®
Antacid
Daiichi Sankyo
〇
4
Amisaline®
Antiarrhythmic agent
Daiichi Sankyo
〇
5
Allergin®
Antihistamine
Daiichi Sankyo
〇
6
Iscotin®
Antituberculous agent
Daiichi Sankyo
〇
7
Indigocarmine
Function test reagent
Daiichi Sankyo
〇
8
Gammalon®
Other circulatory organ agent
Daiichi Sankyo
〇
9
Chlomy®
Antibiotic
Daiichi Sankyo
〇
10
Chloromycetin®
Antibiotic
Daiichi Sankyo
〇
11
Cefmetazon®
Antibiotic
Daiichi Sankyo
〇
12
Serenal®
Sedative, anxiolytic
Daiichi Sankyo
〇
13
Somelin®
Sedative, anxiolytic
Daiichi Sankyo
〇
14
Daipin®
Antispasmodic
Daiichi Sankyo
〇
15
Tarivid® tablets
Synthetic antibacterial
Daiichi Sankyo
〇
Tarivid® ear drops
Daiichi Sankyo
16
Dopasol®
Antiparkinson agent
Daiichi Sankyo
〇
17
Tolopelon®
Psychoneurosis agent
Daiichi Sankyo
〇
18
Droleptan®
General anesthetic
Daiichi Sankyo
〇
19
Neoiscotin®
Antituberculous agent
Daiichi Sankyo
〇
20
Neodopasol®
Antiparkinson agent
Daiichi Sankyo
〇
21
Nelbon®
Sedative, anxiolytic
Daiichi Sankyo
〇
22
Nor-Adrenalin®
Adrenal hormone preparation
Daiichi Sankyo
〇
23
Sodium para-aminohippurate
Function test reagent
Daiichi Sankyo
〇
24
Bal®
Antidote
Daiichi Sankyo
〇
25
Pyramide®
Antituberculous agent
Daiichi Sankyo
〇
26
Phenolsulfonphthalein
Function test reagent
Daiichi Sankyo
〇
27
Forit®
Psychoneurosis agent
Daiichi Sankyo
〇
28
Liverall®
Liver disease agent
Daiichi Sankyo
〇
29
Amyl nitrite
Vasodilator, antidote
Daiichi Sankyo
〇
30
Glucose
Saccharide preparation
Daiichi Sankyo
〇
31
Gabalon®
Antispasmodic
Daiichi Sankyo
32
Cortrosyn®
Pituitary hormone preparation
Daiichi Sankyo
33
Sedrena®
Antiparkinson agent
Daiichi Sankyo
34
Sepazon®
Sedative, anxiolytic
Daiichi Sankyo
35
Vitamedin®
Mixed vitamin preparation
Daiichi Sankyo
36
S・M
Digestant
Daiichi Sankyo Espha
△
37
Sinlestal®
Hyperlipidemia agent
Daiichi Sankyo Espha
△
38
Neuer®
Peptic ulcer agent
Daiichi Sankyo Espha
△
39
Hyamine®
External disinfectant
Daiichi Sankyo Espha
△
40
Pantosin®
Vitamin B preparation
Daiichi Sankyo Espha
△
41
Captoril®
Hypotensive agent
Daiichi Sankyo Espha
(Note): Products marked ○ in the reference column are products subject to the company split scheme of Daiichi Sankyo and products marked △ are products subject to the company split scheme of Daiichi Sankyo Espha.
Next, Daiichi Sankyo hereby notifies regarding the Daiichi Sankyo’s company split of 30 long-listed products as follows. Since this is a simple absorption-type company split in which the decrease in Daiichi Sankyo’s net assets is projected to be less than 10% of the total amount of net assets on the last day of the immediately preceding fiscal year and the decrease in Daiichi Sankyo’s net sales is projected to be less than 3% of the total net sales in the immediately preceding fiscal year, this disclosure is made omitting some of the disclosure items and contents.
1. Summary of Daiichi Sankyo’s company split
1) Reason for the company split
Because the number of products being transferred in this transaction is large and the number of contracts, etc. related to the products to be transferred is also large, for the comprehensive transfer of the products and each contract, etc., a succession scheme via simple absorption-type company split was selected.
2) Schedule of the company split
Board of Directors resolution date (Daiichi Sankyo) July 31, 2018 Contract conclusion date July 31, 2018 Effective date (scheduled) March 1, 2019 Payment date (scheduled) March 1, 2019
Board of Directors resolution date (Daiichi Sankyo)
July 31, 2018
Contract conclusion date
July 31, 2018
Effective date (scheduled)
March 1, 2019
Payment date (scheduled)
March 1, 2019
(Note) Since this company split being implemented by Daiichi Sankyo is a simple absorption-type split based on the provisions of Article 784 Paragraph 2 of the Companies Act, it is being implemented without the passage of a resolution at a general shareholders’ meeting.
3) Method of the company split
This is a simple absorption-type split with Daiichi Sankyo as the spliting company and Alfresa Pharma as the succeeding company.
4) Contents of allotments pertaining to the company split
Upon this company split, Daiichi Sankyo is scheduled to receive an approximately ¥4.2 billion payment from Alfresa Pharma.
5) Treatment of share options and bonds by the company split
There will be no changes to the treatment of share options issued by Daiichi Sankyo by this company split. Also, Daiichi Sankyo has not issued any bonds with share options.
6) Capital increase or decrease from the company split
There will be no capital increase or decrease caused by this company split.
7) Rights and obligations assumed by the succeeding company
Upon this company split, the succeeding company will succeed assets, contract positions, approvals, intellectual property rights and rights and obligations incidental thereto concerning the split business (excluding labor contracts with employees and rights and obligations incidental thereto). However, operating credits and debts that arise until the date the absorption-type split comes into effect (accounts receivable, accounts payable, amounts outstanding, and other monetary transactions) are vested in the splitting company, which is Daiichi Sankyo.
8) Outlook for Fulfillment of Debt Obligations
There are no debt obligations borne by the succeeding company under this company split.
2. Approach to Calculating the Contents of Allotments Pertaining to the company Split
Since Alfresa Pharma will continue to operate value the split business after this company split, it deemed that adopting the discount cash flow (DCF) method to value the assets based on the future cash flow expected from the split business is appropriate and conducted a calculation using a third party.
Alfresa Pharma calculated the business value based on the results of value calculation by the third party and presented the amount to Daiichi Sankyo. In addition to that, comprehensively considering the status of the transferred products at Daiichi Sankyo, and the book value of assets pertaining to the products being transferred, and as a result of discussions and negotiations between the two parties, Daiichi Sankyo finally judged that the amount mutually agreed on is suitable and concluded this absorption-type split contract pertaining to this company split with Alfresa Pharma. No significant increases or decreases are projected in the financial projections that were used as assumptions for the calculation.
3. Outline of the Parties
(Splitting Company)
1. Corporate name Daiichi Sankyo Company, Limited 2. Address 3-5-1 Nihonbashi-honcho, Chuo-ku, Tokyo 3. Representative’s title and name Representative Director, President & COO Sunao Manabe 4. Business contents Research and development, manufacture, marketing, etc. of pharmaceuticals 5. Share Capital ¥50,000 million 6. Established September 28, 2005 7. Number of shares issued 709,011,343 shares 8. Fiscal year-end March 31 9. Major shareholders and shareholding ratios (as of March 31, 2018) The Master Trust Bank of Japan (trust account): 8.73% JP MORGAN CHASE BANK 380055: 8.66% Japan Trustee Services Bank, Ltd. (trust account): 7.21% Nippon Life Insurance Company: 5.52% Trust & Custody Services Bank, Ltd. as trustee for Mizuho Trust and Banking Co., Ltd. Retirement Benefit Trust Account re-entrusted by Mizuho Bank, Ltd. 2.22% 10. Financial conditions and business performance in the immediately preceding fiscal year (ended March 31, 2018) international standard (consolidated) Equity attributable to owners of the company ¥1,132,982 million Total assets ¥1,897,754 million Equity attributable to owners of the Company per share ¥1,749.33 Revenues ¥960,195 million Operating Profit ¥76,282 million Profit attributable to owners of the Company ¥60,282 million Basic earnings per share ¥91.31
1. Corporate name
Daiichi Sankyo Company, Limited
2. Address
3-5-1 Nihonbashi-honcho, Chuo-ku, Tokyo
3. Representative’s title and name
Representative Director, President & COO Sunao Manabe
4. Business contents
Research and development, manufacture, marketing, etc. of pharmaceuticals
5. Share Capital
¥50,000 million
6. Established
September 28, 2005
7. Number of shares issued
709,011,343 shares
8. Fiscal year-end
March 31
9. Major shareholders and shareholding ratios (as of March 31, 2018)
The Master Trust Bank of Japan (trust account): 8.73%
JP MORGAN CHASE BANK 380055: 8.66%
Japan Trustee Services Bank, Ltd. (trust account): 7.21%
Nippon Life Insurance Company: 5.52%
Trust & Custody Services Bank, Ltd. as trustee for Mizuho Trust and Banking Co., Ltd. Retirement Benefit Trust Account re-entrusted by Mizuho Bank, Ltd. 2.22%
10. Financial conditions and business performance in the immediately preceding fiscal year (ended March 31, 2018) international standard (consolidated)
Equity attributable to owners of the company
¥1,132,982 million
Total assets
¥1,897,754 million
Equity attributable to owners of the Company per share
¥1,749.33
Revenues
¥960,195 million
Operating Profit
¥76,282 million
Profit attributable to owners of the Company
¥60,282 million
Basic earnings per share
¥91.31
(Succeeding Company)
1. Corporate name Alfresa Pharma Corporation 2. Address 2-2-9 Kokumachi, Chuo-ku, Osaka City, Osaka Prefecture 3. Representative’s title and name President & CEO Koichi Shimada 4. Business contents Manufacture, import, export and marketing of pharmaceuticals, diagnostic products, medical devices, pharmaceutical raw materials, etc. 5. Capital ¥1,000 million 6. Established December 14, 1939 7. Number of shares issued 10,000,000 shares 8. Fiscal year-end March 31 9. Major shareholders and shareholding ratios (as of March 31, 2018) Alfresa Holdings Corporation: 100% 10. Financial conditions and business performance in the immediately preceding fiscal year (ended March 31, 2018) Japanese standard Net assets ¥22,945 million Total assets ¥36,528 million Net assets per share ¥2,294.5 Net sales ¥29,677 million Operating income ¥2,155 million Ordinary income ¥2,226 million Net income ¥1,549 million Net income per share ¥154.9
1. Corporate name
Alfresa Pharma Corporation
2. Address
2-2-9 Kokumachi, Chuo-ku, Osaka City, Osaka Prefecture
3. Representative’s title and name
President & CEO Koichi Shimada
4. Business contents
Manufacture, import, export and marketing of pharmaceuticals, diagnostic products, medical devices, pharmaceutical raw materials, etc.
5. Capital
¥1,000 million
6. Established
December 14, 1939
7. Number of shares issued
10,000,000 shares
8. Fiscal year-end
March 31
9. Major shareholders and shareholding ratios (as of March 31, 2018)
Alfresa Holdings Corporation: 100%
10. Financial conditions and business performance in the immediately preceding fiscal year (ended March 31, 2018) Japanese standard
Net assets
¥22,945 million
Total assets
¥36,528 million
Net assets per share
¥2,294.5
Net sales
¥29,677 million
Operating income
¥2,155 million
Ordinary income
¥2,226 million
Net income
¥1,549 million
Net income per share
¥154.9
4. Outline of the Split Business Division
1) Business contents of the split division
The business to be split on March 1, 2019 by this absorption-type split is 30 long-listed products that Daiichi Sankyo manufactures and sells in Japan (see “Table: List of 41 Long-listed Products,” Page 2-3).
2) Business Performance of Split Division (year ended March 31, 2018)
Sales revenues ¥3,386 million
Sales revenues
¥3,386 million
3) Split assets and liabilities items and amounts (as of March 31, 2018)
Assets Liabilities Item Book value Item Book value Current assets ¥1,154 million Current liabilities ― Fixed assets ― Fixed liabilities ― Total ¥1,154 million Total ―
Assets
Liabilities
Item
Book value
Item
Book value
Current assets
¥1,154 million
Current liabilities
―
Fixed assets
―
Fixed liabilities
―
Total
¥1,154 million
Total
―
(Note): The amounts of the split assets and liabilities will be determined considering increases and decreases to the above-stated amounts until the day before the date this company split comes into effect.
5. Status after the company split
There will be no changes in the corporate name, address, title and name of representative, business contents, capital, or fiscal year-end of Daiichi Sankyo and Alfresa Pharma upon the completion of the company split.
6. Future Outlook
The impact on Daiichi Sankyo’s consolidated performance from this company split is negligible.
Financial Statement
100 Deals associated with Haloxazolam
Login to view more data
R&D Status
10 top approved records. to view more data
Login
| Indication | Country/Location | Organization | Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sleep Initiation and Maintenance Disorders | Japan | 10 Jun 1980 | |
| Sleep Initiation and Maintenance Disorders | Japan | 10 Jun 1980 |
Login to view more data
Clinical Result
Clinical Result
Indication
Phase
Evaluation
View All Results
| Study | Phase | Population | Analyzed Enrollment | Group | Results | Evaluation | Publication Date |
|---|
No Data | |||||||
Login to view more data
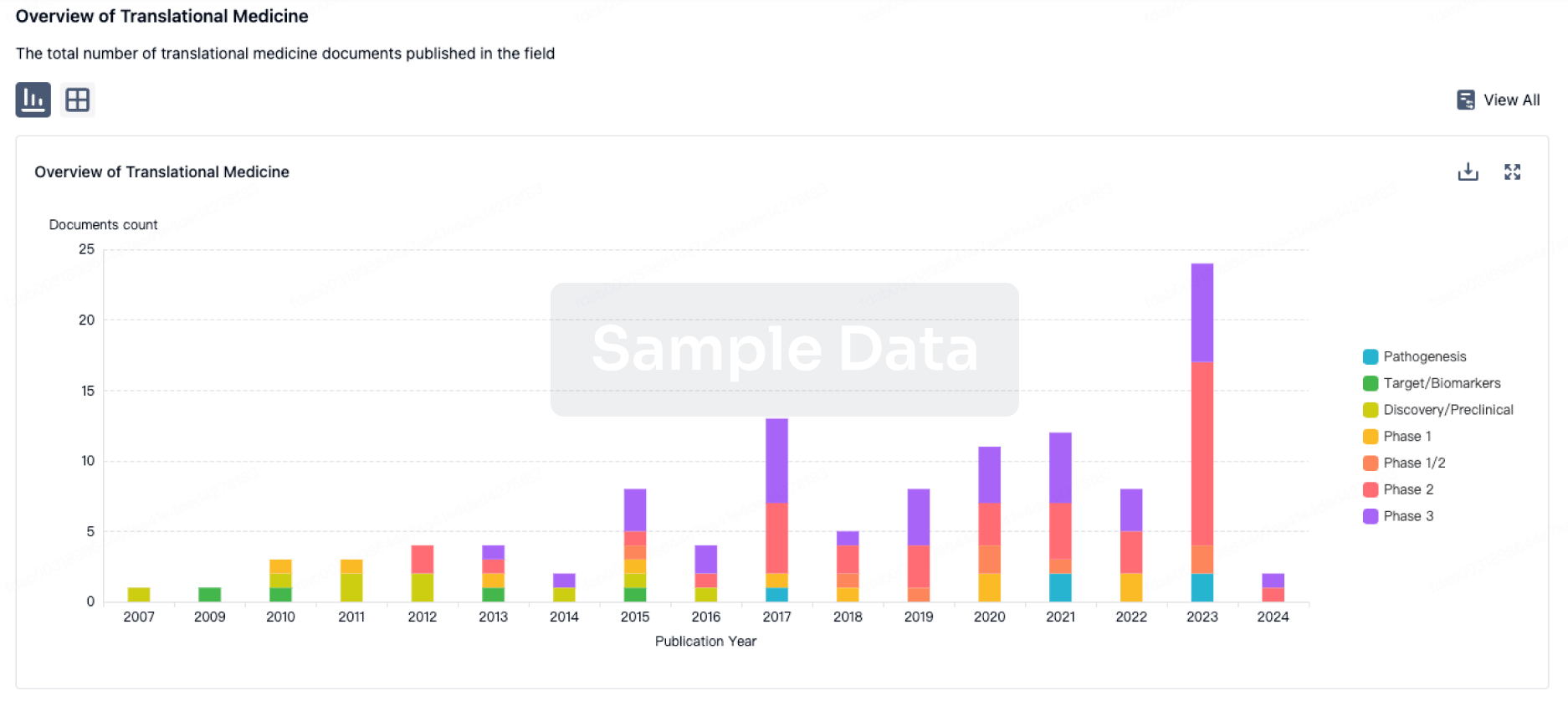
Translational Medicine
Boost your research with our translational medicine data.
login
or
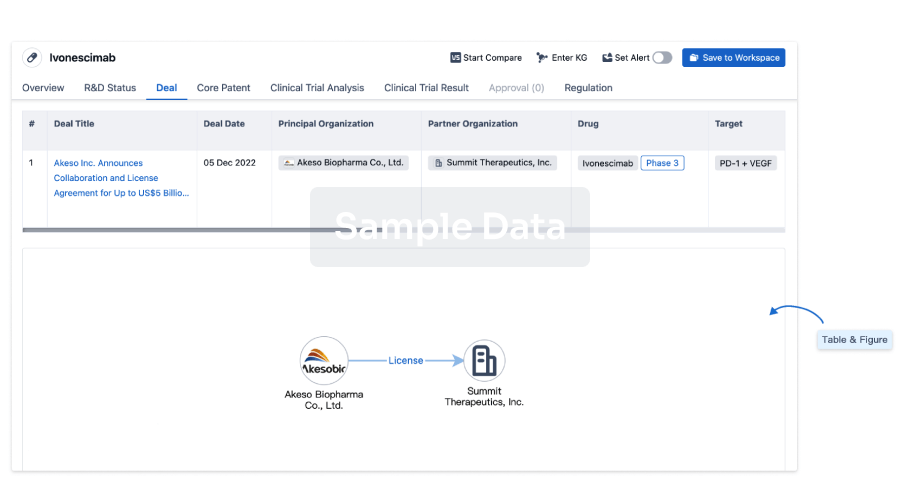
Deal
Boost your decision using our deal data.
login
or
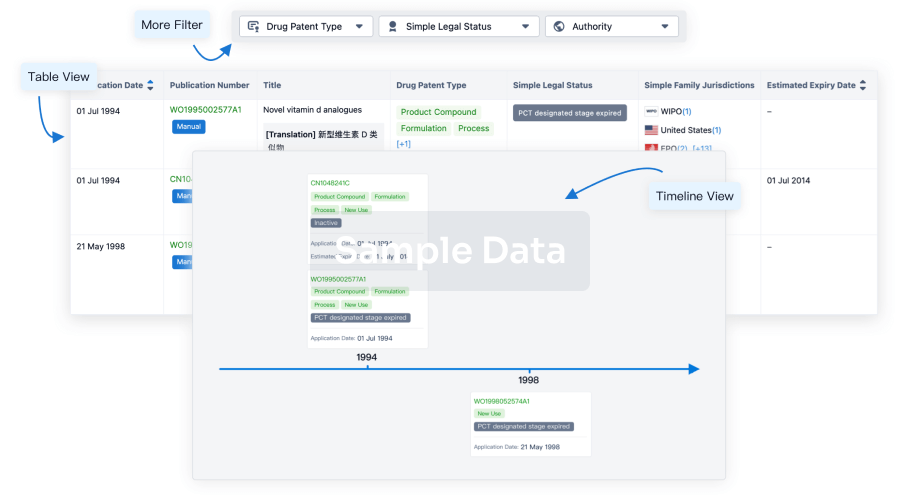
Core Patent
Boost your research with our Core Patent data.
login
or
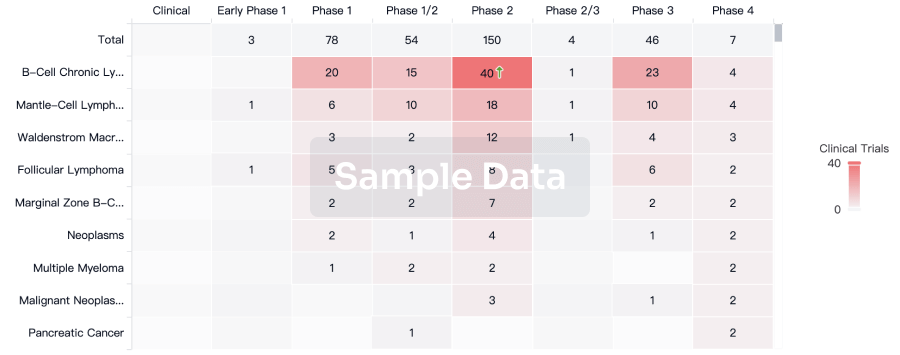
Clinical Trial
Identify the latest clinical trials across global registries.
login
or
Approval
Accelerate your research with the latest regulatory approval information.
login
or
Regulation
Understand key drug designations in just a few clicks with Synapse.
login
or
AI Agents Built for Biopharma Breakthroughs
Accelerate discovery. Empower decisions. Transform outcomes.
Get started for free today!
Accelerate Strategic R&D decision making with Synapse, PatSnap’s AI-powered Connected Innovation Intelligence Platform Built for Life Sciences Professionals.
Start your data trial now!
Synapse data is also accessible to external entities via APIs or data packages. Empower better decisions with the latest in pharmaceutical intelligence.
Bio
Bio Sequences Search & Analysis
Sign up for free
Chemical
Chemical Structures Search & Analysis
Sign up for free

