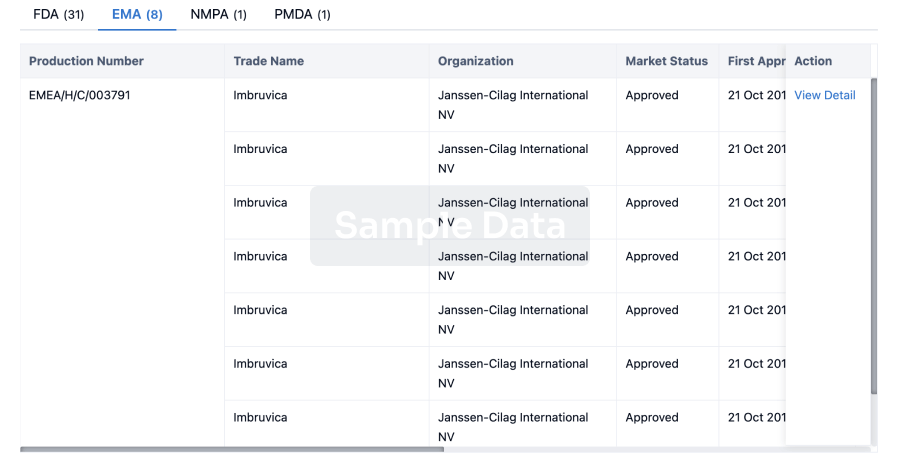
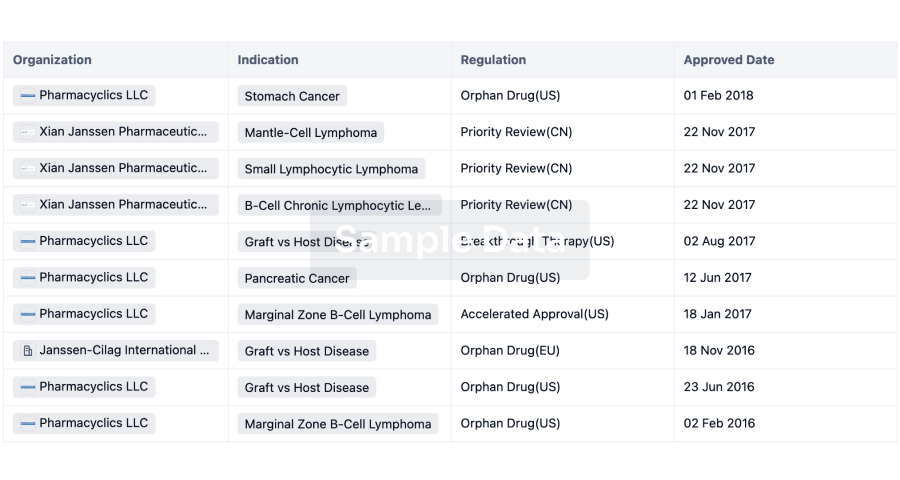
2
Clinical Trials associated with Allogeneic NK cells(National University Hospital (Singapore)) / Unknown statusPhase 1/2IIT Pilot Study of Expanded , Activated Haploidentical Natural Killer Cell Infusions for Sarcomas
Progress in the treatment of children with leukemia and lymphoma results in high cure rates but progress in the treatment of children and adolescents with solid tumors has been slow. Despite aggressive therapy with multimodality treatment involving surgery, radiation and chemotherapy, about two thirds of the patients with metastatic Ewing sarcoma (EWS), and intermediate and high risk rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) will relapse. The available second line therapies for relapse are limited and often not effective. There is a dire need to look for treatment options beyond conventional means for the treatment of these patients.
Infusions of allogeneic natural killer (NK) cells in leukemia patients have shown to be tolerated well without inducing graft versus host disease (GVHD). There is also mounting evidence that NK cells have activity against solid tumors.
In the lab the investigators tested NK cell activity against cell lines from different paediatric solid tumors. Among paediatric solid tumors, EWS and RMS are exquisitely sensitive to killing by expanded NK cells; NK cells also have activity against OS cells. Preliminary clinical data suggest that donor NK cells may exert antitumor activity in children with solid tumors undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.
Taking into account the safety of adaptive NK cell infusion, and their efficacy against EWS, RMS and OS, NK cells could be a powerful new tool in the treatment of paediatric solid tumors.
The great anti-tumor activity of expanded and activated NK cells, together with the feasibility of infusing haploidentical NK cells in a non-transplant setting form a compelling rationale for the clinical testing of these NK cells in patients with sarcoma.
/ Unknown statusPhase 1IIT Pilot Study of Expanded, Activated Haploidentical Natural Killer Cell Infusions for Non-B Lineage Acute Leukaemia and Myelodysplastic Syndrome
A novel method has been developed to expand natural (NK) cells and enhance their cytotoxicity against cancer cells while maintaining low killing capacity against non-transformed cells. In this method, donor NK cells are expanded by co-culture with the irradiated K562 cell line modified to express membrane bound IL-15 and 41BB ligand (K562-mb15-41BBL). Expression of these proteins in conjunction with unknown stimuli provided by K562 cells promotes selective growth of NK cells. Then, the expanded NK cell population is depleted of T cells to prevent graft versus host disease (GVHD). Expanded and activated NK cells showed powerful anti-leukemic activity against acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells in vitro and in animal models of leukemia.Unpublished laboratory results also demonstrated that T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (T-ALL) is extremely sensitive to the cytotoxicity exerted by the expanded and activated NK cells.
The present study represents the translation of the laboratory findings into clinical application. The study proposes to determine the feasibility, safety and efficacy of infusing expanded NK cells into patients who have AML or T-lineage ALL which is resistant to standard therapy as demonstrated by persistent minimal residual disease (MRD). Patients with myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), who are at high risk to develop AML will also be eligible for the study. In this patient cohort, the study will also investigate the in vivo lifespan and phenotype of the expanded NK cells.
The main hypothesis to be tested in this study is that infusion of expanded activated NK cells can produce measurable clinical responses in patients with AML or T-ALL.
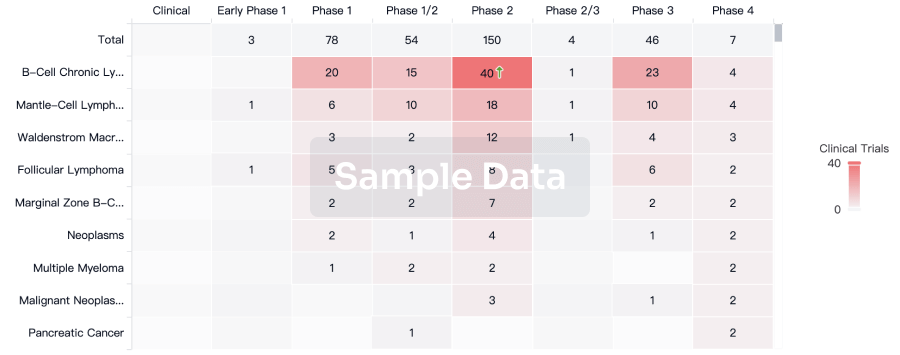
100 Clinical Results associated with Allogeneic NK cells(National University Hospital (Singapore))
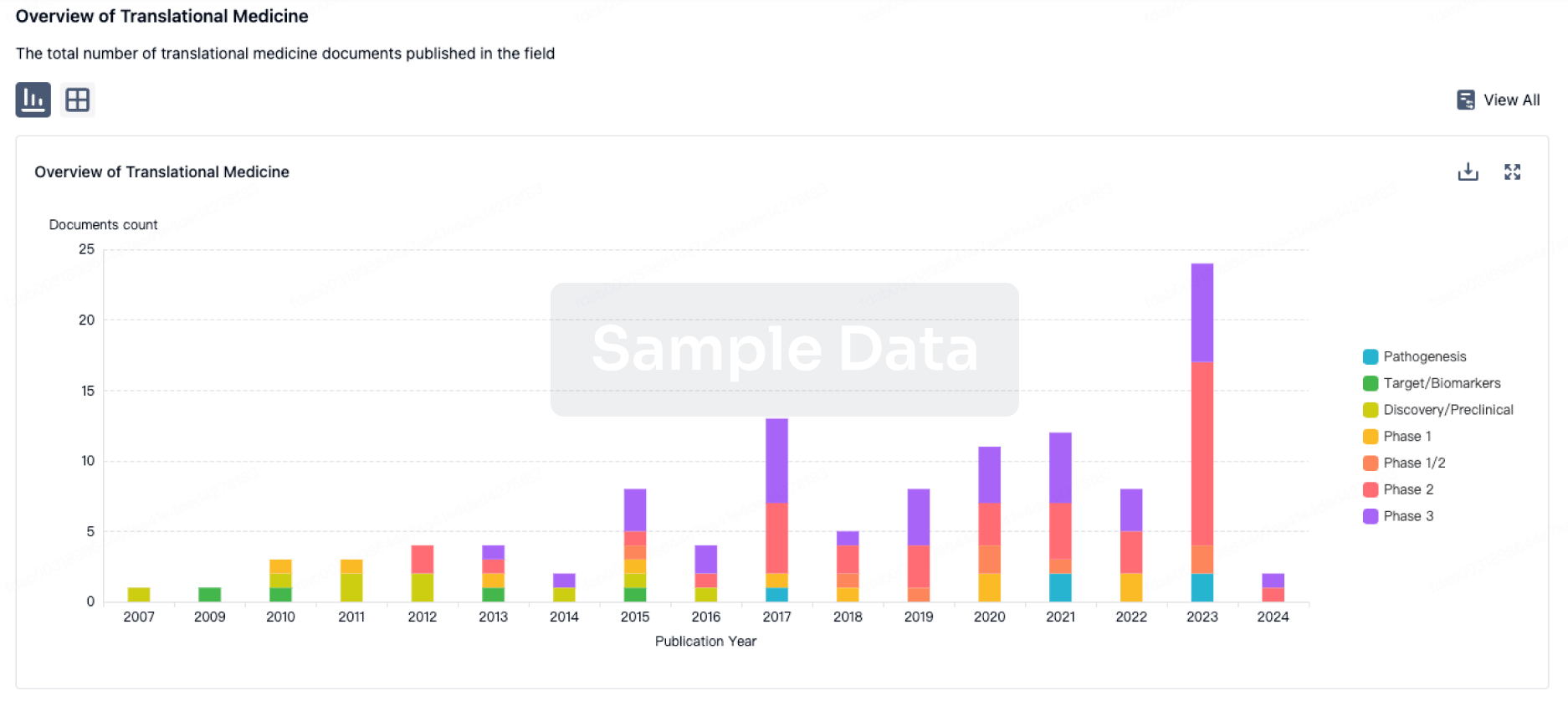
100 Translational Medicine associated with Allogeneic NK cells(National University Hospital (Singapore))
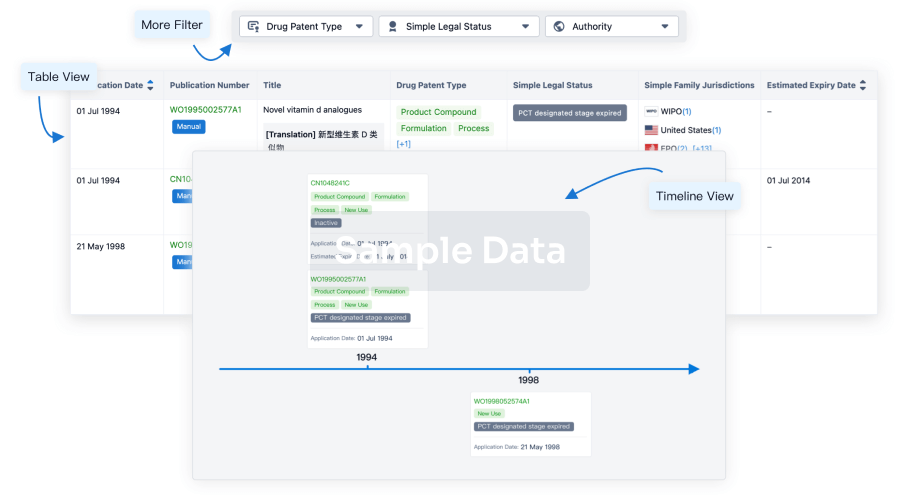
100 Patents (Medical) associated with Allogeneic NK cells(National University Hospital (Singapore))
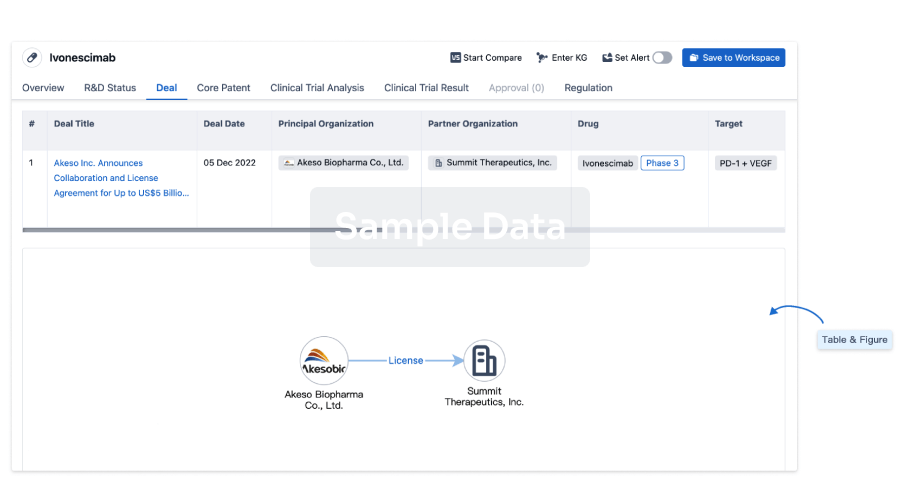
100 Deals associated with Allogeneic NK cells(National University Hospital (Singapore))