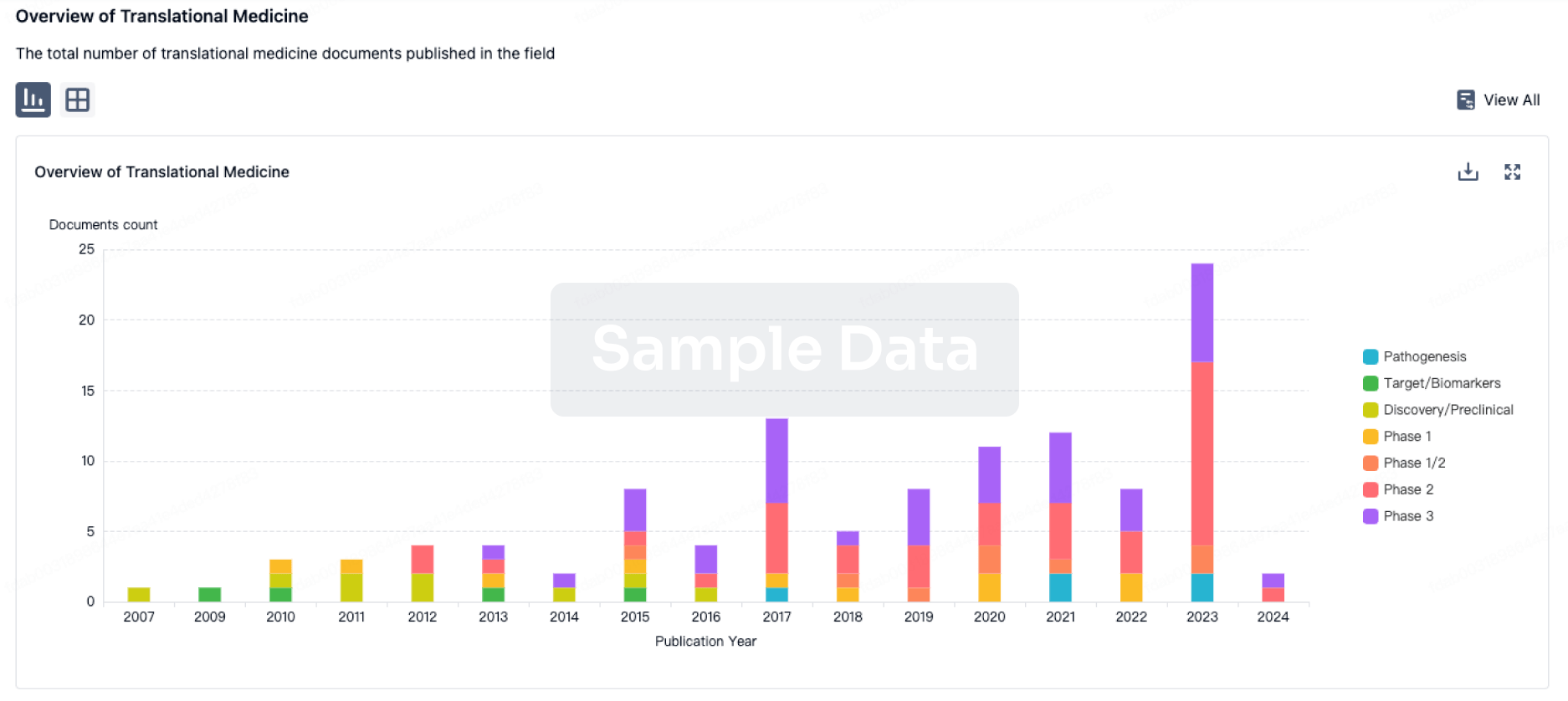
To explore the effect of miR‐1 on neuronal apoptosis in rats with stroke through the ERK signaling pathway. Methods. Forty male rats (180‐220 g) were selected and randomly divided into the sham, model, miR‐1 inhibitor, and miR‐1 mimic groups (10 rats per group) by average body weight. Cerebral ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) models were established using a modified middle cerebral artery wire thrombosis (MCAO) method in rats in the model group, miR‐1 inhibitor group, and miR‐1 mimic group. After the successful model establishment, the miR‐1inhibitor group and miR‐1 mimic group were intravenously injected with miR‐1 inhibitor and miR‐1 mimic, respectively, once a day for 3 days. The sham and model groups were given the same dose of normal saline. TTC staining was applied to detect the cerebral infarct size and calculate the infarct volume. Histopathological changes in the hippocampus of rat brains were observed by HE staining. Flow cytometry was used to detect neuronal apoptosis in rat brains. The mRNA expressions of miR‐1, ERK1/2, Bcl‐2, and Bax in rat brain tissues were determined by QRT PCR, and the protein levels of ERK1/2, Bcl‐2, Bax, and caspase‐3 were determined by Western blot analysis. Results. Compared with the sham group, the neurological impairment score, cerebral infarct size, and volume of rats in the model group were significantly increased (p < 0.05). Compared with the model group, the neurological impairment score, cerebral infarct size, and volume were significantly increased in the miR‐1 mimic group and significantly decreased in the miR‐1 inhibitor group (p < 0.05). In the model group, the hippocampal tissue of rats had malaligned cells, neuron cell atrophy became smaller, the intercellular spaces became larger, and vacuoles appeared. Compared with the model group, the miR‐1 inhibitor group could effectively alleviate the pathological changes in the hippocampus, and the miR‐1 mimic group could significantly add to the pathological changes in the rat hippocampus. Compared with the sham group, the mRNA expression of miR‐1 and Bax in the brain of model rats increased significantly (p < 0.05), and the mRNA expression of ERK1/2 decreased significantly; Compared with the model group, the miR‐1 and Bax mRNA expressions in the brain tissues of rats in the miR‐1 inhibitor group were significantly decreased, the ERK1/2 and bcl‐2 mRNA expressions were significantly increased, and the miR‐1 and Bax mRNA expressions in the brain tissues of rats in the miR‐1 inhibitor group were significantly decreased, and the Bcl‐2 mRNA expression was significantly increased (p < 0.05). Compared with the sham group, neuronal apoptosis was increased in the brain tissues of rats in the model group and miR‐1 mimic group. Compared with the model group, neuronal apoptosis was decreased in the brain tissues of rats in the miR‐1 inhibitor group. Compared with the sham group, the ERK1/2 proteins in the model group were significantly decreased, the Bcl‐2, Bax, and caspase‐3 proteins were significantly increased, and the ERK1/2, Bcl‐2, Bax, and caspase‐3 proteins in the miR‐1 inhibitor group and miR‐1 mimic group were significantly increased. Compared with the model group, the protein levels of ERK1/2 and Bcl‐2 in the miR‐1 inhibitor group were significantly increased, the proteins of Bax and caspase‐3 were significantly decreased, and the protein levels of ERK1/2 and Bcl‐2 in the miR‐1 inhibitor group were significantly increased (p < 0.05). Conclusions. miR‐1 can interfere with neuronal apoptosis in rats with stroke through the ERK signaling pathway.