/ RecruitingNot ApplicableIIT The Effect of Pyridoxamine Supplementation on Microvascular Function in Type 2 Diabetes: a Double-blind Randomized Placebo-controlled Crossover Trial
Patients with type 2 diabetes have an increased risk of developing vascular complications. Microvascular dysfunction might be caused by the increased production of methylglyoxal under hyperglycaemic conditions. Methylglyoxal is a by-product of glycolysis and forms advanced glycation endproducts (AGEs) on proteins and DNA, thereby disrupting their function. Preventing methylglyoxal accumulation and AGEs formation may offer a therapeutic option for treating microvascular complications in diabetics. Pyridoxamine is a vitamin B6 vitamer that scavenges methylglyoxal and thereby inhibits the formation of AGEs. In this study, the researchers investigate whether pyridoxamine supplementation in type 2 diabetes improves microvascular function in the eye, kidney and skin, and reduces markers of endothelial dysfunction and glycation.
/ Active, not recruitingNot Applicable PLASOMA Ultimate Safety & Efficacy Study
The purpose of the PULSE study are the followingL
A.To perform post market clinical follow up (PMCF) on safety and efficacy:
Safety: To confirm transient short-terms side effects and verify long-term/outstanding risks.
Efficacy: To confirm the performance of PLASOMA, i.e. the beneficial effect on bacterial load. B. Determine the effect of PLASOMA on wound surface area.
A secondary purpose is to examine the beneficial effects of PLASOMA on wound healing and to perform a health technology assessment (HTA).
This clinical study will be an open label two-armed randomized controlled trial (RCT), performed at at least three sites (multi-center) in the Netherlands.
The two arms are:
Control group: Standard wound care for 12 weeks or until healing, whichever occurs first;
Treatment group: Standard wound care + PLASOMA treatment for 12 weeks or until healing, whichever occurs first.
The frequency of PLASOMA treatment will be determined by the treating (para)medical professional based on the number of visits they would schedule for the standard wound care at the study site.
For all study subjects, the treatment frequency will be at least once per week (in order to have enough treatments for safety evaluation) and should not exceed once per day.
Follow up (FU) will be performed at three timepoints for both arms:
FU1: 2 weeks after end treatment period
FU2: 12 weeks after end treatment period
FU3: 12 months after start treatment.
/ CompletedNot ApplicableIIT Cardiac Mitochondrial Function: Comparison of in and ex Vivo Measurements
It has been suggested that mitochondrial dysfunction might play a role in the development of diabetic cardiomyopathy. From animal studies, it has been suggested that an altered PPAR and PGC1 expression is involved in the reduced cardiac mitochondrial function, however human data on cardiac mitochondrial function and PPAR regulation is scarce. The latter is due to the fact that there is no validated measurement for assessing cardiac mitochondrial function non-invasively in vivo. It has been suggested that measuring PCr/ATP ratio with 31P-MRS in the heart reflects cardiac mitochondrial function. However, so far no direct validation of this method has been performed. The aim of this study will be to validate in vivo 31P-MRS with ex vivo measurements of mitochondrial function. To this end, the hypothesis is that in vivo 31P-MRS is a valid method for measuring cardiac mitochondrial function when compared with ex vivo mitochondrial respirometry.
100 Clinical Results associated with Diabetes Fonds
0 Patents (Medical) associated with Diabetes Fonds
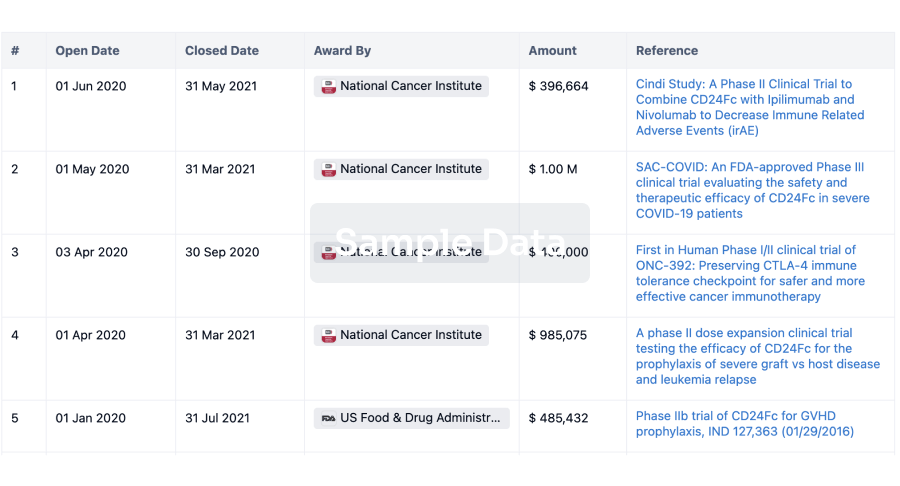
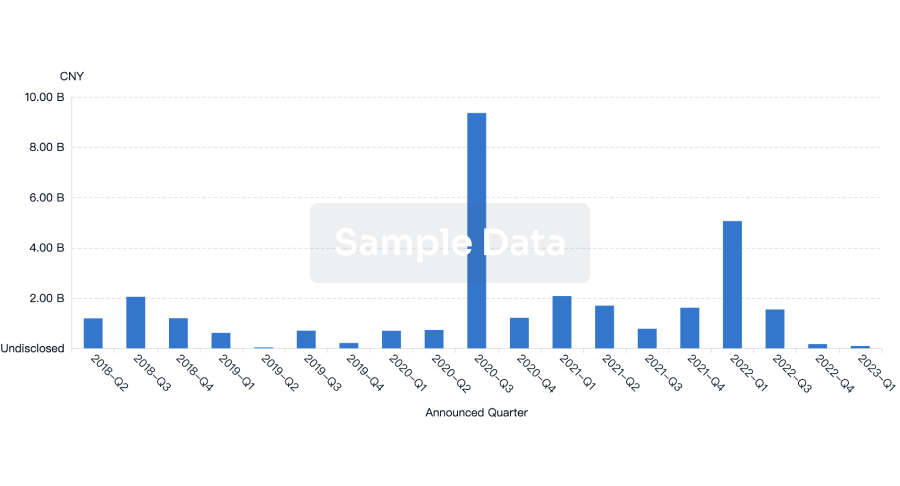
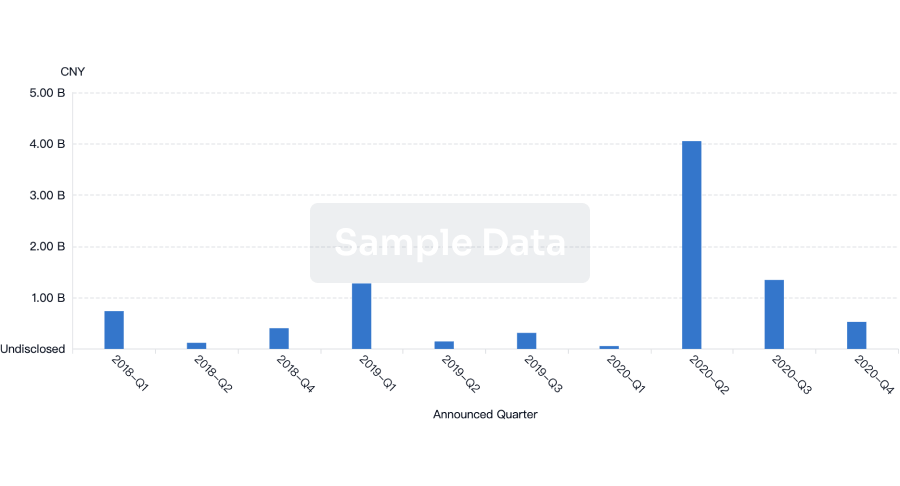
100 Deals associated with Diabetes Fonds
100 Translational Medicine associated with Diabetes Fonds