Request Demo
Last update 14 Aug 2025

Indee Labs
Last update 14 Aug 2025
Overview
Related
100 Clinical Results associated with Indee Labs
Login to view more data
0 Patents (Medical) associated with Indee Labs
Login to view more data
2
Literatures (Medical) associated with Indee LabsbioRxiv, Bioengineering
Intracellular delivery of mRNA to human primary T cells with microfluidic vortex shedding
Author: Pawell, Ryan S. ; Priest, Craig ; Twite, Amy A. ; Gottlieb, David ; Kashani, Moein N. ; Nieva, Jorge ; Lau, Katherine H. W. J.
Intracellular delivery is a critical process in biol. and medicine.During intracellular delivery, different constructs (e.g., functional macromols. such as DNA, RNA, and protein, and various complexes) are delivered across the cell membrane and into the cytosol.Herein, we use a microfluidic post array to induce hydrodynamic conditions for cell membrane poration with microfluidic vortex shedding (μVS). μVS is then used for the intracellular delivery of mRNA to primary human pan T cells.The specific microfluidic device and exptl. rig used in this study contains a 960μm wide by 40μm deep flow cell capable of processing more than 2 x 106 cells s-1 at volumes ranging from 100μL to 1.5 mL.Furthermore, we demonstrate efficient enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) mRNA expression (e.g., 57.4 ± 6.8% of viable, recovery cells, mean ± stdev) after mRNA delivery to human pan T cells with high cell viability (e.g., 83.7 ± 0.7% of recovered cells) and high cell recovery (e.g., 96.3 ± 1.1% of processed cells), resulting in net yield of 46.3 ± 5.6% viable, recovered, and GFP expressing human pan T cells at mRNA concentrations of 80μg ml-1.We also demonstrate μVS does not alter human pan T cell growth nor activation.These results demonstrated that μVS is a rapid intracellular delivery platform with promising potential for cytosolic delivery of mRNA to human primary T cells for (1) clin. applications, where larger volumes of cells are required and demonstrated value for (2) research applications, where rapid screening and minimal reagent consumption is preferable.
bioRxiv
Intracellular delivery of mRNA to human primary T cells with microfluidic vortex shedding
Author: Pawell, Ryan S. ; Lievano, Adrian A. ; Nieva, Jorge ; Gottlieb, David ; Priest, Craig ; Jarrell, Justin A. ; Twite, Amy A. ; Kashani, Moein N. ; Lau, Katherine H. W. J. ; Acevedo, Julyana
Intracellular delivery of functional macromols., such as DNA and RNA, across the cell membrane and into the cytosol, is a critical process in both biol. and medicine.Herein, we develop and use microfluidic chips containing post arrays to induce microfluidic vortex shedding, or μVS, for cell membrane poration that permits delivery of mRNA into primary human T lymphocytes.We demonstrate transfection with μVS by delivery of a 996-nucleotide mRNA construct encoding enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) and assessed transfection efficiencies by quantifying levels of EGFP protein expression.We achieved high transfection efficiency (63.6 ± 3.44% EGFP+ viable cells) with high cell viability (77.3 ± 0.58%) and recovery (88.7 ± 3.21%) in CD3+ T cells 19 h after μVS processing.Importantly, we show that processing cells via μVS does not neg. affect cell growth rates or alter cell states.We also demonstrate processing speeds of greater than 2.0 x 106 cells s-1 at volumes ranging from 0.1 to 1.5 mL.Altogether, these results highlight the use of μVS as a rapid and gentle delivery method with promising potential to engineer primary human cells for research and clin. applications.
3
News (Medical) associated with Indee Labs25 May 2023
Indee Labs announces an exclusive marketing and distribution deal with Sunko Instruments in China for Hydropore Research Use Only.
BERKELEY, Calif., May 25, 2023 /PRNewswire/ -- Indee Labs is a biotechnology company developing the Hydropore™ for non-viral intracellular delivery. Sunko Instruments is a professional distributor of scientific and laboratory instruments in China.
Indee Labs announces an exclusive marketing and distribution deal with Sunko Instruments in China for Hydropore.
"Sunko has worked with many suppliers from the United States and Europe, and is excited to join forces with Indee Labs. We are certain the Hydropore RUO is complementary to our current product lines and will have good exposure in the Chinese market." stated Aaron Liu, CEO of Sunko.
As part of the partnership, Indee Lab provides Sunko Instruments with exclusive marketing and distribution rights in China for Hydropore RUO. Sunko has significant experience distributing microfluidic instruments for the life science industry in China. This partnership will provide Indee Labs with a China marketing and distribution channel for Hydropore RUO and future versions like Hydropore Cell Therapy.
"Hydropore improves the function of modified immune cells and enables high throughput screening in cell-based assays. We are excited to expand Hydropore's reach to China with an exclusive marketing and distribution agreement with Sunko Instruments." elaborated Ryan Pawell, CEO of Indee Labs.
Key advantages of the Hydropore™ platform include increased yield, reduced reagent consumption and improved function of modified cells relative to multiple industry standard electroporation and nascent delivery platforms. The partnership with Sunko will help researchers in China access Hydropore to miniaturize and improve the quality of their cell-based research efforts. Sunko Instruments' existing customer base includes leading biopharma, biotechnology and life science companies in China.
About Indee Labs
Indee Labs is a biotechnology startup developing Hydropore™. Hydropore™ enables modified immune cell research and development with improved yield and function using a simple workflow, commercial GMP-grade buffers and a small footprint. The team at Indee Labs works with 3 of the top 10 pharmaceutical companies, various life science and biotechnology companies along with UCSF, Medical University of South Carolina and Stanford. Indee Labs is backed by IndieBio/SOSV, Y Combinator, Social Capital, Founders Fund among others including the National Institutes of Health. More information is available at indeelabs.com.
About Sunko
Sunko Instruments is a professional and leading scientific and laboratory instruments distributor in China with strong customer base in biopharma, biotechnology and life science. We are an exclusive distributor of many equipment suppliers from the United States and European countries. We have offices in Shanghai, Beijing and Guangzhou. Our professional pre-sales, sales, marketing and after-sales team serve and cover the entire China market.
View original content to download multimedia:
SOURCE indee labs
Cell TherapyLicense out/in
01 Dec 2022
Indee Labs partners with Monomer Bio to automate Hydropore™ workflows for engineered T cells and similar immune cell types.
BERKELEY, Calif. and PACIFICA, Calif., Dec. 1, 2022 /PRNewswire/ -- Indee Labs is a biotechnology company developing the Hydropore™ for non-viral intracellular delivery. Monomer Bio enables cell culture at scale by providing intelligent automation software that allows labs to build fully automated workcells using readily available equipment.
Continue Reading
Indee Labs partners with Monomer Bio to automate cell culture workflows for engineered immune cells.
Tweet this
Illustration of the latest version of Hydropore for Research Use Only.
"We've been interested in cell culture automation for some time, but it has been out-of-reach. We look forward to working with Monomer Bio to implement their automation platform for Hydropore™ processing of engineered immune cells using standard equipment, in a matter of a couple months and in our current lab space," stated Ryan Pawell, CEO of Indee Labs.
As part of the partnership, Monomer Bio will provide Indee Labs with the software and automation expertise required to implement their pre- and post- Hydropore™ processing workflows using off-the-shelf instrumentation with a reasonable footprint. Long-term, this collaboration will result in a fully automated workcell that supports the Hydropore™ workflow end-to-end.
"Monomer Bio has the privilege to work with innovative companies at the cutting edge of science. We're excited to partner with Indee Labs to grow and engineer T cells reliably at high yield," stated Jimmy Sastra, CEO of Monomer Bio.
Key advantages of the Hydropore™ platform include increased yield, reduced reagent consumption and improved function of modified cells relative to multiple industry standard electroporation and nascent delivery platforms. The collaboration with Monomer will empower scientists working with Hydropore™ to spend less time managing their immune cell cultures and more time designing experiments and analyzing results. Monomer customers report increasing experiment throughput and reproducibility while decreasing manual tasks and weekend work.
About Indee Labs
Indee Labs is a biotechnology startup developing Hydropore™. Hydropore™ enables modified immune cell research and development with improved yield and function using a simple workflow, commercial GMP-grade buffers and a small footprint. The team at Indee Labs works with 3 of the top 10 pharmaceutical companies, various life science and biotechnology companies along with UCSF, Medical University of South Carolina and Stanford. Indee Labs is backed by IndieBio/SOSV, Y Combinator, Social Capital, Founders Fund among others including the National Institutes of Health. More information is available at indeelabs.com.
About Monomer Bio
Monomer Bio enables massive parallelization of cell culture studies by providing intelligent automation software combined with optimization and machine learning algorithms designed to analyze characteristics like cell morphology. Monomer Bio is a venture backed team of experienced operators and works with some of the most cutting-edge biotech companies like Indee Labs, Science, E11, and Modulo Bio. More information is available at monomerbio.com.
SOURCE indee labs
Cell Therapy
02 Nov 2022
Indee Labs announces a $2M contract with the National Cancer Institute to scale up and out the Hydropore™ platform for cell therapy with Eyquem Lab at UCSF.
BERKELEY, Calif., Nov. 2, 2022 /PRNewswire/ -- Indee Labs is a biotechnology company developing the Hydropore™ for non-viral intracellular delivery. The team at Indee Labs was recently awarded an additional contract from the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health to scale up and out the Hydropore™ platform for cell therapy.
Continue Reading
Indee Labs announces a $2M contract with the National Cancer Institute to scale the Hydropore platform for cell therapy.
Tweet this
Illustration of the latest version of Hydropore for Research Use Only.
"With the help of Justin Eyquem's lab at UCSF, we were successful in completing our first contract with the National Cancer Institute covering knock-ins to T cells with improved in vitro function over electroporation. The team at Indee Labs is excited to continue our work together in scaling up and out Hydropore™ for cell therapy development and manufacturing" stated Ryan Pawell, Chief Executive Officer of Indee Labs.
As part of the Phase II contract, the Hydropore™ platform and protocols will be optimized for single-step, leukapheresis-scale processing of gene-edited CAR-T cells using both adeno-associated virus (AAV) and DNA for knock-ins. Improvements in CAR-T cell function and efficacy will be further verified relative to industry standard electroporation platforms in vivo using established mouse models at UC San Francisco.
The team at Indee Labs has already made multiple advancements in the field of intracellular delivery. Key advantages of the Hydropore™ platform include increased yield and improved function of modified cells relative to multiple industry standard electroporation and nascent delivery platforms. Currently, a single microfluidic Hydropore™ chip can rapidly process tens of millions of cells in seconds using existing, non-toxic GMP-grade buffers without the need for multiple instruments to go from small to medium scale processing. This contract will enable single-step, large-scale processing of CAR-T cells and similar modified immune cells – the gentle nature of Hydropore™ has already been shown to improve the expansion of rare and challenging cell types such as genome edited regulatory T cells and NK cells.
This project has been funded in whole or in part with Federal funds from the National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, Department of Health and Human Services, under Contract No. 7591022C00053.
About Indee Labs
Indee Labs is a biotechnology startup developing Hydropore™ for cell-based immunotherapy research, development and manufacturing. The team at Indee Labs works with 3 of the top 10 pharmaceutical companies, various life science and biotechnology companies along with UCSF, Medical University of South Carolina and Stanford. Hydropore™ enables modified immune cell development and manufacturing with improved yield and function using a simple workflow, commercial GMP-grade buffers and a small footprint. Indee Labs is backed by IndieBio/SOSV, Y Combinator, Social Capital, Founders Fund among others including the National Institutes of Health. More information is available at indeelabs.com.
SOURCE indee labs

Cell TherapyImmunotherapy
100 Deals associated with Indee Labs
Login to view more data
100 Translational Medicine associated with Indee Labs
Login to view more data
Corporation Tree
Boost your research with our corporation tree data.
login
or
Pipeline
Pipeline Snapshot as of 27 Aug 2025
No data posted
Login to keep update
Deal
Boost your decision using our deal data.
login
or
Translational Medicine
Boost your research with our translational medicine data.
login
or
Profit
Explore the financial positions of over 360K organizations with Synapse.
login
or
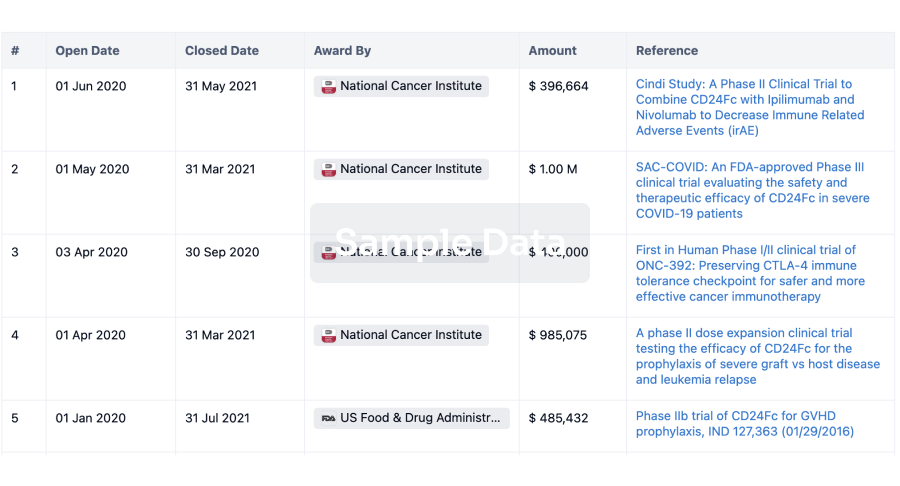
Grant & Funding(NIH)
Access more than 2 million grant and funding information to elevate your research journey.
login
or
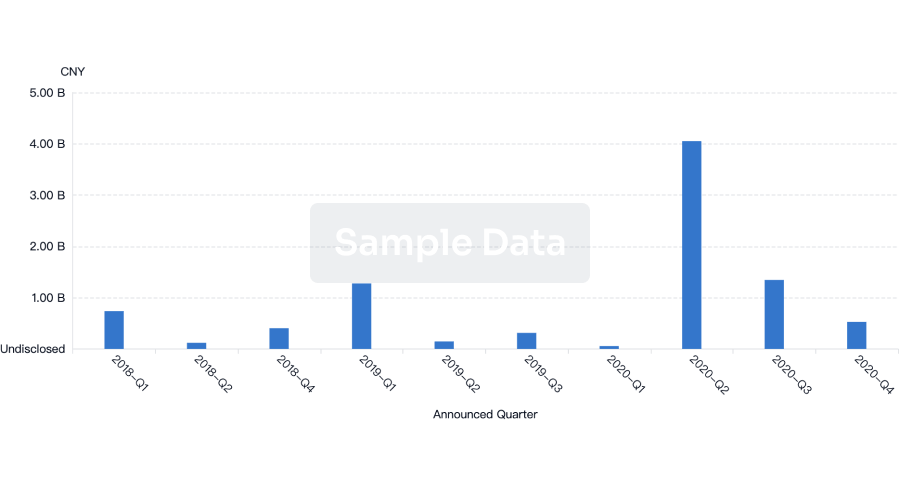
Investment
Gain insights on the latest company investments from start-ups to established corporations.
login
or
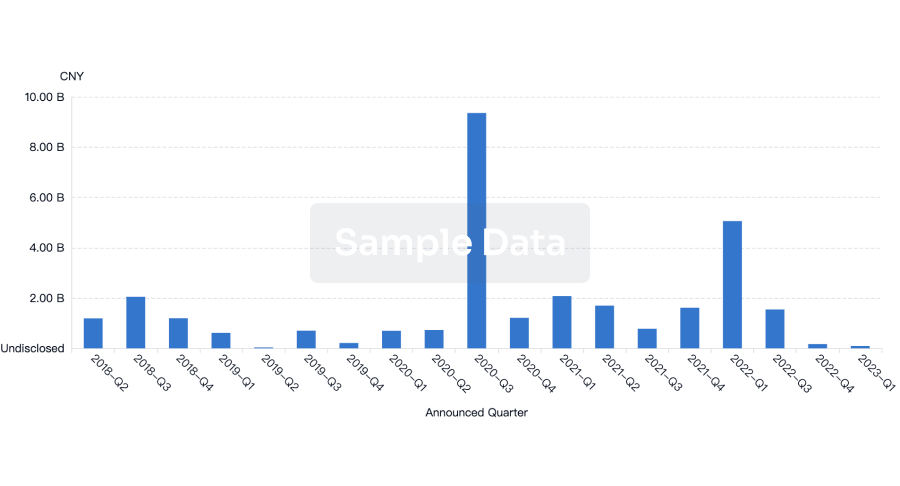
Financing
Unearth financing trends to validate and advance investment opportunities.
login
or
AI Agents Built for Biopharma Breakthroughs
Accelerate discovery. Empower decisions. Transform outcomes.
Get started for free today!
Accelerate Strategic R&D decision making with Synapse, PatSnap’s AI-powered Connected Innovation Intelligence Platform Built for Life Sciences Professionals.
Start your data trial now!
Synapse data is also accessible to external entities via APIs or data packages. Empower better decisions with the latest in pharmaceutical intelligence.
Bio
Bio Sequences Search & Analysis
Sign up for free
Chemical
Chemical Structures Search & Analysis
Sign up for free