/ Not yet recruitingNot ApplicableIIT Impact Assessment of a Clinical Decision Support Tool for Non-invasive Antibiotic Allergy Label Delabeling and Refinement
Antibiotic allergy labels (AAL) are reported in 7% of inpatient's charts, especially for beta-lactams (86% of AAL, i.e., prevalence of 6%). They are associated with increased length of hospital stay, and use of second-line and broad-spectrum antibiotics. Allergy workups are able to invalidate the majority of these AAL but are time-consuming and require invasive skin and provocation testing. The investigators recently evaluated, for the first time in Europa, a strictly non-invasive delabeling protocol using a questionnaire, medical file search and contact with primary care health care workers in 200 adult internal medicine inpatients with a beta-lactam AAL. Up to half of the AAL could be removed or refined, demonstrating the potential of this strategy. In this project, they aim to assess the impact of using the non-invasive 'AAL-fact-check' tool in a multicenter study, on antibiotic selection, and clinical, antimicrobial, and economic endpoints, as compared with the standard of care (i.e., no AAL-fact-check tool).
Semaglutide for the Treatment of Glucose Intolerance in Women with Prior Gestational Diabetes: a Double Blind RCT
Gestational diabetes (GDM) is an important contributor to the increasing prevalence of type 2 diabetes (T2DM). Women with glucose intolerance in early postpartum are a particularly high-risk group with about 50% who will develop T2DM within 5 years after the delivery. Moreover, women with a history of GDM progress more rapidly to T2DM compared to women with similarly elevated glucose levels. Early intervention after the index pregnancy is therefore crucial to prevent T2DM. With the SERENA project, the investigators aim to reduce the risk to develop T2DM with the long-acting GLP-1 agonist semaglutide in women with a recent history of GDM and glucose intolerance in early postpartum.
Brain Injury and Ketamine: a Prospective, Randomized Controlled Double Blind Clinical Trial to Study the Effects of Ketamine on Sedative Sparing and Intracranial Pressure in Traumatic Brain Injury Patients.
Although, in the past years, an increasing use of ketamine in Traumatic Brain injury (TBI) has been reported as an adjunct to other sedatives, there is no evidence from randomized clinical trial to support this practice.
The BIKe (Brain Injury and Ketamine) study is a double-blind placebo controlled randomized multicenter clinical trial to examine the safety and feasibility of using ketamine as an adjunct to a standard sedative strategy in TBI patients.
100 Clinical Results associated with AZ TURNHOUT VZW
0 Patents (Medical) associated with AZ TURNHOUT VZW
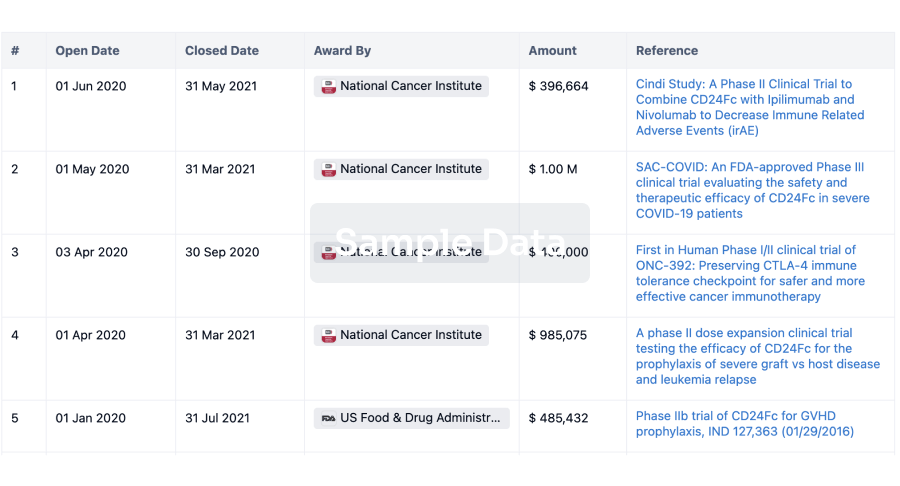
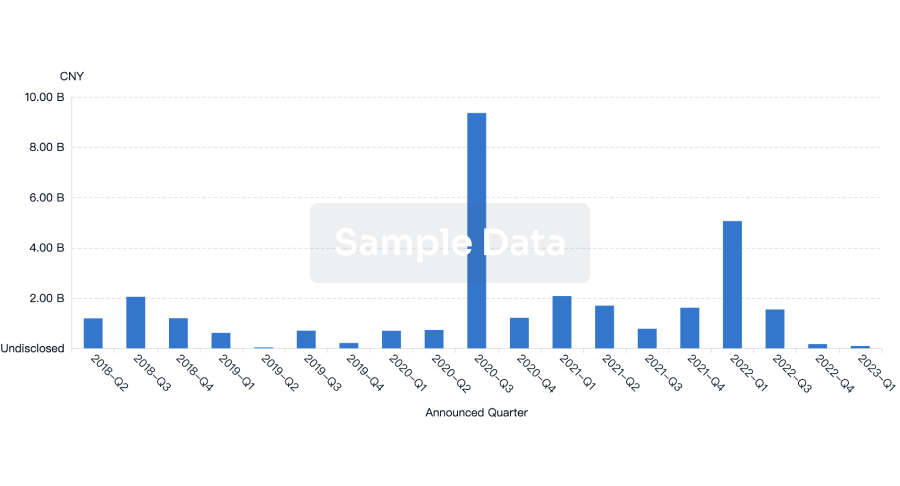
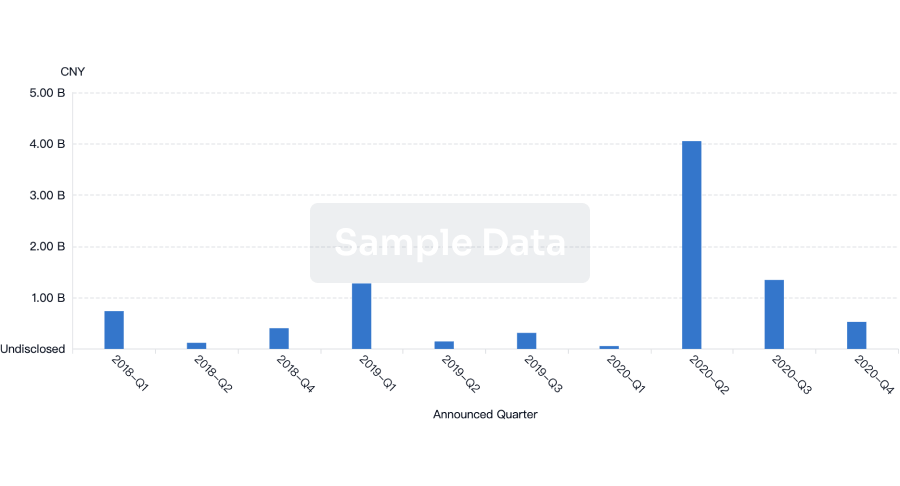
100 Deals associated with AZ TURNHOUT VZW
100 Translational Medicine associated with AZ TURNHOUT VZW