Request Demo
Last update 30 Sep 2024
PCSK9
Last update 30 Sep 2024
Basic Info
Related Targets |
Related
66
Drugs associated with PCSK9Target |
Mechanism PCSK9 inhibitors |
Active Org. |
Originator Org. |
Active Indication |
Inactive Indication |
Drug Highest PhaseApproved |
First Approval Ctry. / Loc. China |
First Approval Date30 Sep 2024 |
Target |
Mechanism PCSK9 inhibitors |
Active Org. |
Originator Org. |
Active Indication |
Inactive Indication |
Drug Highest PhaseApproved |
First Approval Ctry. / Loc. China |
First Approval Date15 Aug 2023 |
575
Clinical Trials associated with PCSK9JPRN-UMIN000040727
The crossover randomized controlled clinical trial with Alirocumab and Evolocumab:CROSS ALIVE Study - The crossover randomized controlled clinical trial with Alirocumab and Evolocumab:CROSS ALIVE Study
Start Date01 Jul 2025 |
Sponsor / Collaborator- |
NCT06597019
Two Part (Double-blind Inclisiran Versus Placebo [Year 1] Followed by Open-label Inclisiran [Year 2]) Randomized Multicenter Study to Evaluate Safety, Tolerability and Efficacy of Inclisiran in Children (6 to Less Than 12 Years) With Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia and Elevated LDL- Cholesterol
This is a pivotal phase III study designed to evaluate safety, tolerability, and efficacy of inclisiran in children (aged 6 to <12 years) with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HeFH) and elevated low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDLC).
Start Date31 Mar 2025 |
Sponsor / Collaborator |
NCT06597006
Two Part (Double-blind Inclisiran Versus Placebo [Year 1] Followed by Open-label Inclisiran [Year 2]) Randomized Multicenter Study to Evaluate Safety, Tolerability, and Efficacy of Inclisiran in Children (2 to Less Than 12 Years) With Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia and Elevated LDL-cholesterol
This is a pivotal phase III study designed to evaluate safety, tolerability, and efficacy of inclisiran in children (aged 2 to <12 years) with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HeFH) and elevated low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDLC).
Start Date31 Mar 2025 |
Sponsor / Collaborator |
100 Clinical Results associated with PCSK9
Login to view more data
100 Translational Medicine associated with PCSK9
Login to view more data
0 Patents (Medical) associated with PCSK9
Login to view more data
5,025
Literatures (Medical) associated with PCSK931 Dec 2024·Pharmaceutical biology
Shenqi Fuzheng injection restores the sensitivity to gefitinib in non-small cell lung cancer by inhibiting the IL-22/STAT3/AKT pathway
Article
Author: Ding, Xuansheng ; Long, Yaling ; Hou, Mengjun ; Jia, Zhirong ; Liu, Shuo ; Yan, Aiwen ; He, Xianhai ; Xiao, Kang ; Wang, Jiali
CONTEXT:
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the most common type of lung cancer. Gefitinib is a first-line treatment for NSCLC. However, its effectiveness is hindered by the development of drug resistance. At present, Shenqi Fuzheng injection (SFI) is widely accepted as an adjuvant therapy in NSCLC.
OBJECTIVE:
This study investigates the molecular mechanism of SFI when combined with gefitinib in regulating cell progression among EGFR-TKI-resistant NSCLC.
MATERIALS AND METHODS:
We established gefitinib-resistant PC9-GR cells by exposing gefitinib escalation from 10 nM with the indicated concentrations of SFI in PC9 cells (1, 4, and 8 mg/mL). Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction was performed to assess gene expression. PC9/GR and H1975 cells were treated with 50 ng/mL of interleukin (IL)-22 alone or in combination with 10 mg/mL of SFI. STAT3, p-STAT3, AKT, and p-AKT expression were evaluated using Western blot. The effects on cell proliferation, clonogenicity, and apoptosis in NSCLC cells were assessed by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT), colony formation and flow cytometry assays.
RESULTS:
SFI treatment alleviated the development of gefitinib resistance in NSCLC. PC9/GR and H1975 cells treated with SFI significantly exhibited a reduction in IL-22 protein and mRNA overexpression levels. SFI effectively counteracted the activation of the STAT3/AKT signaling pathway induced by adding exogenous IL-22 to PC9/GR and H1975 cells. Moreover, IL-22 combined with gefitinib markedly increased cell viability while reducing apoptosis. In contrast, combining SFI with gefitinib and the concurrent treatment of SFI with gefitinib and IL-22 demonstrated the opposite effect.
DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION:
SFI can be a valuable therapeutic option to address gefitinib resistance in NSCLC by suppressing the IL-22/STAT3/AKT pathway.
01 Dec 2024·Current medicinal chemistry
The Link between miRNAs and PCKS9 in Atherosclerosis
Article
Author: Rizzo, Manfredi ; Klisic, Aleksandra N. ; Gluvic, Zoran M. ; Macvanin, Mirjana T. ; Suri, Jasjit S. ; Manojlovic, Mia S. ; Isenovic, Esma R.
Abstract::
Cardiovascular disease (CDV) represents the major cause of death globally.
Atherosclerosis, as the primary cause of CVD, is a chronic immune-inflammatory
disorder with complex multifactorial pathophysiology encompassing oxidative stress, enhanced
immune-inflammatory cascade, endothelial dysfunction, and thrombosis. An initiating
event in atherosclerosis is the subendothelial accumulation of low-density lipoprotein
(LDL), followed by the localization of macrophages to fatty deposits on blood vessel
walls, forming lipid-laden macrophages (foam cells) that secrete compounds involved
in plaque formation. Given the fact that foam cells are one of the key culprits
that underlie the pathophysiology of atherosclerosis, special attention has been paid to
the investigation of the efficient therapeutic approach to overcome the dysregulation of
metabolism of cholesterol in macrophages, decrease the foam cell formation and/or to
force its degradation. Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) is a secretory
serine proteinase that has emerged as a significant regulator of the lipid metabolism
pathway. PCSK9 activation leads to the degradation of LDL receptors (LDLRs), increasing
LDL cholesterol (LDL-C) levels in the circulation. PCSK9 pathway dysregulation
has been identified as one of the mechanisms involved in atherosclerosis. In addition, microRNAs
(miRNAs) are investigated as important epigenetic factors in the pathophysiology
of atherosclerosis and dysregulation of lipid metabolism. This review article summarizes
the recent findings connecting the role of PCSK9 in atherosclerosis and the involvement
of various miRNAs in regulating the expression of PCSK9-related genes. We
also discuss PCSK9 pathway-targeting therapeutic interventions based on PCSK9 inhibition,
and miRNA levels manipulation by therapeutic agents.
01 Dec 2024·PHYTOMEDICINE
Metabolomics combined with network pharmacology reveals the protective effect of astragaloside IV on alcoholic liver disease
Article
Author: Hu, Ruixian ; Zhang, Xiaoyan ; Li, Yuanhong ; Li, Qingshan ; Hao, JinFang ; Hao, Jinfang ; Zhao, Jianming
BACKGROUND:
Alcoholic liver disease (ALD) is a significant contributor to liver damage. However, the clinical options for the treatment of ALD are limited. Astragaloside IV (AST-IV) is a saponin isolated from Astragalus membranaceus (AM). This study aimed to explore the underlying mechanisms of action of AST-IV in ALD by integrating metabolomics and network pharmacology.
METHODS:
Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were used to establish a rat model of ALD. AST-IV and polyene phosphatidyl choline (PPC; a positive control drug) were administered to rats with ALD for 4 weeks. We measured the body weight, liver index, ALT, AST, TC, TG, inflammatory markers (IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α), and oxidative stress markers (SOD, MDA) and used H&E and ORO staining to evaluate the hepatoprotective effect of both AST-IV and PPC on ALD. Subsequently, we performed untargeted metabolomics to predict the influence of AST-IV on lipid metabolism in rats with ALD. We then used a network pharmacology approach to identify the core targets through which AST-IV corrected lipid metabolism disorders and validated these targets through molecular docking, qRT-PCR and western blot analyses. Finally, we calculated the relationships between ALD-related biochemical markers, differential liver metabolites, and core targets using Spearman's correlation analysis.
RESULTS:
AST-IV improved pathological damage and reduced lipid accumulation in the hepatocytes of rats with ALD. Furthermore, AST-IV inhibited oxidative stress and inflammatory responses in rats with ALD. The metabolomic results showed that AST-IV corrected hepatic lipid metabolism disorders by targeting linoleic acid, necrosis, sphingolipid, and glycerophospholipid metabolism. The Network pharmacology analysis revealed that the core targets of AST-IV exerting the above effects were p-RIPK3, p-MLKL, CYP1A2, CYP2C19, PPARα, PCSK9. Spearman's correlation analysis showed a strong correlation between ALD-related serum biochemical indices, core targets, and liver differential metabolites.
CONCLUSION:
AST-IV corrects the metabolic disorders of linoleic acid, sphingolipid, and glycerophospholipid, and alleviates necrosis in rats with ALD through the core targets p-RIPK3, p-MLKL, CYP1A2, CYP2C19, PPARα, and PCSK9. This study is the first to reveal the mechanism of ALD protection through AST-IV from the perspective of metabolomics and network pharmacology. Therefore, a novel target has been identified to exert protection against ALD. This study provides a reference for ALD treatment.
272
News (Medical) associated with PCSK925 Sep 2024
NEW YORK, Sept. 25, 2024 /PRNewswire/ -- Pomerantz LLP announces that a class action lawsuit has been filed against Verve Therapeutics, Inc. ("Verve" or the "Company") (NASDAQ: VERV). Such investors are advised to contact Danielle Peyton at [email protected] or 646-581-9980, (or 888.4-POMLAW), toll-free, Ext. 7980. Those who inquire by e-mail are encouraged to include their mailing address, telephone number, and the number of shares purchased.
The class action concerns whether Verve and certain of its officers and/or directors have engaged in securities fraud or other unlawful business practices.
You have until October 28, 2024, to ask the Court to appoint you as Lead Plaintiff for the class if you are a shareholder who purchased or otherwise acquired Verve securities during the Class Period. A copy of the Complaint can be obtained a
t
.
[Click here for information about joining the class action]
On April 2, 2024, Verve Therapeutics issued a press release entitled "Verve Therapeutics Announces Updates on its PCSK9 Program." The press release disclosed that the Company was halting enrollment in the Heart-1 clinical trial of VERVE-101 as a treatment for patients with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HeFH). Verve cited an adverse event in an individual who had been dosed at 0.45 mg/kg of VERVE-101, stating that "at potentially therapeutic dose levels of VERVE-101, we have observed certain asymptomatic laboratory abnormalities, which we believe are attributable to the [lipid nanoparticle] delivery system."
On this news, Verve's stock price fell $4.47 per share, or 34.95%, to close at $8.32 per share on April 2, 2024.
Pomerantz LLP, with offices in New York, Chicago, Los Angeles, London, Paris, and Tel Aviv, is acknowledged as one of the premier firms in the areas of corporate, securities, and antitrust class litigation. Founded by the late Abraham L. Pomerantz, known as the dean of the class action bar, Pomerantz pioneered the field of securities class actions. Today, more than 85 years later, Pomerantz continues in the tradition he established, fighting for the rights of the victims of securities fraud, breaches of fiduciary duty, and corporate misconduct. The Firm has recovered billions of dollars in damages awards on behalf of class members. See .
Attorney advertising. Prior results do not guarantee similar outcomes.
CONTACT:
Danielle Peyton
Pomerantz LLP
[email protected]
646-581-9980 ext. 7980
SOURCE Pomerantz LLP
WANT YOUR COMPANY'S NEWS FEATURED ON PRNEWSWIRE.COM?
440k+
Newsrooms &
Influencers
9k+
Digital Media
Outlets
270k+
Journalists
Opted In
GET STARTED
Clinical StudyPatent Infringement
05 Sep 2024
Participants in front of the logo of the European Society of Cardiology at a previous meeting. The 2024 conference was held in London 30 August-2 September. Image credit: Shutterstock/hydebrink
The results of two subanalyses of the PACMAN-AMI trial were presented on the final day (2 September) of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) 2024 Congress.
Coronary heart disease is the most frequent cause of mortality in the industrialised world, and hypercholesterolaemia is a major risk factor. Statins are the first-line therapy, but are often not wholly effective.
Several studies have demonstrated low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) reduction with PCSK9 inhibition, in addition to decreased adverse cardiovascular events. The Phase III PACMAN-AMI trial (NCT03067844) investigated the effect of Regeneron Pharmaceutials’ PCSK9 inhibitor Praluent (alirocumab), a PCSK9 inhibitor, in patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI).
Some data from the study was presented earlier at the conference during a session outlining the
efficacy of antibodies like Praluent in reducing LDL-C levels
.
In the study, patients received Praluent or placebo every two weeks alongside statin therapy. After 52 weeks, PCSK9 inhibition significantly reduced percent atheroma volume (PAV), the difference between vessel and lumen volumes, and other measures of blood vessel occlusion compared to statin therapy alone.
See Also:
Novavax wins FDA emergency approval for updated Covid-19 vaccine
Global Calcium hit with Form 483 after Indian factory inspection
Subanalyses provide more insights
Dr. Yasushi Ueki from Shinshu University Hospital in Japan first presented a subanalysis of the PACMAN-AMI trial. His team used risk stratification to identify patients with the greatest potential for benefit from plaque regression.
Ueki explained his group divided patients into three groups based on risk factors for chronic coronary disease—those with none, with one, or with two or more major risk factors. Blood vessel imaging for these patients was compared before and after 52 weeks of Praluent treatment or placebo between risk-stratified groups.
Ueki’s team found PAV was only significantly reduced among patients with one or no risk factors, with, “no significant difference between patients with two or more risk factors”. This was also true regarding changes in maximum lipid core burden index and macrophage angle.
According to Ueki, “among AMI patients with no or one atherothrombotic risk factors, the addition of alirocumab to high-intensity statin demonstrated greater coronary plaque regression; patients with fewer risk factors thus appear to be more susceptible for atheroma regression”.
Dr. Flavio Biccirè from the University Hospital of Bern in Switzerland then spoke about his team’s subanalysis. They focused on vessel lesions, regions at which plaque buildup is most pronounced, as opposed to the PACMAN-AMI trial’s wider, vessel-level analysis.
Identifying vessel lesions using imaging data from 245 patients, Biccirè and his colleagues remeasured clinical outcomes. They found that at the lesion level, PAV change with Praluent at 52 weeks was -4.9 compared to placebo, far greater than the -2.1 change stated in the original analysis.
Biccirè concluded, “LDL-C lowering induced an extensive atheroma burden reduction at lesion-level”, and that, “significant changes in coronary lesions, rather than mild effects described at vessel-level, underlie the protective vascular effects of contemporary lipid-lowering therapies”.

Clinical ResultPhase 3Drug ApprovalVaccine
03 Sep 2024
New NHP data indicate robust silencing at clinically relevant dose levels and highlight potential best-in-class potency achievable with Chroma's epigenetic editors
Chroma's epigenetic editor achieved efficient and durable reductions in blood PCSK9 (84%) and LDL-cholesterol (68%) following a single 1.0 mg/kg dose
Potential for life-long durability supported by mechanistic data confirming robust and stable CpG methylation at the PCSK9 locus in NHPs
BOSTON, Sept. 3, 2024 /PRNewswire/ -- Chroma Medicine, Inc., (Chroma) a genomic medicine company pioneering single-course epigenetic editing therapeutics, presented new preclinical data demonstrating the potency, durability, and specificity of its PCSK9-targeted epigenetic editor in an oral presentation at the 2024 European Society of Cardiology Congress, held August 30-September 2 in London.
The data showcase the potential best-in-class potency achievable in NHPs with Chroma's optimized epigenetic editors. They also indicate the company's epigenetic editing platform can effectively silence expression of PCSK9 in the liver, inducing durable reductions in low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL-C) levels without cutting or nicking the DNA.
The PCSK9 gene actively promotes the degradation of LDL receptors, thereby reducing the ability of the liver to clear cholesterol from the blood. This can result in chronically elevated blood levels of LDL-C and lead to increased risk for early onset atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD). Genetic and pharmacologic reductions in PCSK9 levels have been shown to correlate with decreased cardiovascular events, making it an established and compelling target for prevention of ASCVD.
"These results underscore the successful optimization and development of a highly potent, durable, and specific PCSK9-targeted therapeutic," said Catherine Stehman-Breen, M.D., Chroma's Chief Executive Officer. "By demonstrating potency at clinically relevant doses, we have achieved a key requirement for successful translation of a lipid nanoparticle-delivered genomic medicine into an efficacious and well-tolerated therapeutic, supporting continued advancement toward clinical studies."
Data from the presentation demonstrate best-in-class potency, with Chroma's human PCSK9-targeting epigenetic editor reaching saturating pharmacology at 1.0 mg/kg in NHPs. A significant reduction in circulating PCSK9 (84%) levels was achieved, resulting in a 68% reduction in LDL-C levels, maintained out to three months. Additional data show that the company's epigenetic editor efficiently and durably reduced PCSK9 levels in vivo for one year after a single administration in human transgenic mice. The silencing was maintained in mice pre- and post-partial hepatectomy, the standard surgical model for induction of liver regeneration.
"We believe single-course therapies are crucial in the creation of genomic medicines that can disrupt the current treatment paradigm for lowering LDL-cholesterol and reduce the risk of serious cardiovascular disease," said Jenny Marlowe, Ph.D., Chroma's Chief Development Officer. "These data presented at ESC confirm the potential of our epigenetic editing platform to produce a highly potent therapeutic that can bring the promise of better treatment options within reach."
Find the presentation on the Chroma website here.
About ASCVD
Chronically elevated blood levels of low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL-C) can lead to increased risk for early onset atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD), heart attack, and stroke. ASCVD is the leading cause of death in the United States and globally. Current therapeutic interventions often fail to lower LDL-C below designated therapeutic thresholds and require frequent dosing, leading to treatment adherence challenges. The PCSK9 gene actively promotes the degradation of LDL receptors, which are responsible for clearing LDL-C from the blood, thereby reducing the ability of the liver to clear cholesterol from the blood. Genetic and pharmacologic reductions in PCSK9 have been associated with decreased LDL-C levels and reduced risk for cardiovascular events. Chroma is advancing an in vivo epigenetic editing therapeutic designed to effectively and durably silence the PCSK9 gene without cutting or nicking the DNA, resulting in decreased PCSK9 protein levels and leading to lower LDL-C levels and reduced risk of ASCVD.
About Chroma Medicine
Chroma Medicine is a biotechnology company pioneering a new class of genomic medicines that harness epigenetics, nature's innate mechanism for gene regulation, to deliver precise, programmable single-course therapeutics while preserving genomic integrity. The company's modular platform enables development of medicines that can address a wide range of complex diseases, whether they require silencing, activation, or targeting multiple genes at once. Chroma was founded by the world's foremost experts in genomic research and is led by a veteran team of industry leaders and scientists with deep experience in genomic medicine, drug discovery, and development. For more information, please visit chromamedicine.com or follow us on LinkedIn and X.
SOURCE Chroma Medicine
Clinical Result
Analysis
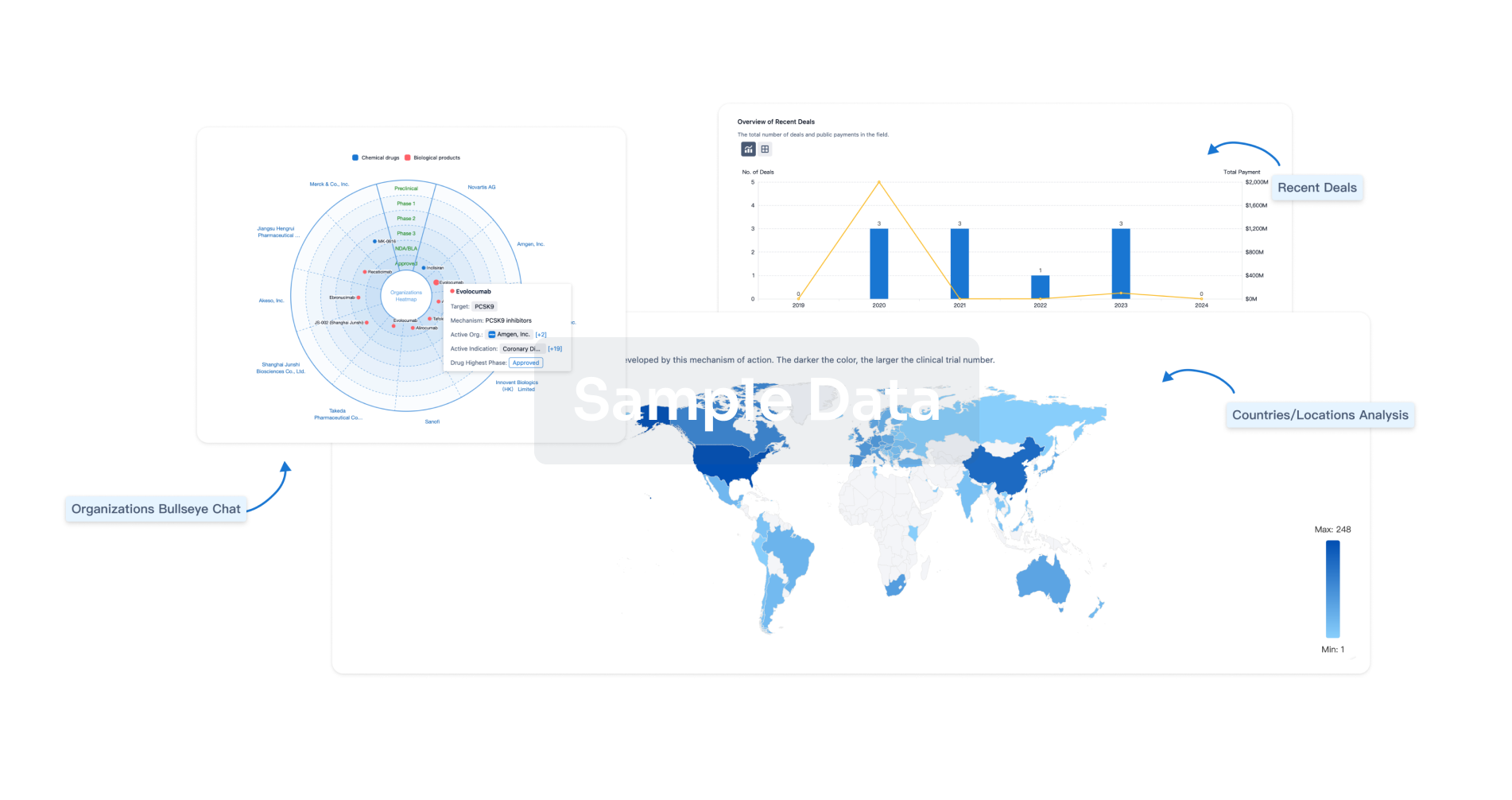
Perform a panoramic analysis of this field.
login
or
AI Agents Built for Biopharma Breakthroughs
Accelerate discovery. Empower decisions. Transform outcomes.
Get started for free today!
Accelerate Strategic R&D decision making with Synapse, PatSnap’s AI-powered Connected Innovation Intelligence Platform Built for Life Sciences Professionals.
Start your data trial now!
Synapse data is also accessible to external entities via APIs or data packages. Empower better decisions with the latest in pharmaceutical intelligence.
Bio
Bio Sequences Search & Analysis
Sign up for free
Chemical
Chemical Structures Search & Analysis
Sign up for free



