Request Demo
Last update 08 May 2025
MIR155HG
Last update 08 May 2025
Basic Info
Synonyms BIC, miPEP155, MIR155 host gene + [3] |
Introduction- |
Related
100 Clinical Results associated with MIR155HG
Login to view more data
100 Translational Medicine associated with MIR155HG
Login to view more data
0 Patents (Medical) associated with MIR155HG
Login to view more data
282
Literatures (Medical) associated with MIR155HG01 Apr 2025·Archives of Medical Research
Deficiency of miR-155 in Leukemic B-Cells Results in Cell Cycle Arrest and Deregulation of MIR155HG/TP53INP1/CDKN1A/CCND1 network
Article
Author: Sebela, Marek ; Sefc, Ludek ; Vargova, Karina Savvulidi ; Kokavec, Juraj ; Stopka, Tomas ; Bajecny, Martin ; Tost, Jorg ; Kazantsev, Dmitry ; Savvulidi, Filipp Georgijevic ; Herynek, Vit ; Yurikova, Oxana ; Zemanova, Zuzana ; Lenobel, Rene ; Golovina, Elena ; Klener, Pavel ; Simersky, Radim
01 Feb 2025·The Journal of Hand Surgery
Optimal Distal Tendon Insertion Point for Elbow Flexion in Free-Functioning Gracilis Muscle Transfer for Panbrachial Plexus Injuries: A Cadaveric Study
Article
Author: Lieber, Richard L ; Hooke, Alexander W ; Wu, Kitty Y ; Persad, Lomas S ; Shin, Alexander Y ; Kaufman, Kenton R
01 Jan 2025·Clinical Oral Implants Research
Hyperbranched Poly‐l ‐Lysine Modified Titanium Surface With Enhanced Osseointegration, Bacteriostasis, and Anti‐Inflammatory Properties for Implant Application: An Experimental In Vivo Study
Article
Author: Miao, Xiaoyan ; Wang, Zhikang ; Jiang, Qifeng ; Chen, Chaozhen ; Gao, Changyou ; Dai, Wei ; Yang, Guoli ; Qin, Xiaoru ; Zhang, Yanmin ; Jiang, Zhiwei ; Xi, Yue ; Wang, Zhaolong
Analysis
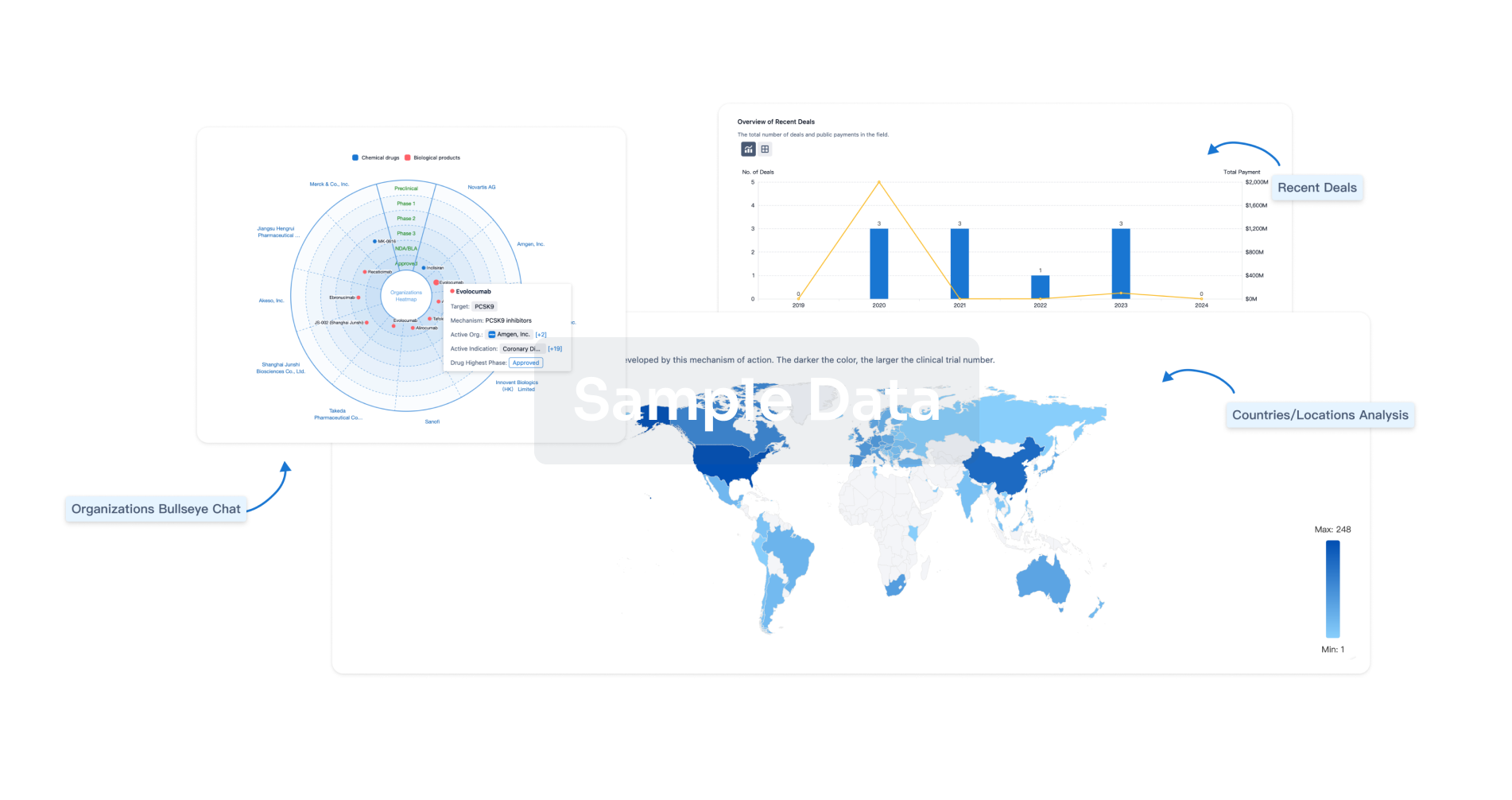
Perform a panoramic analysis of this field.
login
or
AI Agents Built for Biopharma Breakthroughs
Accelerate discovery. Empower decisions. Transform outcomes.
Get started for free today!
Accelerate Strategic R&D decision making with Synapse, PatSnap’s AI-powered Connected Innovation Intelligence Platform Built for Life Sciences Professionals.
Start your data trial now!
Synapse data is also accessible to external entities via APIs or data packages. Empower better decisions with the latest in pharmaceutical intelligence.
Bio
Bio Sequences Search & Analysis
Sign up for free
Chemical
Chemical Structures Search & Analysis
Sign up for free