Analysis on the Clinical Research Progress of PDL1 inhibitors
Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) is a protein found on the surface of certain cells in the human body, including immune cells and some cancer cells. Its primary role is to regulate the immune response by interacting with a receptor called PD-1 on T cells. When PD-L1 binds to PD-1, it sends inhibitory signals that suppress the activity of T cells, preventing them from attacking healthy cells. However, some cancer cells exploit this mechanism by overexpressing PD-L1, which helps them evade immune detection and destruction. Targeting the PD-L1/PD-1 pathway with specific drugs, known as immune checkpoint inhibitors, has shown promising results in cancer immunotherapy by restoring the immune system's ability to recognize and eliminate cancer cells.
PDL1 Competitive Landscape
According to the data provided by Patsnap Synapse-Global Drug Intelligence Database: the following figure shows that as of 22 Sep 2023, there are a total of 423 PDL1 drugs worldwide, from 386 organizations, covering 217 indications, and conducting 3001 clinical trials.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or login directly if you have freemium accounts, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs , indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target.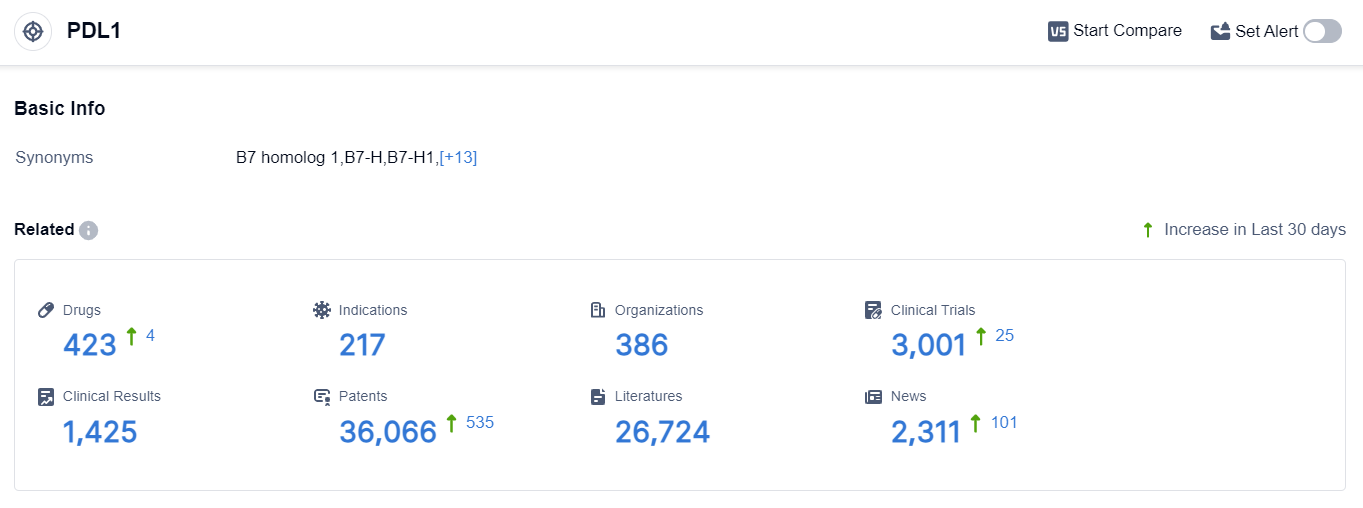
The analysis of the target PDL1 reveals a competitive landscape with multiple companies actively involved in its development. Roche Holding AG, Jiangsu Hengrui Pharmaceutical Group Co. Ltd., and AstraZeneca PLC are among the companies with the highest growth and diverse R&D progress.
The approved drugs under the target PDL1 cover a wide range of indications, including various types of cancer. Monoclonal antibodies and biosimilars, such as Bispecific antibodies and Antibody drug conjugates (ADC), are the most rapidly progressing drug types.
China, along with the United States, European Union, and Japan, is at the forefront of PDL1-targeted drug development. The future development of the target PDL1 is expected to witness further advancements in drug approvals, indication expansion, and international collaborations.
Key Drug: Atezolizumab
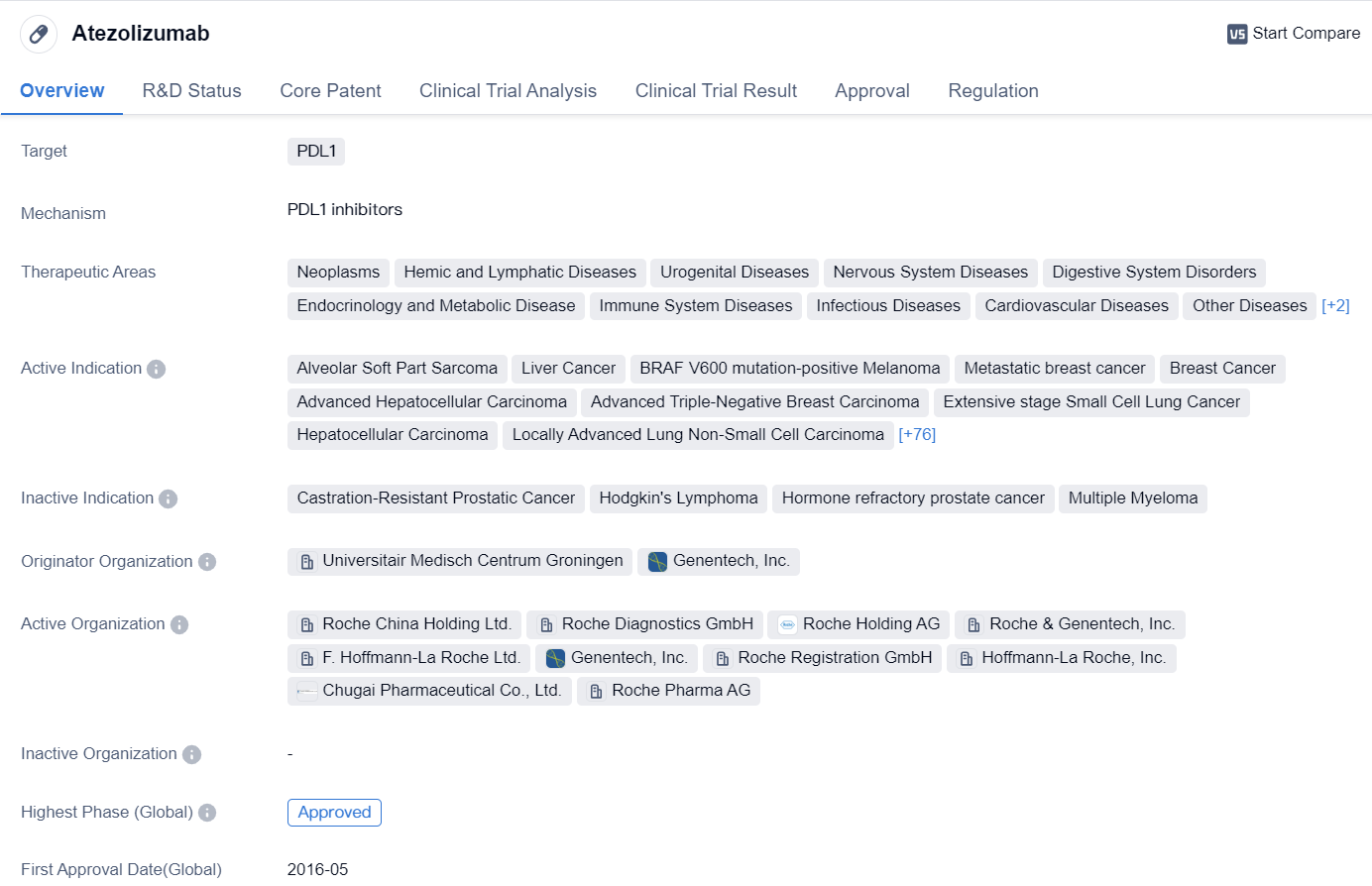
Atezolizumab is a monoclonal antibody drug that targets PDL1, a protein involved in regulating the immune system. It has been approved for use in various therapeutic areas, including neoplasms (tumors), hemic and lymphatic diseases, urogenital diseases, nervous system diseases, digestive system disorders, endocrinology and metabolic diseases, immune system diseases, infectious diseases, cardiovascular diseases, other diseases, skin and musculoskeletal diseases, and respiratory diseases.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
The drug has shown efficacy in treating several types of cancer, including alveolar soft part sarcoma, liver cancer, BRAF V600 mutation-positive melanoma, metastatic breast cancer, breast cancer, advanced hepatocellular carcinoma, advanced triple-negative breast carcinoma, extensive stage small cell lung cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, locally advanced lung non-small cell carcinoma, locally advanced urothelial carcinoma, metastatic non-squamous non-small cell lung carcinoma, metastatic triple-negative breast carcinoma, metastatic urothelial carcinoma, small cell lung cancer, triple-negative breast cancer, unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma, bladder cancer, metastatic non-small cell lung cancer, urogenital neoplasms, non-small cell lung cancer, transitional cell carcinoma, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, esophageal carcinoma, adenocarcinoma of the prostate, prostatic cancer metastatic, prostatic cancer, mesothelioma, endometrioid carcinoma, uterine cervical cancer, squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck, head and neck neoplasms, urethral neoplasms, ovarian cancer, fallopian tube carcinoma, Krukenberg tumor, peritoneal neoplasms, melanoma, urologic neoplasms, colorectal cancer, non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer, renal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma of the anus, bile duct neoplasms, biliary tract neoplasms, pheochromocytoma, adrenocortical carcinoma, thymoma, cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, anus neoplasms, myelodysplastic syndromes, endometrial carcinoma, unknown primary neoplasms, gallbladder neoplasms, stomach cancer, thyroid cancer, anaplastic thyroid carcinoma, Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia, brain metastases, pancreatic cancer, pancreatic ductal carcinoma, mantle-cell lymphoma, marginal zone B-cell lymphoma, reproductive tract disorder NOS, female urogenital diseases, rectal cancer, Merkel cell carcinoma, acute myeloid leukemia, chronic myelomonocytic leukemia, follicular lymphoma, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, liposarcoma, B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, solid tumors, gastroesophageal junction cancer, neuroendocrine tumors, pancreatic adenocarcinoma, sarcoma, vulvar neoplasms, glioblastoma multiforme, glioblastoma, kidney neoplasms, hematologic neoplasms, and thymus neoplasms.
The drug was developed by Universitair Medisch Centrum Groningen and Genentech, Inc. It received its first approval in the United States in May 2016. Atezolizumab has undergone various regulatory processes, including priority review, accelerated approval, fast track designation, orphan drug designation, and breakthrough therapy designation.
In summary, Atezolizumab is a monoclonal antibody drug that targets PDL1 and has been approved for the treatment of multiple types of cancer and other diseases. It has shown promising results in clinical trials and has received regulatory approvals in the United States and China.
Durvalumab
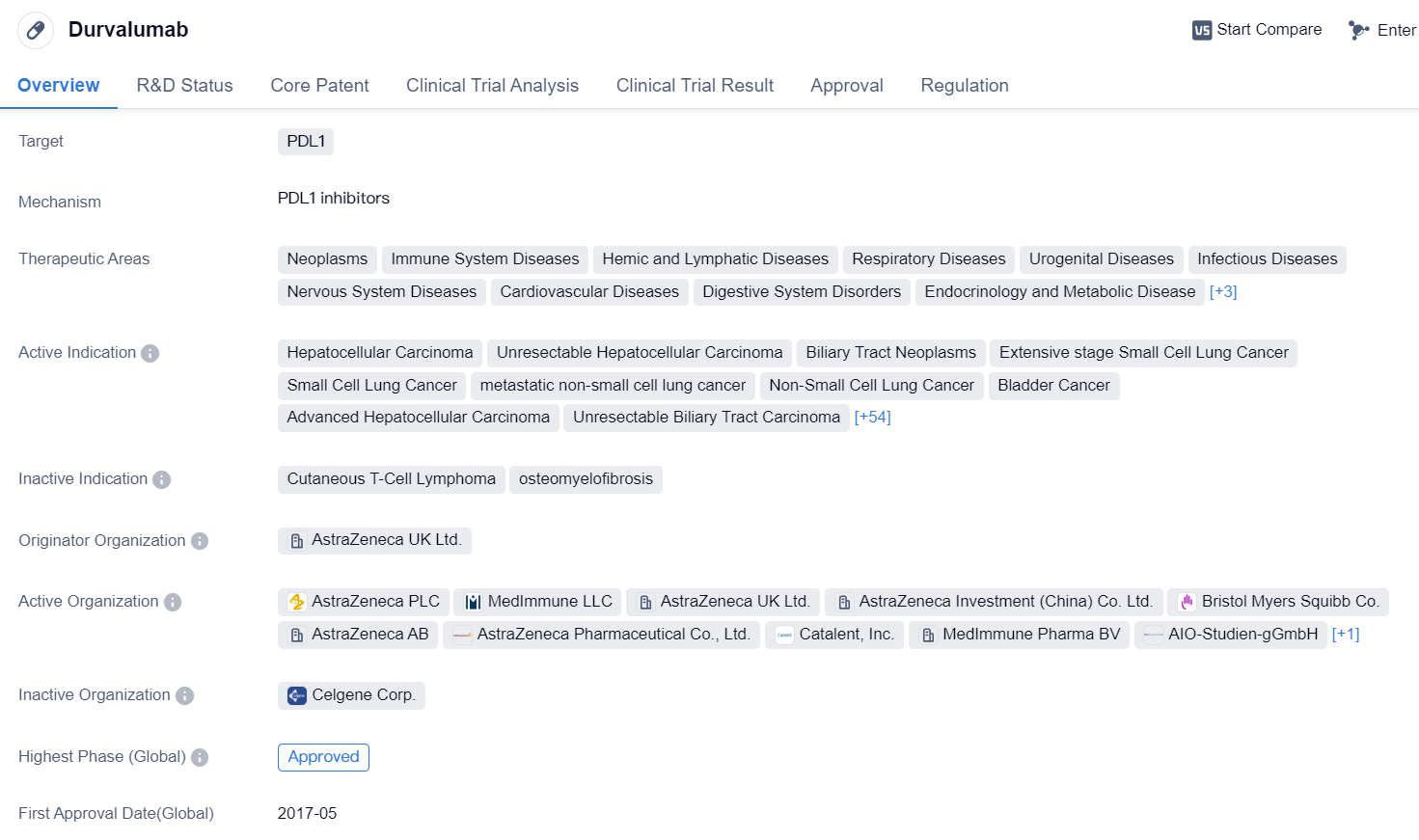
Durvalumab is a monoclonal antibody drug that targets PDL1, a protein involved in regulating the immune system. It has been approved for use in various therapeutic areas, including neoplasms (tumors), immune system diseases, respiratory diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and many others. The drug has shown efficacy in treating a wide range of cancers, including hepatocellular carcinoma, small cell lung cancer, bladder cancer, and renal cell carcinoma, among others.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Durvalumab was first approved in the United States in May 2017 and is manufactured by AstraZeneca UK Ltd. It has also received approval in China. The drug has undergone priority review and has been granted accelerated approval, orphan drug status, and breakthrough therapy designation, indicating its potential to address unmet medical needs.
The approval of durvalumab marks a significant advancement in the field of biomedicine, particularly in the treatment of various cancers. As a monoclonal antibody, it specifically targets PDL1, a protein that can suppress the immune response against cancer cells. By blocking PDL1, durvalumab helps to unleash the body's immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells more effectively.
The wide range of therapeutic areas in which durvalumab has shown efficacy highlights its potential to benefit patients with different types of diseases. From neoplasms to respiratory diseases and urogenital diseases, durvalumab offers a promising treatment option for patients suffering from these conditions.
The regulatory designations received by durvalumab, such as priority review, accelerated approval, orphan drug status, and breakthrough therapy, reflect the drug's potential to address critical medical needs and expedite its availability to patients. These designations also indicate the recognition of durvalumab's significant clinical benefits and the urgency to make it accessible to patients as quickly as possible.
In summary, durvalumab is a monoclonal antibody drug that targets PDL1 and has been approved for use in various therapeutic areas, particularly in the treatment of different types of cancers. Its approval in the United States and China, along with the regulatory designations it has received, highlight its potential to address unmet medical needs and provide a new treatment option for patients.