carglumic acid: Detailed Review of its Transformative R&D Success
Carglumic acid's R&D Progress
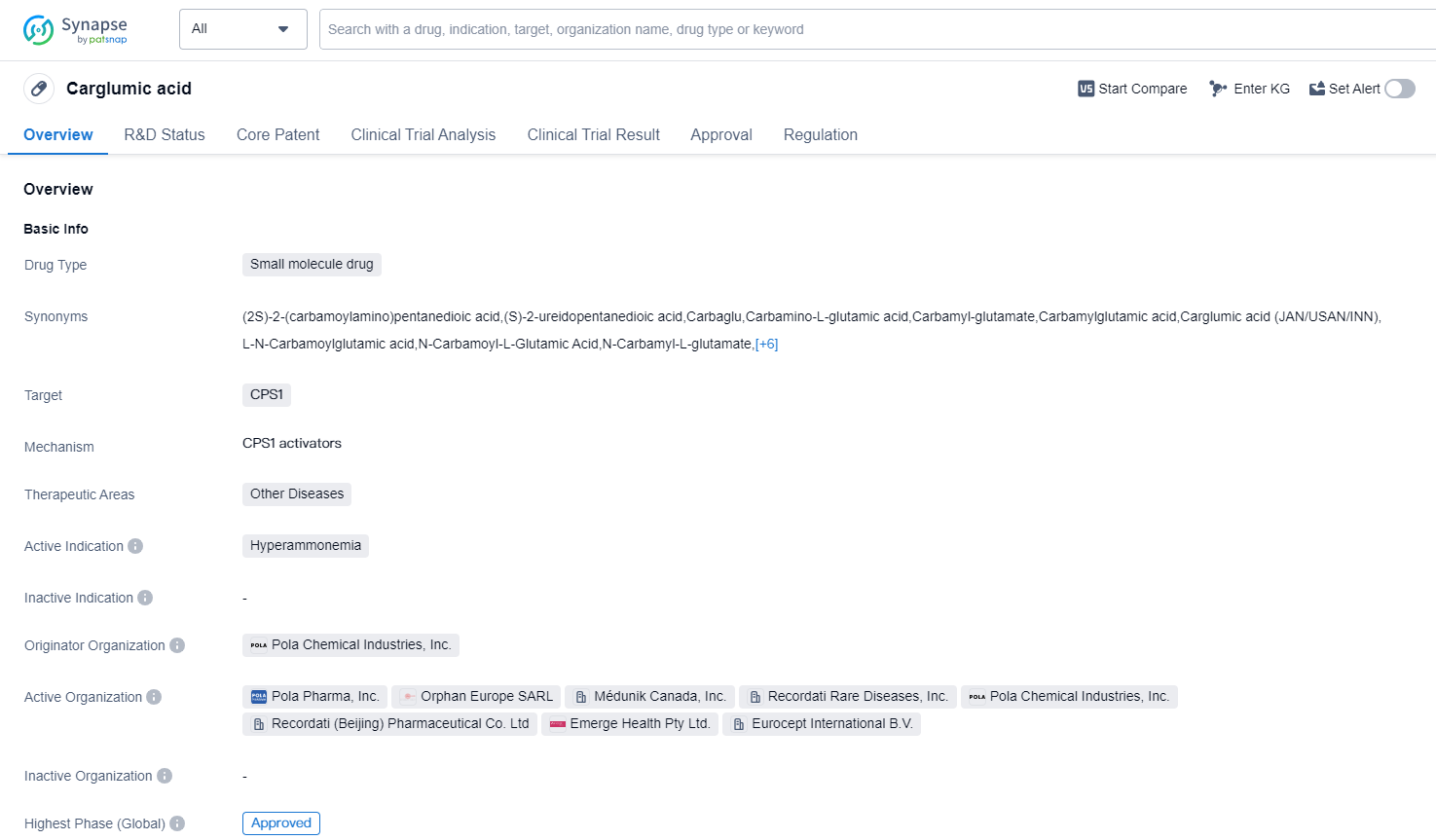
Carglumic acid is a small molecule drug that targets the enzyme CPS1. It is primarily used in the treatment of hyperammonemia, a condition characterized by high levels of ammonia in the blood. Hyperammonemia can be caused by various genetic disorders or liver diseases, and it can lead to serious neurological complications if left untreated.
The drug was developed by Pola Chemical Industries, Inc., and it received its first approval in the European Union and Lithuania in January 2003. It has since been approved in other countries as well. Carglumic acid has been granted priority review status and orphan drug designation, indicating its potential to address unmet medical needs for rare diseases.
As a small molecule drug, carglumic acid is designed to interact with the CPS1 enzyme and modulate its activity. CPS1 plays a crucial role in the urea cycle, which is responsible for removing ammonia from the body. By targeting CPS1, carglumic acid helps to restore the normal function of the urea cycle and reduce ammonia levels in patients with hyperammonemia.
The highest R&D phase of this drug is approved. The drug's highest phase of development is approved, indicating that it has successfully completed all necessary stages of testing and has been deemed suitable for patient use.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for carglumic acid: CPS1 activators
CPS1 activators are substances or compounds that stimulate the activity of the enzyme carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1 (CPS1). CPS1 is an important enzyme involved in the urea cycle, which is responsible for removing toxic ammonia from the body.
From a biomedical perspective, CPS1 activators can be used as potential therapeutic agents for individuals with urea cycle disorders. These disorders are characterized by deficiencies in enzymes involved in the urea cycle, leading to the accumulation of ammonia in the body. By activating CPS1, these activators can enhance the conversion of ammonia into urea, aiding in its elimination from the body.
CPS1 activators may also have implications in other areas of biomedicine, such as liver disease and cancer. The urea cycle plays a role in liver function, and dysregulation of CPS1 activity has been observed in certain liver diseases. By targeting CPS1 with activators, it may be possible to restore normal urea cycle function and improve liver health.
In the context of cancer, CPS1 activators have shown potential as therapeutic agents in certain types of tumors. Cancer cells often exhibit altered metabolic pathways, including increased ammonia production. By activating CPS1, these activators can promote the conversion of ammonia into urea, potentially inhibiting tumor growth.
Overall, CPS1 activators have the potential to be valuable tools in the treatment of urea cycle disorders, liver disease, and cancer. Further research is needed to fully understand their mechanisms of action and evaluate their efficacy and safety in clinical settings.
Drug Target R&D Trends for carglumic acid
CPS1, or carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1, plays a crucial role in the human body as an enzyme involved in the urea cycle. This cycle is responsible for the detoxification of ammonia, a toxic byproduct of protein metabolism, into urea, which can be safely excreted by the kidneys. CPS1 catalyzes the conversion of ammonia and bicarbonate into carbamoyl phosphate, a key intermediate in the urea cycle. This process occurs primarily in the liver, where CPS1 ensures the proper functioning of the urea cycle, maintaining nitrogen balance and preventing the accumulation of toxic ammonia in the body.
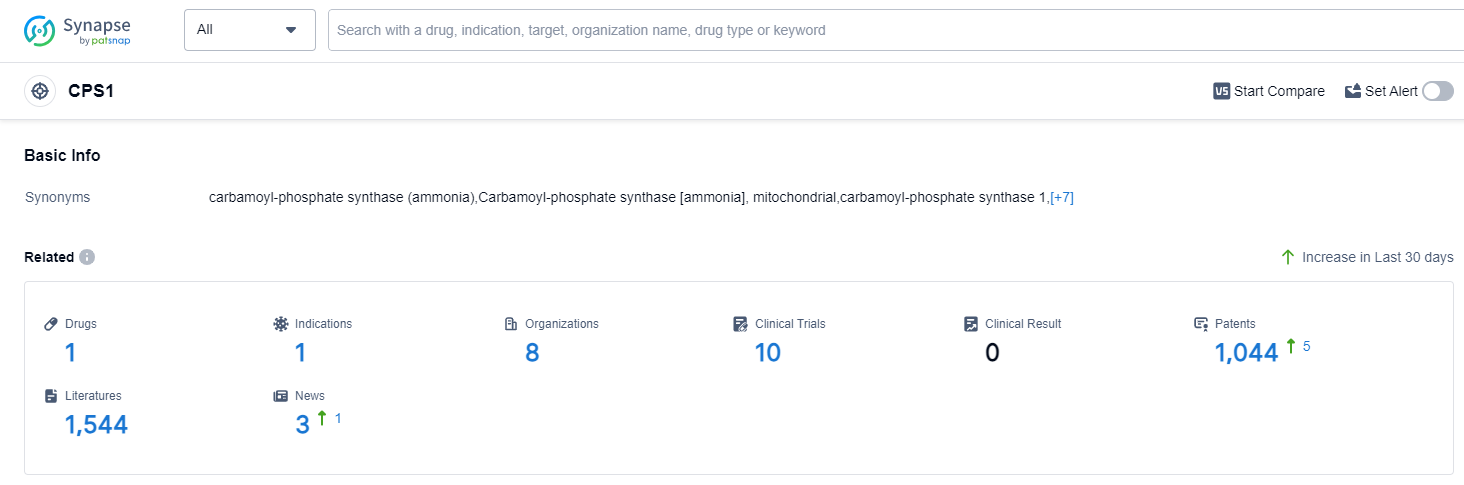
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 13 Sep 2023, there are a total of 1 CPS1 drugs worldwide, from 8 organizations, covering 1 indications, and conducting 10 clinical trials.
Based on the analysis of the provided data, the current competitive landscape for target CPS1 indicates significant growth and progress. Several companies have reached the approved stage of development, indicating successful completion of clinical trials and regulatory requirements. The approved indication for drugs under target CPS1 is Hyperammonemia. Small molecule drugs have shown rapid progress, and various countries/locations, including China, have reached the approved stage.
To fully understand the competitive landscape and future development of target CPS1, additional information on specific R&D progress, biosimilars, and the nature of China's progress is required.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, carglumic acid is a small molecule drug developed by Pola Chemical Industries, Inc. It is approved for the treatment of hyperammonemia and targets the CPS1 enzyme. The drug has received priority review and orphan drug designation, indicating its potential to address unmet medical needs. Its approval in multiple countries suggests its efficacy and safety have been well-established.