Deep Scientific Insights on Lanthanum carbonate's R&D Progress, Mechanism of Action, and Drug Target
Lanthanum carbonate's R&D Progress
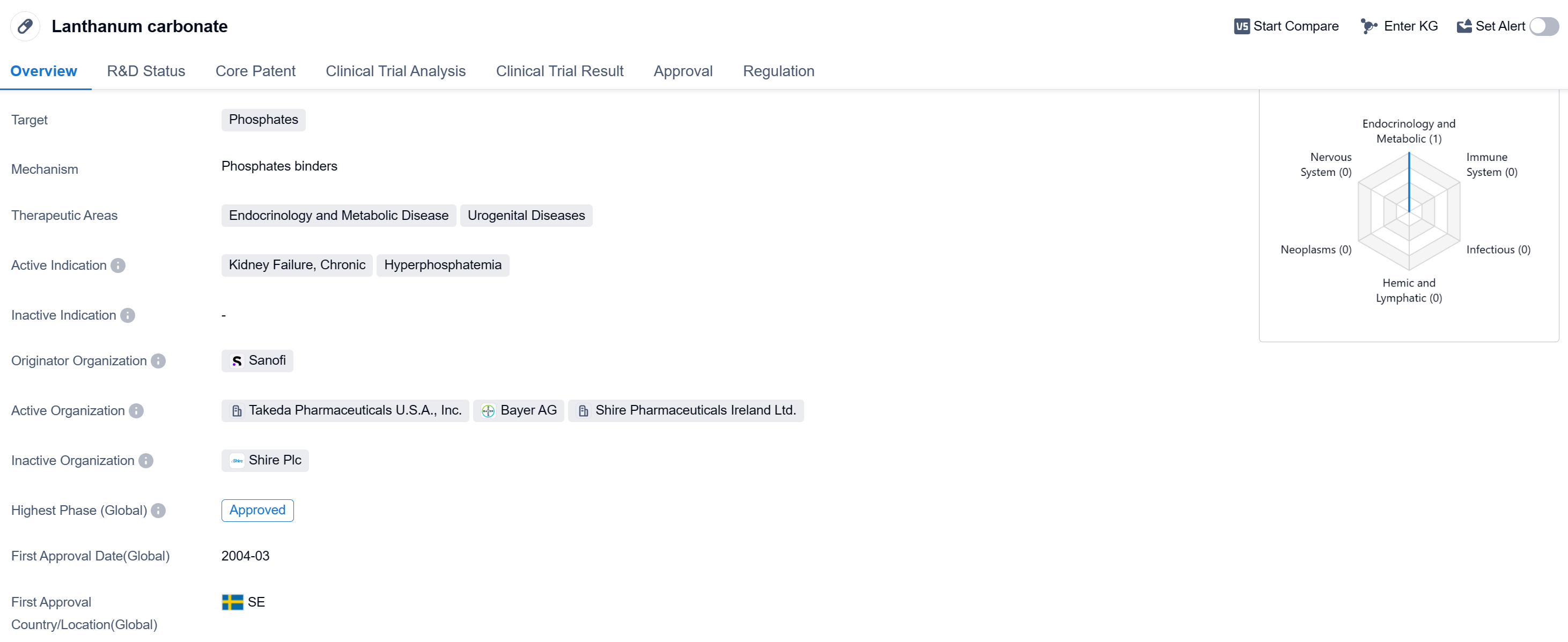
Lanthanum carbonate is a small molecule drug that targets phosphates in the body. It is primarily used in the treatment of kidney failure, chronic, and hyperphosphatemia. The drug falls under the therapeutic areas of endocrinology and metabolic disease, as well as urogenital diseases.
The originator organization of Lanthanum carbonate is Sanofi, a well-known pharmaceutical company. The drug has reached the highest phase of approval globally. It was first approved for use in 2004 in Sweden, making it available for patients in that country.
Lanthanum carbonate is regulated under priority review, indicating that it has undergone an expedited evaluation process by regulatory authorities. This suggests that the drug may have demonstrated significant benefits or addressed an unmet medical need.
As a small molecule drug, Lanthanum carbonate is designed to interact with phosphates in the body, potentially reducing their levels. This is particularly important in patients with kidney failure and hyperphosphatemia, as high phosphate levels can lead to complications and worsen the condition.
The approval of Lanthanum carbonate in multiple countries, including China, highlights its global relevance and potential impact on patients worldwide. The drug's approval in Sweden in 2004 indicates that it has been available for use for over a decade, suggesting a well-established safety and efficacy profile.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Lanthanum carbonate: Phosphates binders
Phosphate binders are medications used to lower the levels of phosphate in the blood. Phosphates are a form of phosphorus, which is an essential mineral for the body. However, when phosphate levels become too high, it can lead to complications in individuals with kidney disease or those on dialysis.
Phosphate binders work by binding to the phosphate in the gastrointestinal tract, preventing its absorption into the bloodstream. This helps to reduce the overall phosphate levels in the body. By controlling phosphate levels, phosphate binders can help prevent complications such as bone problems, heart disease, and mineral imbalances.
There are different types of phosphate binders available, including calcium-based binders, aluminum-based binders, and non-calcium, non-aluminum binders. The choice of binder depends on various factors, including the individual's kidney function, calcium levels, and other medical conditions.
It is important to note that phosphate binders should be taken as prescribed by a healthcare professional and in conjunction with a low-phosphate diet. Regular monitoring of phosphate levels is also necessary to ensure the effectiveness of the treatment.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Lanthanum carbonate
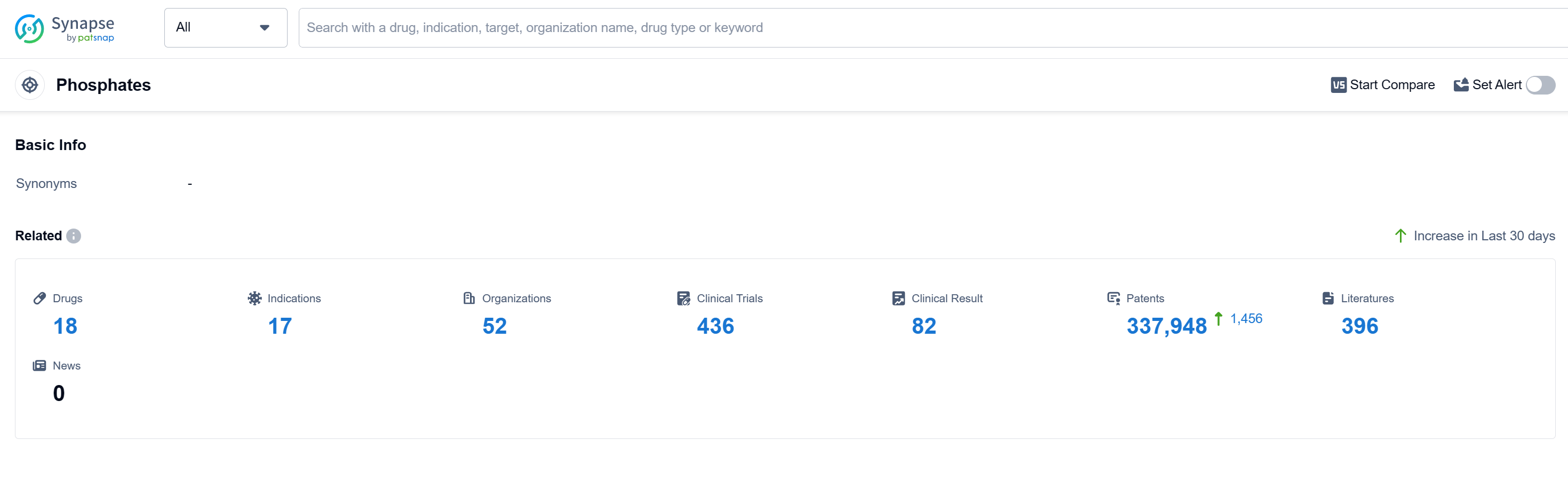
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 12 Sep 2023, there are a total of 18 Phosphates drugs worldwide, from 52 organizations, covering 17 indications, and conducting 436 clinical trials. Based on the analysis of the data provided, it can be concluded that the target Phosphates in the pharmaceutical industry is experiencing significant growth and development. Companies such as Sanofi, CSL Ltd., and Fresenius Medical Care AG & Co. KGaA have shown the highest stage of development, with approved drugs in their portfolio. The most common indication for Phosphates drugs is hyperphosphatemia, followed by kidney failure, chronic, and chronic kidney diseases. Small molecule drugs are progressing most rapidly under the current targets, indicating intense competition in the market. The United States, Japan, the European Union, and China are the countries/locations developing fastest under the current targets, with China showing notable progress. Overall, the target Phosphates market is competitive and holds promise for future development.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Lanthanum carbonate is a small molecule drug developed by Sanofi that targets phosphates. It is primarily used in the treatment of kidney failure, chronic, and hyperphosphatemia. The drug has received approval in multiple countries, including China, and was first approved in Sweden in 2004. Its regulation under priority review indicates its potential significance in addressing unmet medical needs.