Eli Lilly Initiates Phase III Clinical Trials of GLP-1R Agonist Orforglipron in China for the Treatment of Obesity or Overweight
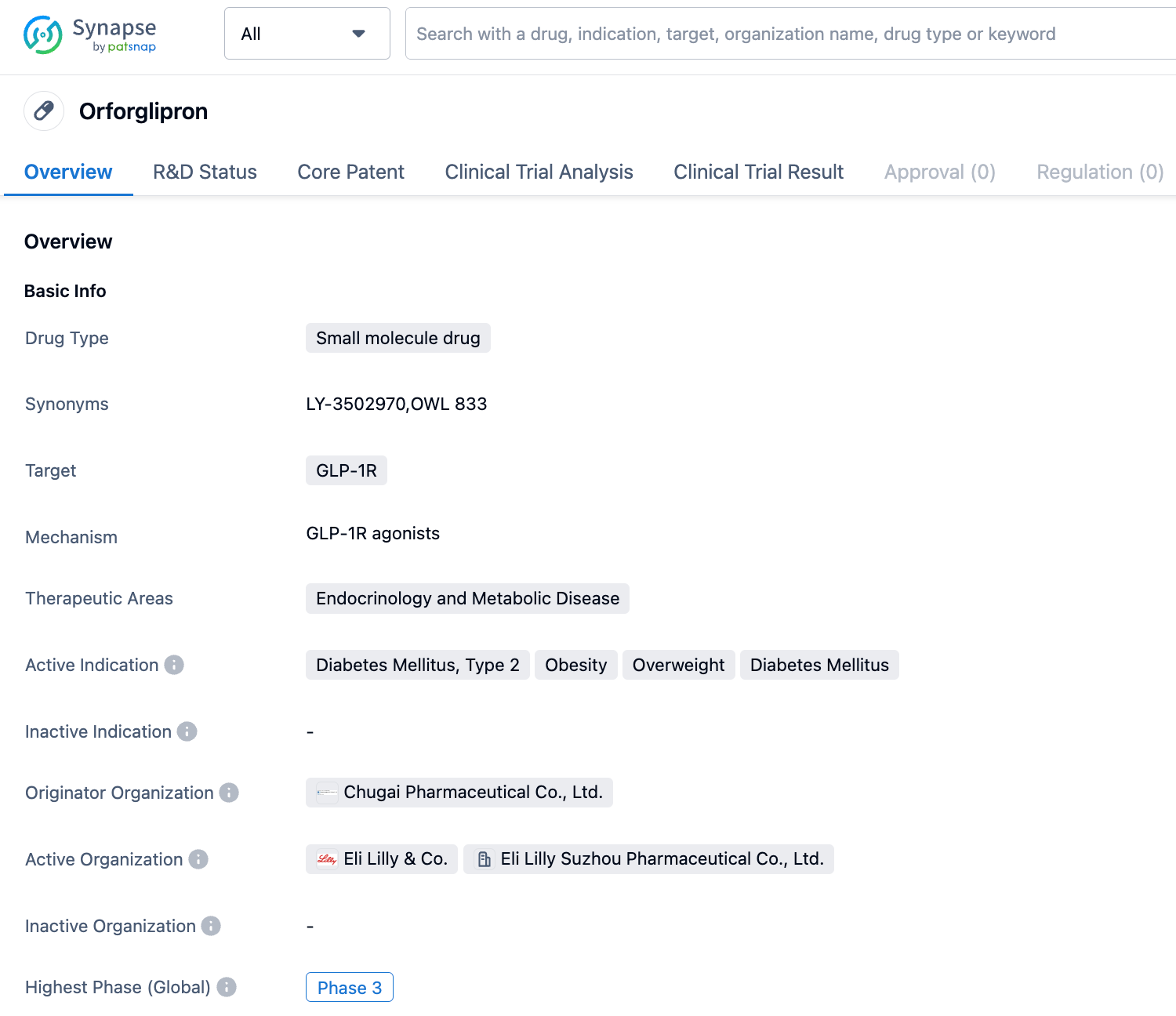
On September 6, 2023, Eli Lilly has registered a Phase III clinical trial (Study Code: ATTAIN-2) of the oral small molecule GLP-1R agonist Orforglipron (LY3502970) for the treatment of type 2 diabetes patients with obesity or overweight.
The investigational oral hypoglycemic agent (Orforglipron) developed by Eli Lilly is a GLP-1 receptor agonist, which shares the same target as the semaglutide injection from Novo Nordisk. Its mechanism of action also includes the activation of blood glucose regulation, delay of gastric emptying, and appetite reduction. The difference is that Orforglipron is a small molecule drug that can be administered orally, while the latter is a peptide drug that needs to be administered by injection.
Orforglipron supports once-daily oral administration. Initially developed by Chugai Pharmaceutical, Eli Lilly and Chugai Pharmaceutical reached a cooperation agreement in 2018, acquiring the global development and commercialization rights of Orforglipron for a down payment of 50 million US dollars. Orforglipron has huge potential in both the hypoglycemic and weight loss fields. Eli Lilly is actively advancing the clinical progress of this drug in the indications of diabetes and weight loss.
Currently, Eli Lilly has initiated multiple phase III clinical studies on Orforglipron, aimed at further investigating its therapeutic effect and safety in treating obesity and overweight (the ATTAIN series of studies) and type II diabetes (the ACHIEVE series of studies). The ATTAIN-1 study is a global phase III study seeking to assess the effectiveness and safety of daily oral Orforglipron in treating adults suffering from obesity or overweight with obesity-associated complications. The study aims to enroll 3000 patients. Furthermore, the ATTAIN-2 study is a global phase III study designed to assess the efficiency and safety of Orforglipron taken orally once daily in overweight or obese adult patients with type-2 diabetes. This study aims to enroll 1500 type-II diabetic adult patients with a BMI ≥27 kg/m2 (HbA1c: 7%~10%) who have had at least one failed attempt at dietary weight loss. The ATTAIN-J study is a phase III test conducted in Japan with the goal of evaluating the efficacy and safety of orally administered Orforglipron once daily in obese adult patients with obesity-related complications.
On June 23, 2023, Eli Lilly announced the latest phase II data for Orforglipron, its first nonpeptide oral glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist. The study is assessing Orforglipron for chronic weight management in obese or overweight patients. The study results were shared in an oral presentation at the 83rd Scientific Sessions of the American Diabetes Association and published concurrently in The New England Journal of Medicine. In the primary endpoint assessment at 26 weeks, the Orforglipron groups (12mg, 24mg, 36mg, or 45mg) all demonstrated statistically significant dose-dependent weight reduction across all doses, ranging from 8.6% (19.8 lbs or 9.0 kgs) to 12.6% (29.3 lbs or 13.3 kgs), whereas the placebo group decreased by 2.0% (4.6 lbs or 2.1 kgs). For those taking Orforglipron, weight continued to decline at 36 weeks, with reductions across all doses ranging from 9.4% (21.6 lbs or 9.8 kgs) to 14.7% (34.0 lbs or 15.4 kgs), while the placebo group decreased in weight by 2.3% (5.3 lbs or 2.4 kgs). The mean baseline weight of the subjects was 240 lbs (109 kgs). The safety profile of Orforglipron was comparable to other incretin-based treatments. Gastrointestinal side effects were the most commonly reported adverse events, generally mild to moderate in severity, and typically occurred during dose escalation.
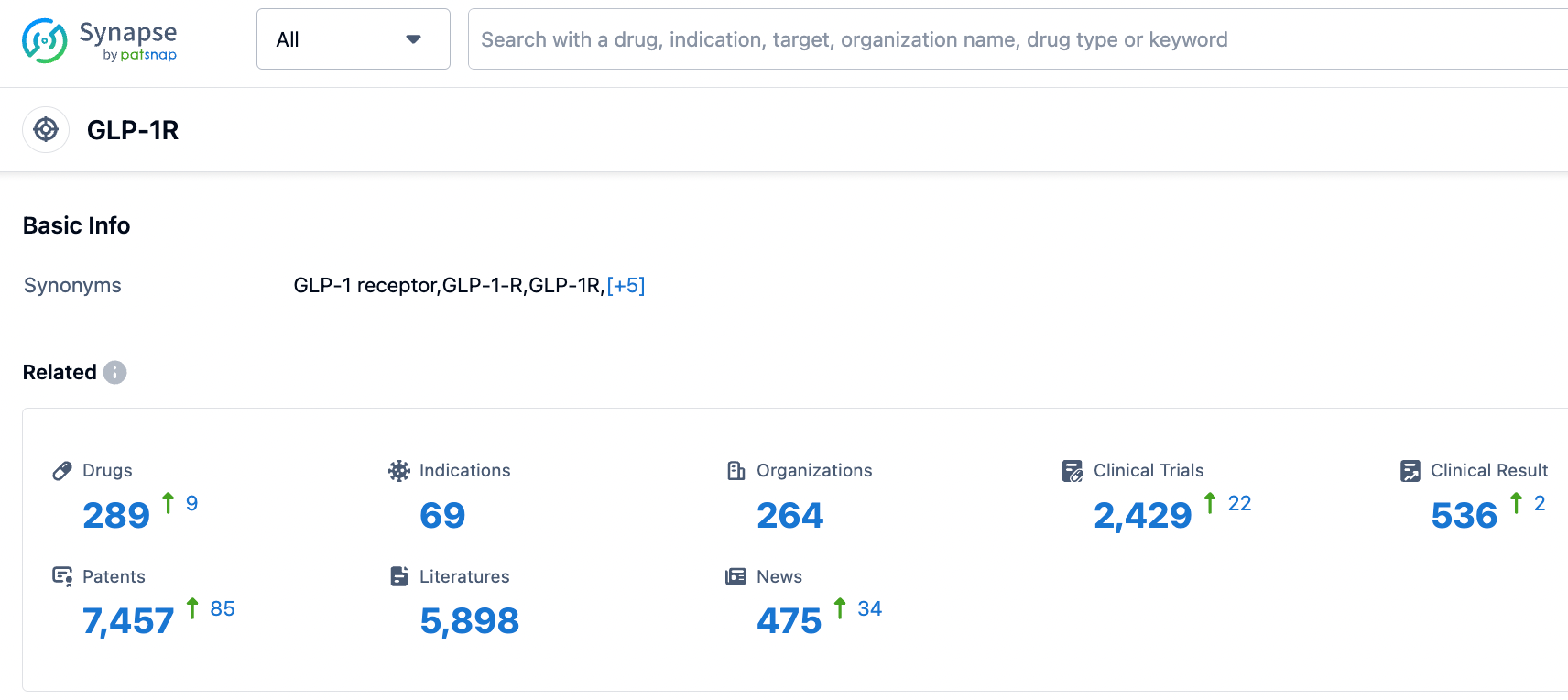
According to Synapse database as of September 8, 2023, there were 289 investigational drugs targeting the GLP-1R , with these drugs being applicable in 69 indications, being researched by 264 different organizations, and involving 2427 related clinical trials, with as many as 7464 patents. New drugs targeting single or multiple GLP-1R are under intense clinical investigation, and a competitive market is emerging.