Exploring BMS-986408: A Novel Small Molecule Drug for Advanced Malignant Neoplasms by Bristol-Myers Squibb
BMS-986408 is a small molecule drug developed by Bristol-Myers Squibb Pharmaceuticals Ltd. The drug targets DGKA and DGKζ and is intended for the treatment of neoplasms, specifically advanced malignant solid neoplasm. As of the latest available information, BMS-986408 has reached the Phase 1/2 of clinical trials globally. This indicates that the drug has undergone initial testing for safety and efficacy in a small number of participants to determine the appropriate dosage and potential adverse effects. Phase 1/2 trials involve further testing to assess the drug's effectiveness and safety in a larger group of participants with the target condition.
The drug's focus on neoplasms highlights its potential impact on the treatment of various forms of cancer, particularly in advanced stages where the treatment options may be limited. As a small molecule drug, BMS-986408 represents a class of pharmaceutical compounds with a low molecular weight, which can potentially offer advantages in terms of ease of administration and cellular penetration.
Below, we will use the drug BMS-986408 as an example to demonstrate how to quickly obtain information about its chemical structure and patent situation using the Patsnap Chemical.
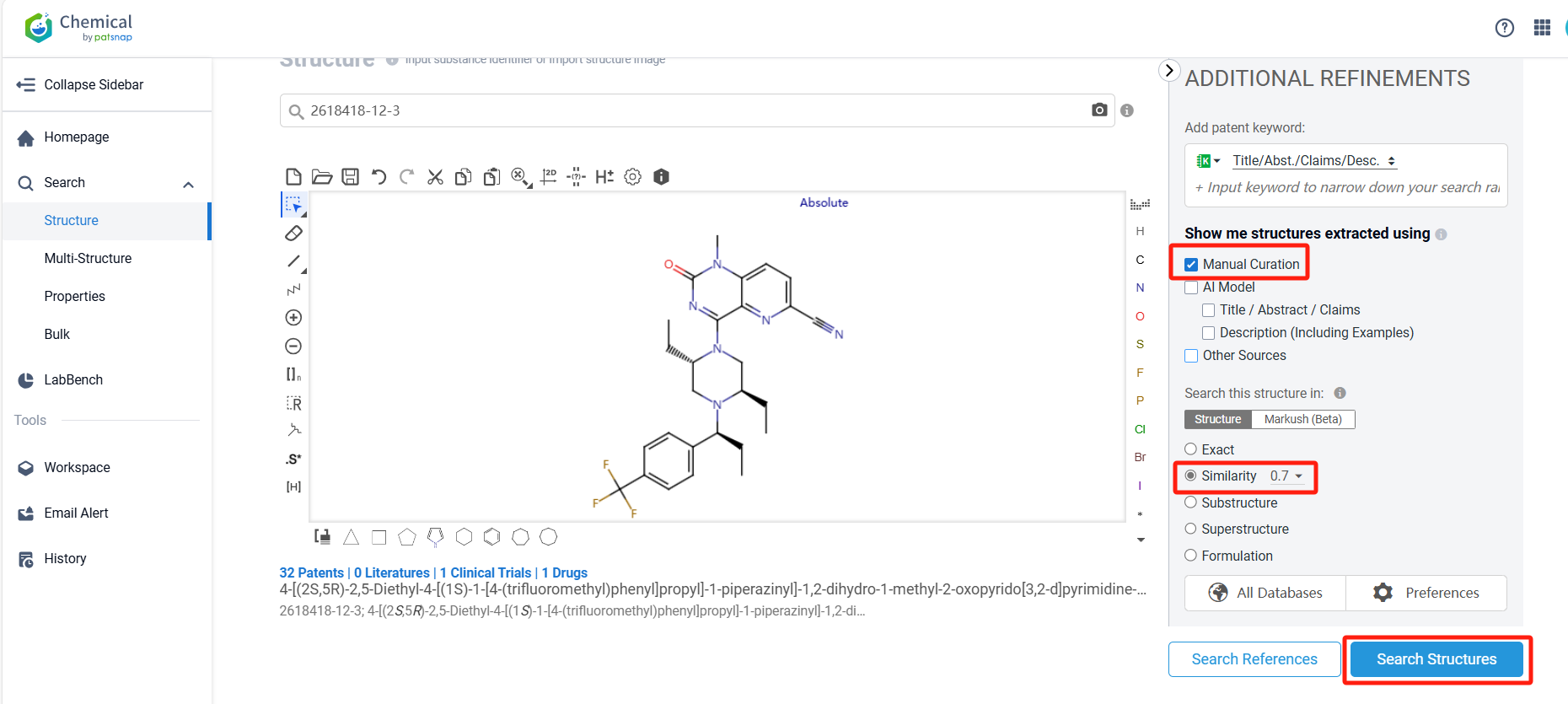
Log in to the Patsnap Chemical. Select the structural search and enter the common identity information of BMS-986408(such as CAS number, generic substance name, molecular formula, SMILES file, etc.). Here, using a similarity search (setting the Tanimoto coefficient to 0.7), check the box for manual curation, click on search structures, and you can find the innovative drug BMS-986408, as disclosed in the patent application with the publication number WO2021041588A1, first made public on 2021-03-04.
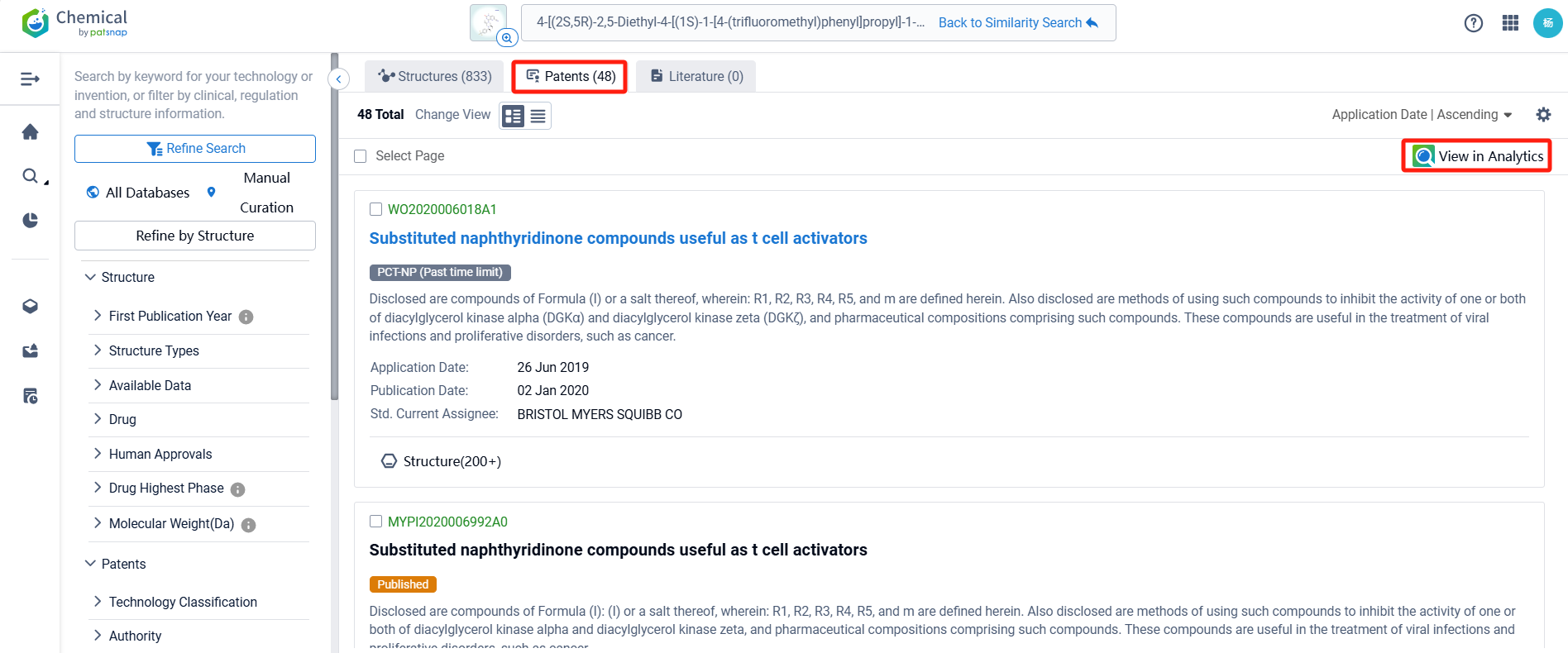
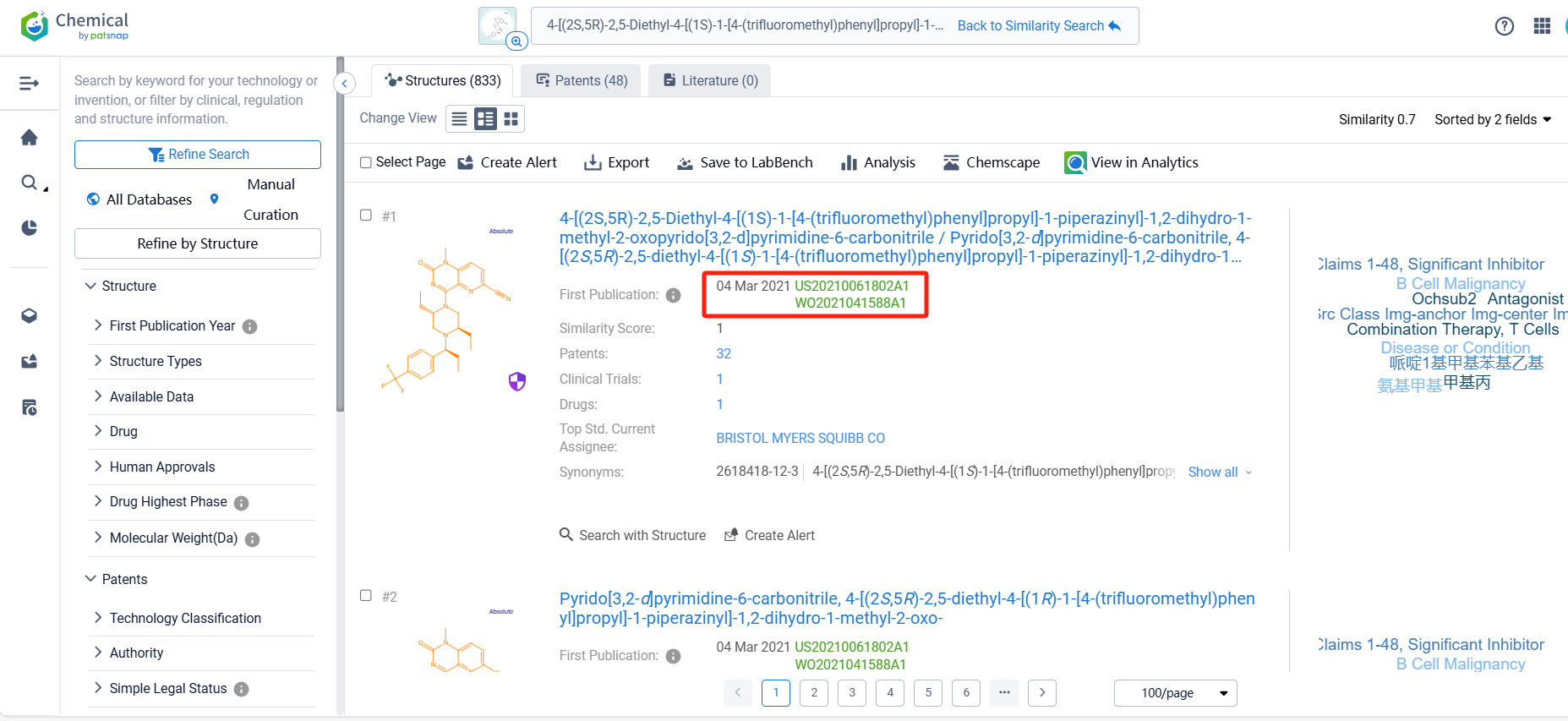 There are 48 patents related to this compound. Clicking the "view in Analytics" will direct you to the Patsnap Patent.
There are 48 patents related to this compound. Clicking the "view in Analytics" will direct you to the Patsnap Patent.
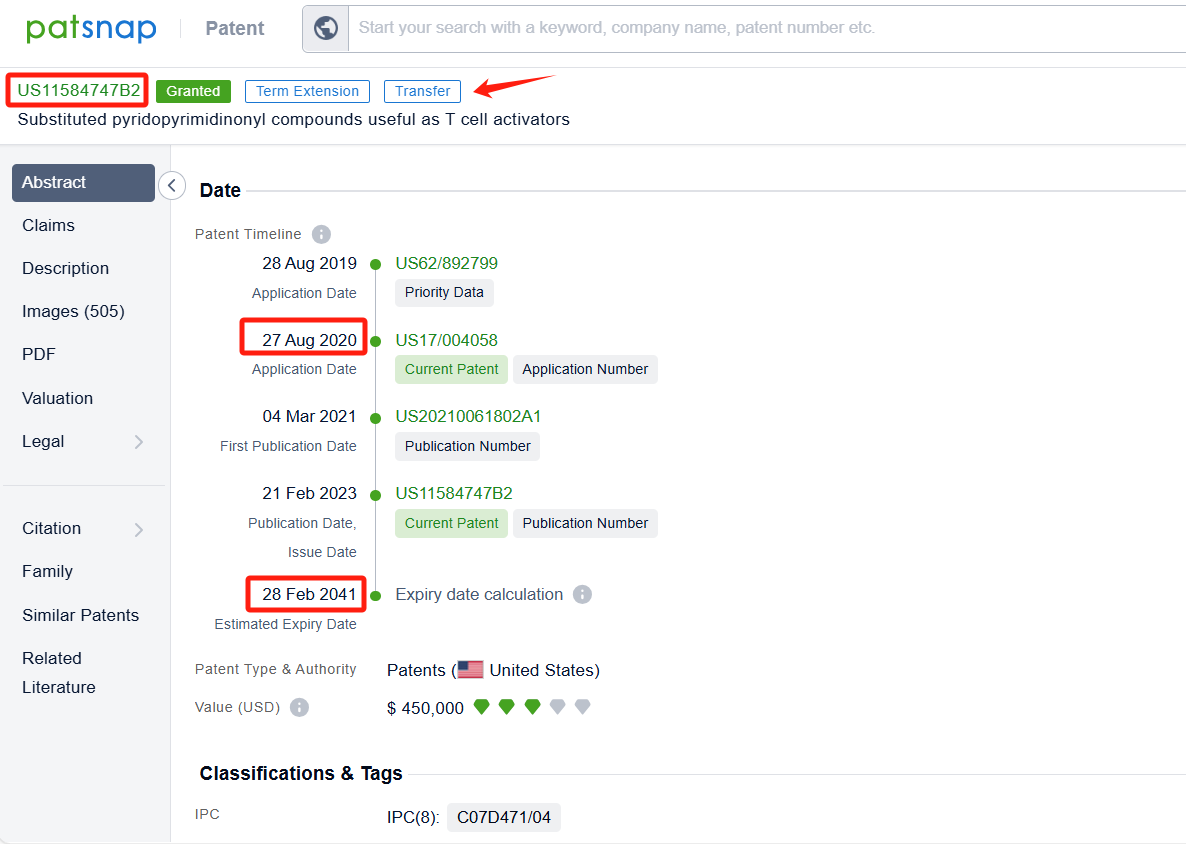
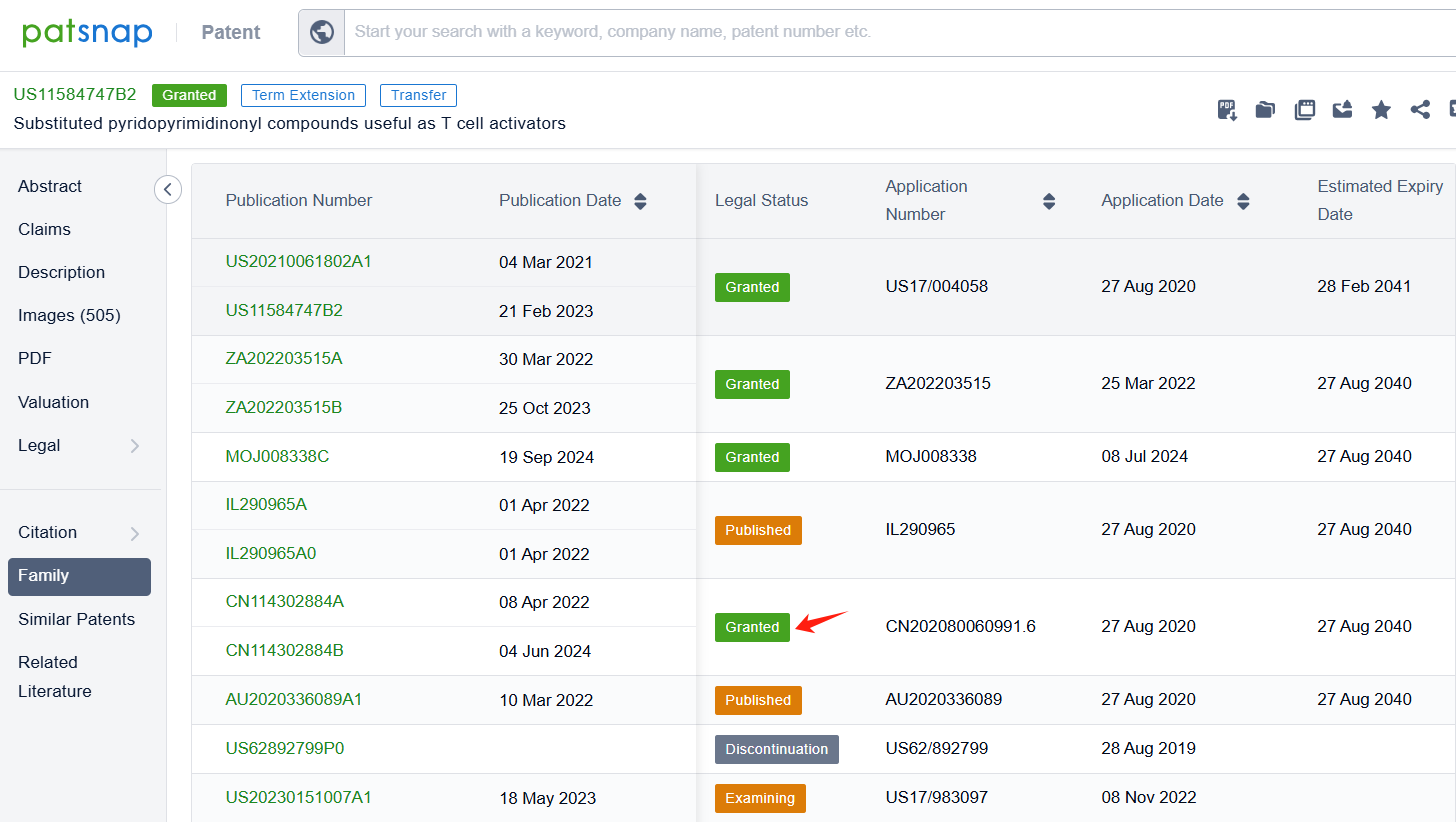
 By reviewing the aforementioned patents, we can observe that the core United States patent related to this compound has been granted, with the grant publication number US11584747B2, the grant date being 21 Feb 2023, and the estimated expiration date 28 Feb 2041. The Chinese counterparts of the compound has also been granted, with the grant publication numbers CN114302884B.
By reviewing the aforementioned patents, we can observe that the core United States patent related to this compound has been granted, with the grant publication number US11584747B2, the grant date being 21 Feb 2023, and the estimated expiration date 28 Feb 2041. The Chinese counterparts of the compound has also been granted, with the grant publication numbers CN114302884B.
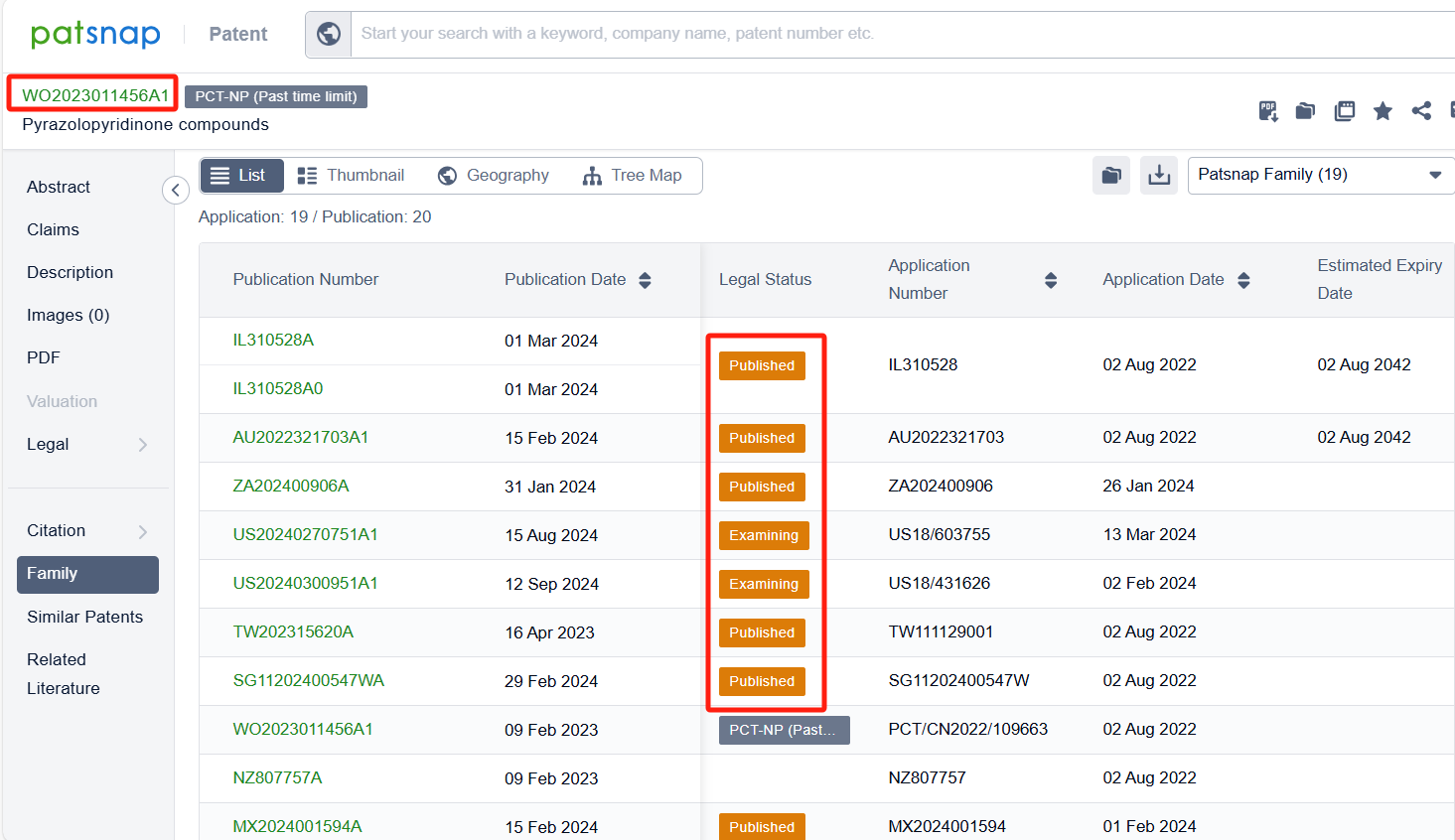
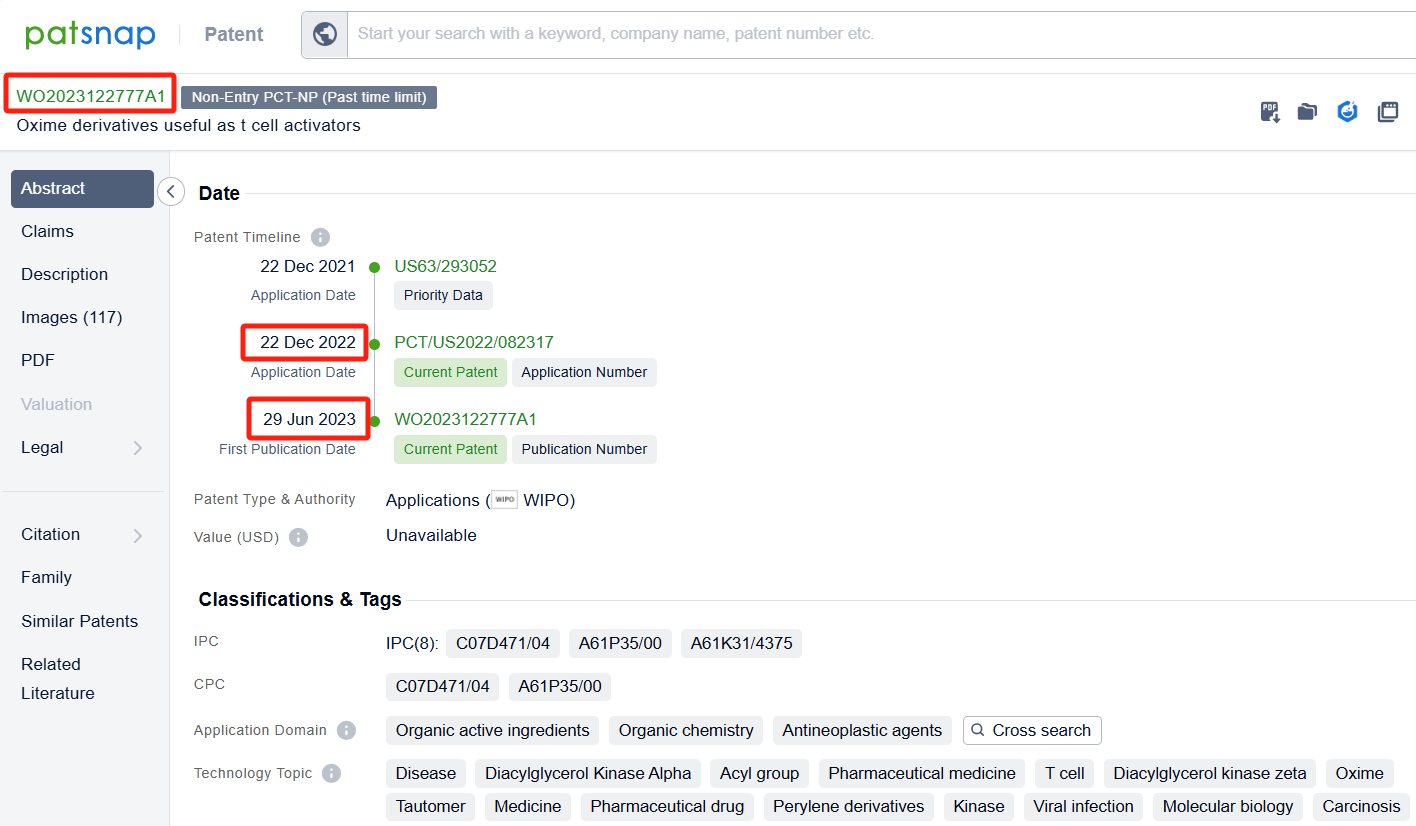
 Among the applicants of the patent, one can find other companies' fast follow patents on Bristol Myers Squibb Co.; for example, BeiGene Ltd.'s international PCT application (WO2023011456A1) has entered the national phase in designated countries and is undergoing substantive examination in countries such as China, South Korea, and Australia. Additionally, Gossamer Bio Services, Inc.'s international patent WO2023122777A1 (application date 20221222, publication date 20230629) describes compounds that can inhibit the activity of DGKα or DGKζ, which are enzymes involved in the regulation of insulin and other hormones. These compounds have a specific structure and can be used in the treatment of proliferative disorders, such as cancer and viral infections.
Among the applicants of the patent, one can find other companies' fast follow patents on Bristol Myers Squibb Co.; for example, BeiGene Ltd.'s international PCT application (WO2023011456A1) has entered the national phase in designated countries and is undergoing substantive examination in countries such as China, South Korea, and Australia. Additionally, Gossamer Bio Services, Inc.'s international patent WO2023122777A1 (application date 20221222, publication date 20230629) describes compounds that can inhibit the activity of DGKα or DGKζ, which are enzymes involved in the regulation of insulin and other hormones. These compounds have a specific structure and can be used in the treatment of proliferative disorders, such as cancer and viral infections.
Given the significance of the drug's target indication and the advanced stage of its development, BMS-986408 has the potential to address unmet medical needs in the field of oncology. The precise mechanism of action of the drug against DGKA and DGKζ, as well as its specific therapeutic effects on advanced malignant solid neoplasms, may provide further insights into the potential impact of BMS-986408 on cancer treatment.
Overall, the development of BMS-986408 signifies Bristol-Myers Squibb Pharmaceuticals Ltd.'s commitment to advancing innovative therapies in the biomedicine and pharmaceutical industry. As the drug progresses through clinical trials, further data on its safety and efficacy will likely become available, shedding more light on its potential as a treatment option for patients with advanced malignant solid neoplasms.
AI built to maximize IP and R&D efficiency
Redefine chemical FTO with a range of structure retrieval options at your fingertips, from exact matches to similarity searches, all powered by deep data processing techniques and proprietary AI algorithms to eliminate the risk of omitting key results.




