The First Approved C5a Antibody – Vilobelimab
Vilobelimab is a monoclonal antibody that targets C5a. It is developed by InflaRx NV for the treatment of COVID-19, pyoderma gangrenosum, anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis, recurrent cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma, cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, pyoderma gangrenosum with vasculitis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, and microscopic polyangiitis.
On April 4, 2023, it received Emergency Use Authorization in the United States for the emergency treatment of adult COVID-19 patients who have received invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV) or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) within 48 hours.
According to the search in the Intelligent Sprout Patent Database, a related authorized patent is titled "Treatment of Inflammatory Diseases with C5a Activity Inhibitors." The invention involves C5a activity inhibitors and their use in the treatment of skin, neutrophils, and inflammatory diseases. The patent number is US20180280530A1, with an application date of June 13, 2018.
C5a is a potent chemotactic agent involved in the recruitment of inflammatory cells such as neutrophils, eosinophils, monocytes, and T lymphocytes, activation of phagocytic cells, release of granule enzymes, and generation of oxidants, all of which can contribute to innate immune function or tissue damage [1].
Increasing evidence suggests that C5a provides an important link between innate and adaptive immune function and plays a critical role in inflammatory diseases, sepsis, acute lung injury, ischemia-reperfusion injury, and asthma development.
The complement system consists of over 30 plasma proteins, glycoproteins, soluble or membrane-bound receptors. This protein system activates enzyme cascades through various protein-protein interactions. Three pathways of complement activation have been recognized: the classical pathway, the alternative pathway, and the lectin pathway (Figure 1) [1].
Vilobelimab (GOHIBIC) is a first-in-class recombinant chimeric IgG4 antibody that efficiently blocks the biological activity of C5a. It specifically binds to C5a in human blood, preventing its interaction with its receptors, both of which are components of the complement system believed to contribute to the inflammation and deterioration seen in COVID-19.
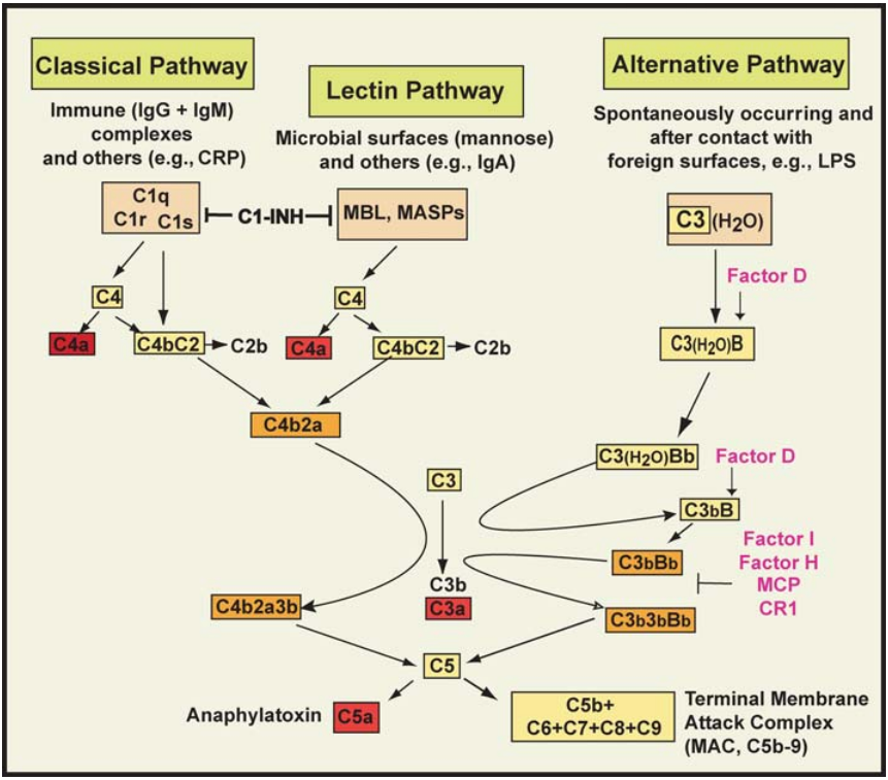
Complement Activation Pathways
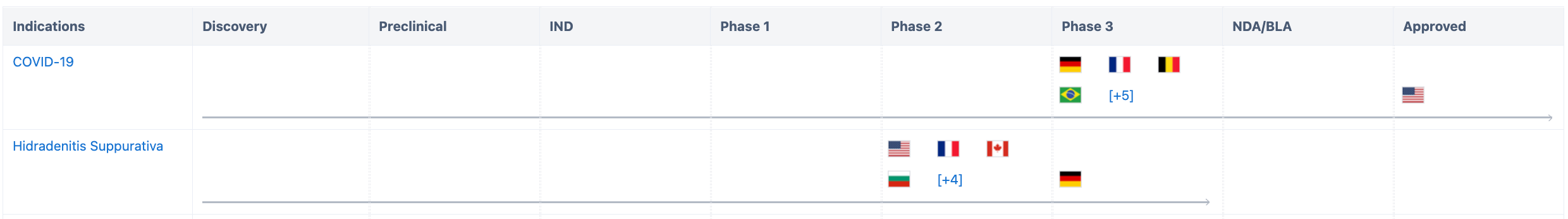
According to Synapse data statistics, development related to COVID-19 has entered Phase 3 clinical trials in nine countries, including the United States where it has received Emergency Use Authorization, as well as Germany, France, Belgium, and others. Clinical trials related to pyoderma gangrenosum have entered Phase 3 in Germany and Phase 2 in the United States, France, Canada, and eight other countries.
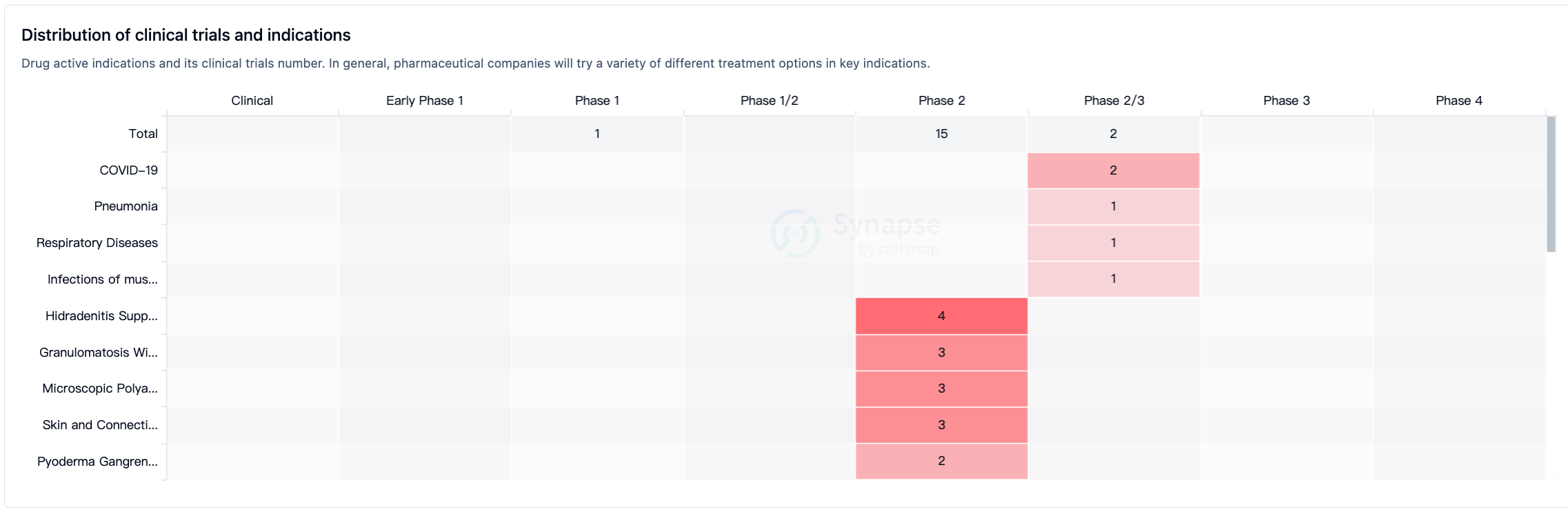
According to Synapse data statistics, all ten indications under investigation have entered Phase 2 or Phase 2/3 clinical trials (Figure 2).
The trial data from NCT04333420 [2] showed that from October 1, 2020, to October 4, 2021, a total of 368 patients were included in the intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis (full analysis set), with 177 patients in the Vilobelimab group and 191 patients in the placebo group. Among the 177 patients in the Vilobelimab group, 54 (31%) died within the first 28 days, compared to 77 (40%) in the placebo group. Kaplan-Meier estimation demonstrated an all-cause mortality rate of 32% (95% CI 25-39) in the Vilobelimab group and 42% (95% CI 35-49) in the placebo group (hazard ratio 0.73, 95% CI 0.50-1.06; p=0.094), as shown in Figure 3A. In a predefined analysis without site stratification, Vilobelimab significantly reduced the all-cause mortality rate at 28 days (HR 0.67, 95% CI 0.48-0.96; p=0.027) [2]. Among the 177 patients in the Vilobelimab group, 62 individuals (35%) had an observed all-cause mortality rate at 60 days, compared to 87 individuals (46%) in the placebo group. Kaplan-Meier estimation showed a death rate of 37% (95% CI 30-44) in the Vilobelimab group and 47% (95% CI 40-55) in the placebo group, as shown in Figure 3B.
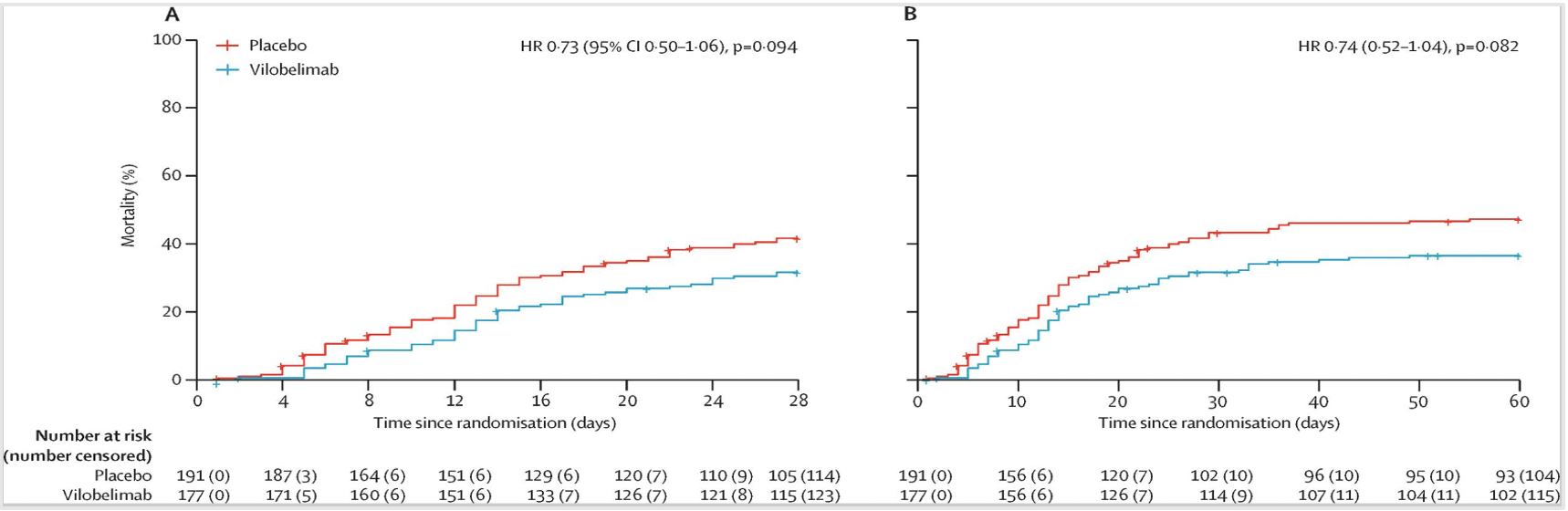
Kaplan-Meier curves for mortality (full analysis set)
The trial data from NCT04333420 [2] showed that the most common treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) during therapy were acute kidney injury (35 cases [20%] in the Vilobelimab group vs. 40 cases [21%] in the placebo group), pneumonia (38 cases [22%] vs. 26 cases [14%]), and septic shock (24 cases [14%] vs. 31 cases [16%]). Among the 175 patients in the Vilobelimab group, 103 individuals (59%) reported serious TEAEs, compared to 120 individuals (63%) in the placebo group.
On April 4, 2023, the FDA issued an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA). Based on available data, including data from the Phase 2/3 clinical trial (NCT04333420), the FDA determined that GOHIBIC has known and potential benefits that outweigh the known and potential risks, which meets the authorization criteria under Section 564(c) of the Act [2]. The EUA allows for the emergency use of GOHIBIC in adult COVID-19 patients who have received invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV) or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) within 48 hours. However, it has not been fully approved for this indication [3]. The indication for Vilobelimab, "pyoderma gangrenosum," has received multiple certifications, including orphan drug designation (US), fast track designation (US), and orphan drug designation (EU) in 2022.
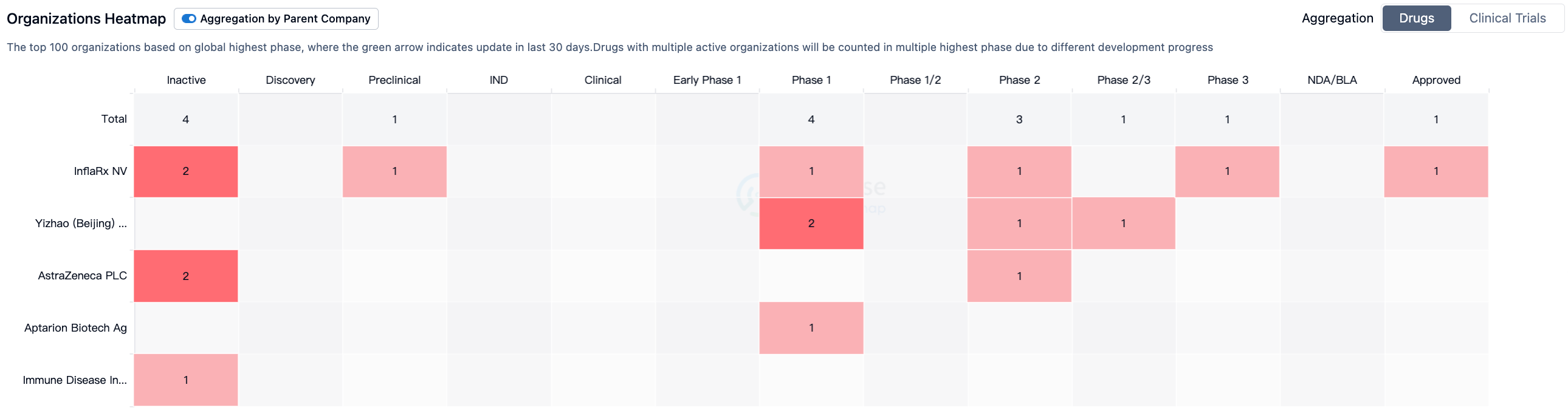
According to Synapse data statistics, there are currently seven drugs worldwide that target C5a (including one drug, Olendalizumab, originally developed by Immune Disease Institute, Inc., but now independently developed by AstraZeneca).

References
1.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15771587/
2.Vlaar APJ, Witzenrath M, van Paassen P, et al. Anti-C5a antibody (vilobelimab) therapy for critically ill, invasively mechanically ventilated patients with COVID-19 (PANAMO): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2022 Dec;10(12):1137-1146. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00297-1. Epub 2022 Sep 7. PMID: 36087611; PMCID: PMC9451499.



