Inventory of Relay Pipeline and Eli Lilly's Acquisition of Kv1.3 Blockers
Relay Therapeutics might not have been doing well recently, with the latest US stock market price being $11 and a market capitalization of around $1.3 billion, a reduction of three-quarters from its peak. As of the end of the first quarter in 2023, Relay Therapeutics held cash and cash equivalents of $937.8 million, lower than the $1 billion at the end of 2022. The company anticipates that these funds will support operations until 2025.
In April of this year, Relay Therapeutics announced the early-stage clinical data of RLY-2608, which led to a 40% plummet in its stock price. RLY-2608 is an isoform-selective PI3K inhibitor, a type of drug that faces challenges in safety and effectiveness, and the FDA has previously issued a black box warning for it. In the phase 1 trial of RLY-2608, only one patient's partial response was observed, and the optimal dose of RLY-2608 has yet to be determined, introducing uncertainty to the drug's safety and efficacy. Although no reports of dose-limiting toxicity (DLT) have emerged so far, unexpected adverse reactions may occur as the drug is still in the early stages of clinical trials, and as the research continues.
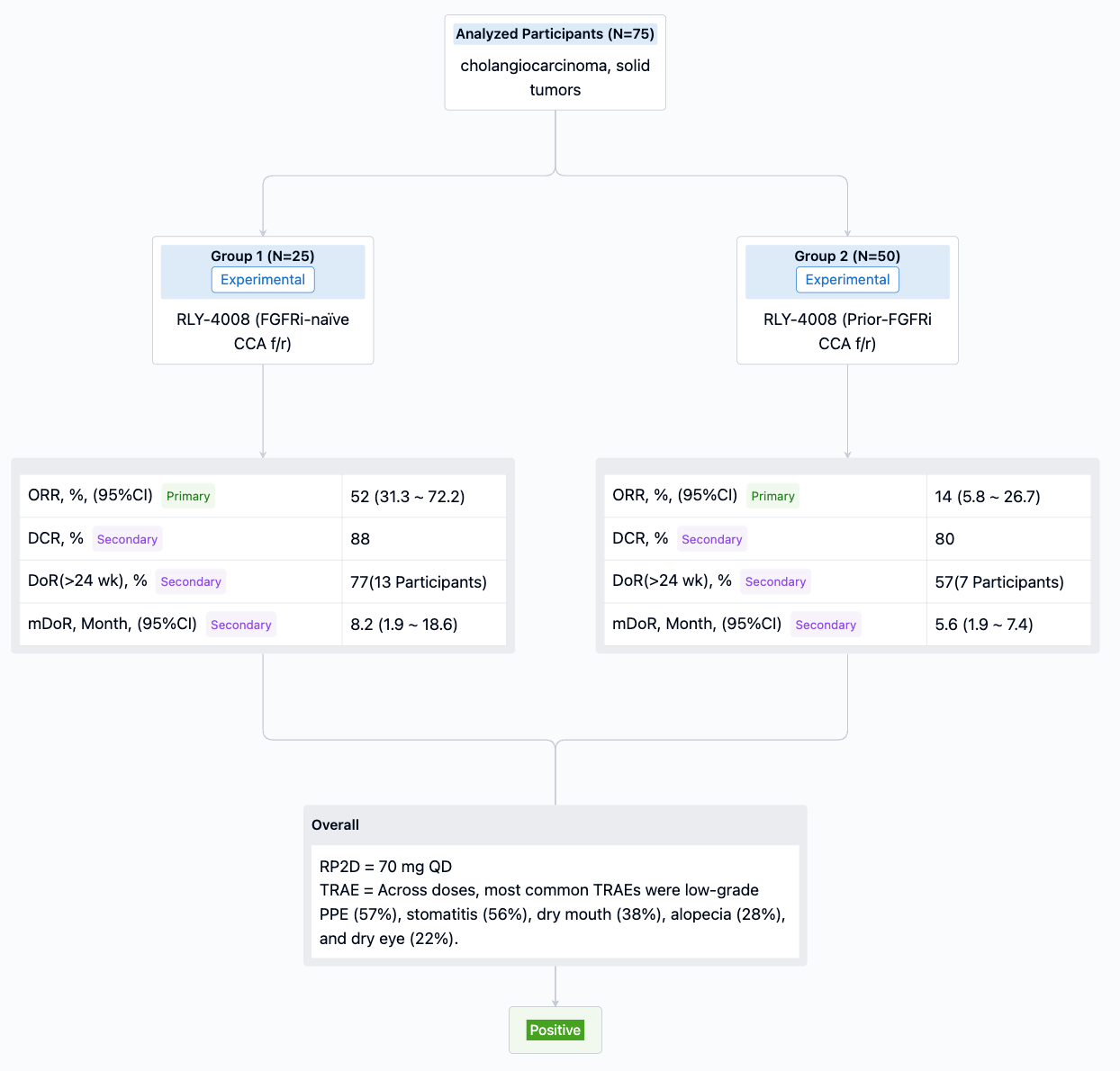
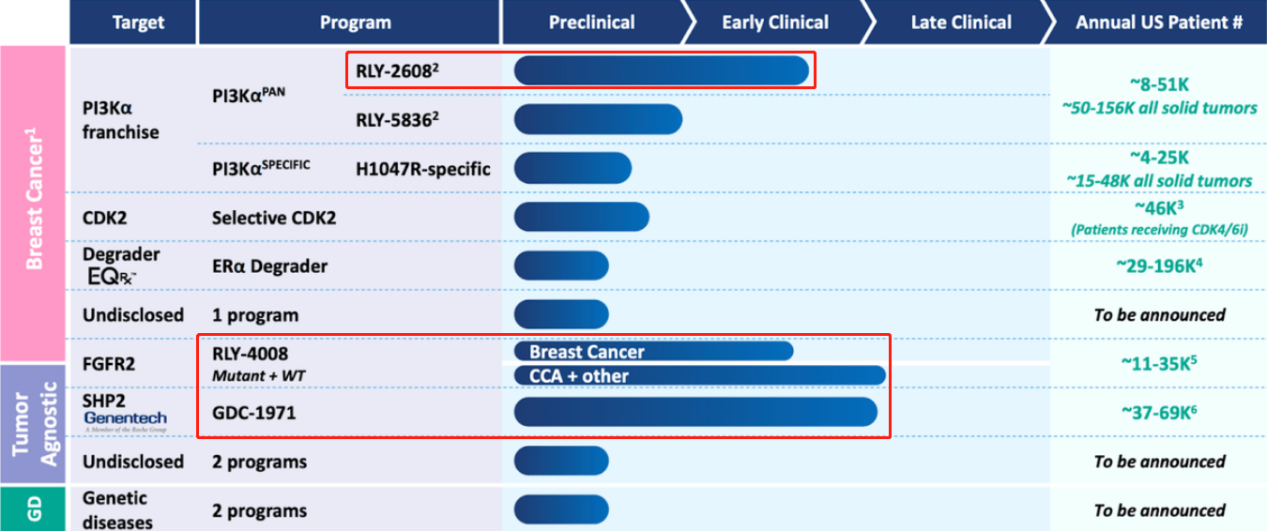
Relay company has two other promising assets. Firstly, RLY-4008 (see above image), a small molecule inhibitor, targets FGFR2 in patients with advanced or metastatic solid tumors with FGFR2 alterations. Preliminary data from its first human trial shows marked inhibition of FGFR2 without the limitation of off-target toxicity (such as hyperphosphatemia). Following discussions with the FDA in 2022, Relay chose to continue the single-arm trial design for FGFR2 fusion CCA treatment-naïve patients to expedite approval. RLY-4008 has received CCA orphan drug designation from both the FDA and EMA.
Information collected from the synapse database up until May 26, 2023, shows a recommended Phase 2 dose of 70 mg QD. For the FGFRi-naïve CCA f/r group, the ORR is as high as 55%. For the Prior-FGFRi CCA f/r group, the ORR is just 14%, indicating a significant decline in ORR among patients who have previously undergone FGFRi treatment. The most common TRAEs at different dosages are low-grade PPE (57%), stomatitis (56%), dry mouth (38%), hair loss (28%), and dry eyes (22%).
Secondly, GDC-1971 (previously RLY-1971) is another main asset of Relay. This drug targets SHP2 in patients with advanced or metastatic solid tumors. The phase Ia trial was completed with its enrollment in 2022. Relay reached a collaboration with Genentech on the development and commercialization of GDC-1971.

As Novartis’ standalone SHP2 clinical trial fails due to insufficient effectiveness, many companies have been actively pursuing combinatory therapies. As shown in the above figure, an Ib phase study released in July 2023 found in the intelligence database aims to evaluate the safety, pharmacokinetics, and effectiveness of GDC-1971 and Osimertinib in the treatment of inoperable locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer, or in combination with cetuximab in the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. The clinical trial recruited 172 patients and is expected to conclude by the end of December 2026. The primary endpoints are the percentage of participants experiencing adverse events and the number of patients exhibiting dose-limiting toxicity.
All the three inhibitors mentioned above from Relay come from D.E. Shaw (Chief Scientist at DESRES), with each drug having a clear differentiation direction, targeting a specific subtype of a particular protein with high selectivity. The three drugs are FGFR2 inhibitor RLY-4008, PI3Kα structuring inhibitor RLY-2608, and SHP2 inhibitor RLY-1971.
In addition, D.E. Shaw has developed the small molecule inhibitor DES-7114 for autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. On June 13, 2022, D.E. Shaw Research announced a global exclusive licensing agreement with Eli Lilly for the clinical development and commercialization of Kv1.3 inhibitor DES-7114. Eli Lilly will pay an upfront fee of $60 million, potential development and commercial milestones up to $475 million, and a royalty on global sales.
Challenges in the Development of Kv1.3 Blockers: Strong Selectivity Required for Multiple Subtypes
KV1.3 voltage-gated potassium channels participate in many physiological processes in the plasma membrane and mitochondria, primarily in the immune and nervous systems. Therapies targeting KV1.3 channels using specific peptides and small molecule inhibitors have shown enormous potential in treating cancer and autoimmune diseases (such as multiple sclerosis, type I diabetes, psoriasis, contact dermatitis, rheumatoid arthritis, and myasthenia gravis). However, so far, no compounds targeting KV1.3 have been approved for marketing. Some small molecule inhibitors with a clear SAR (Structure-Activity Relationship) have been optimized as selective inhibitors delivered to mitochondria, providing therapeutic potential for treating cancer and autoimmune diseases.
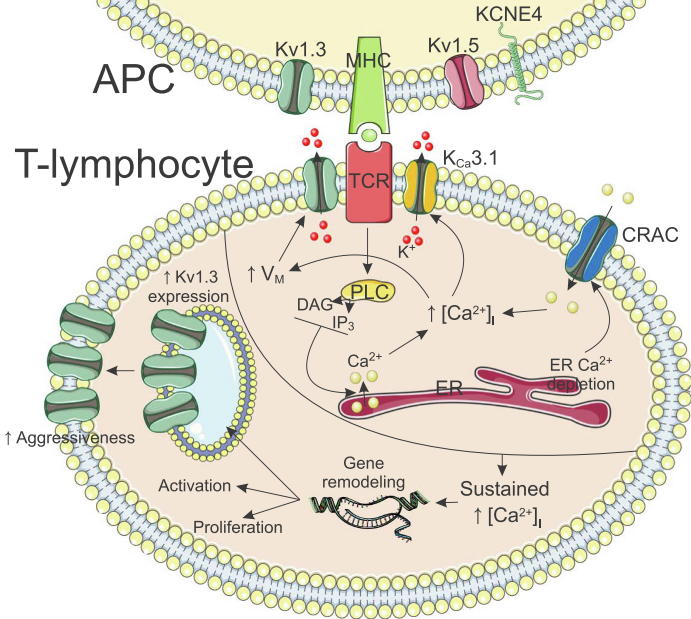
In 1999, small molecules WIN17317-3 and CP-339818 were discovered to target the Kv1.3 channel. However, these molecules lack the selectivity and specificity for the channel, apart from the Kv1.3 channel they have blocking effects on sodium ion channels and Kv1.4 channels, thus leading to potential side effects. Subsequently, various small molecules were discovered, but all failed to adequately address the issue of selectivity. Apart from inhibiting sodium ion channels and Kv1.4, they also produce a block on Kv1.1 and Kv1.2.
Professor D.E. Shaw has stated that DES-7114 can inhibit the ion channel protein Kv1.3 in a highly selective manner. Preclinical studies have confirmed its effectiveness in various models of chronic inflammation and autoimmune diseases (including ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, and atopic dermatitis), and it has successfully completed Phase I clinical trials in healthy volunteers in early 2022. However, a year and a half later, no results of DES-7114 clinical trials have been reported.
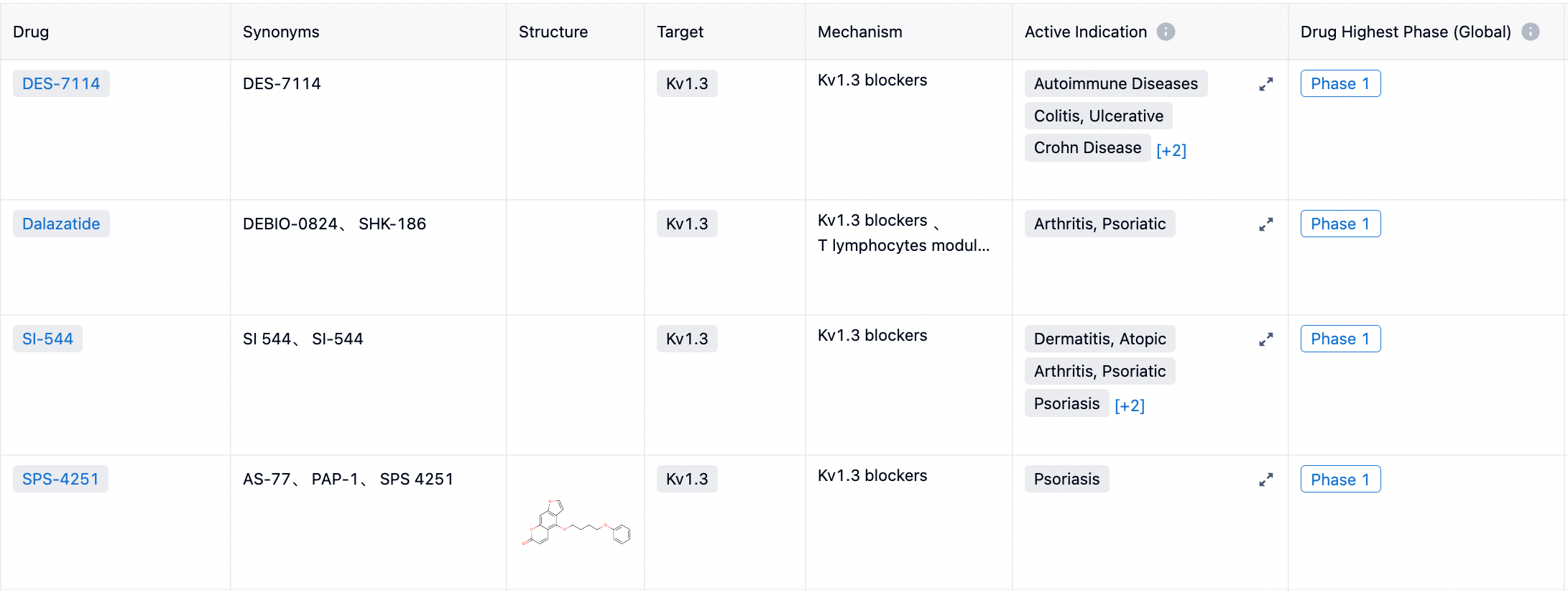
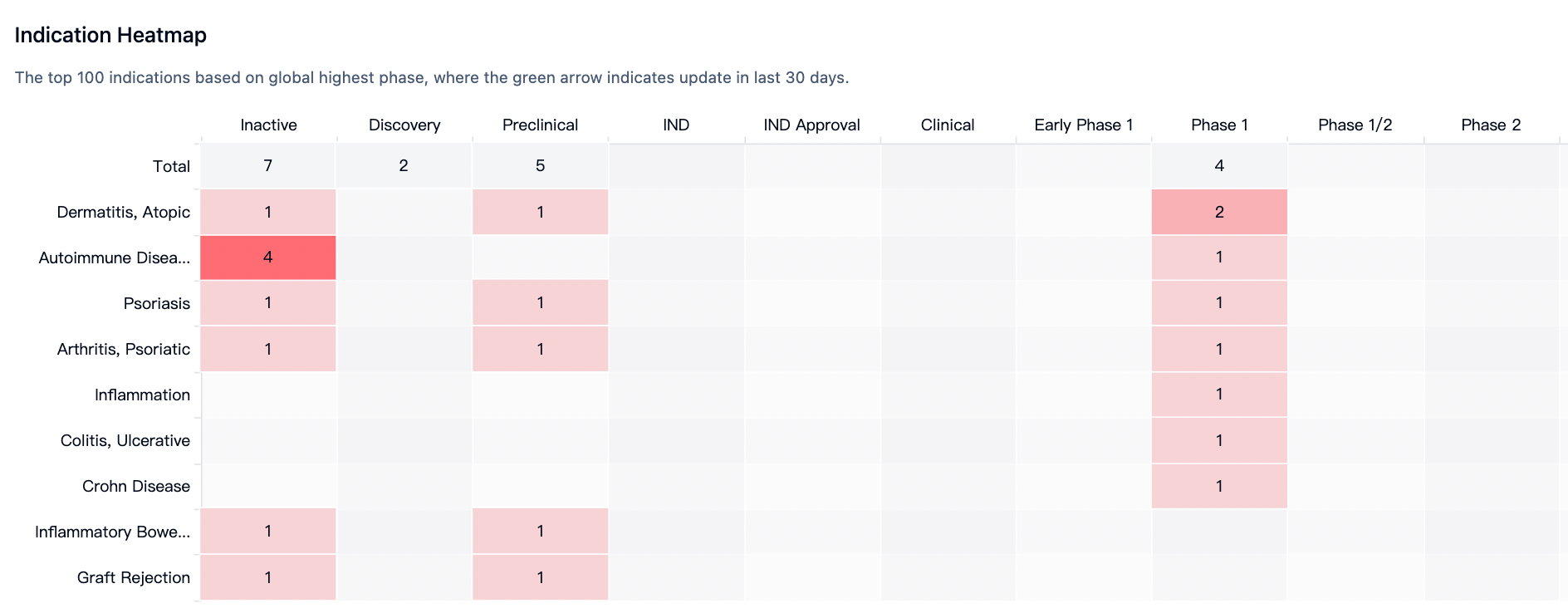
Analyzing the indications, as shown in Figure below, the current clinical indications under study are all in the direction of autoimmunity, specifically psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and atopic dermatitis.
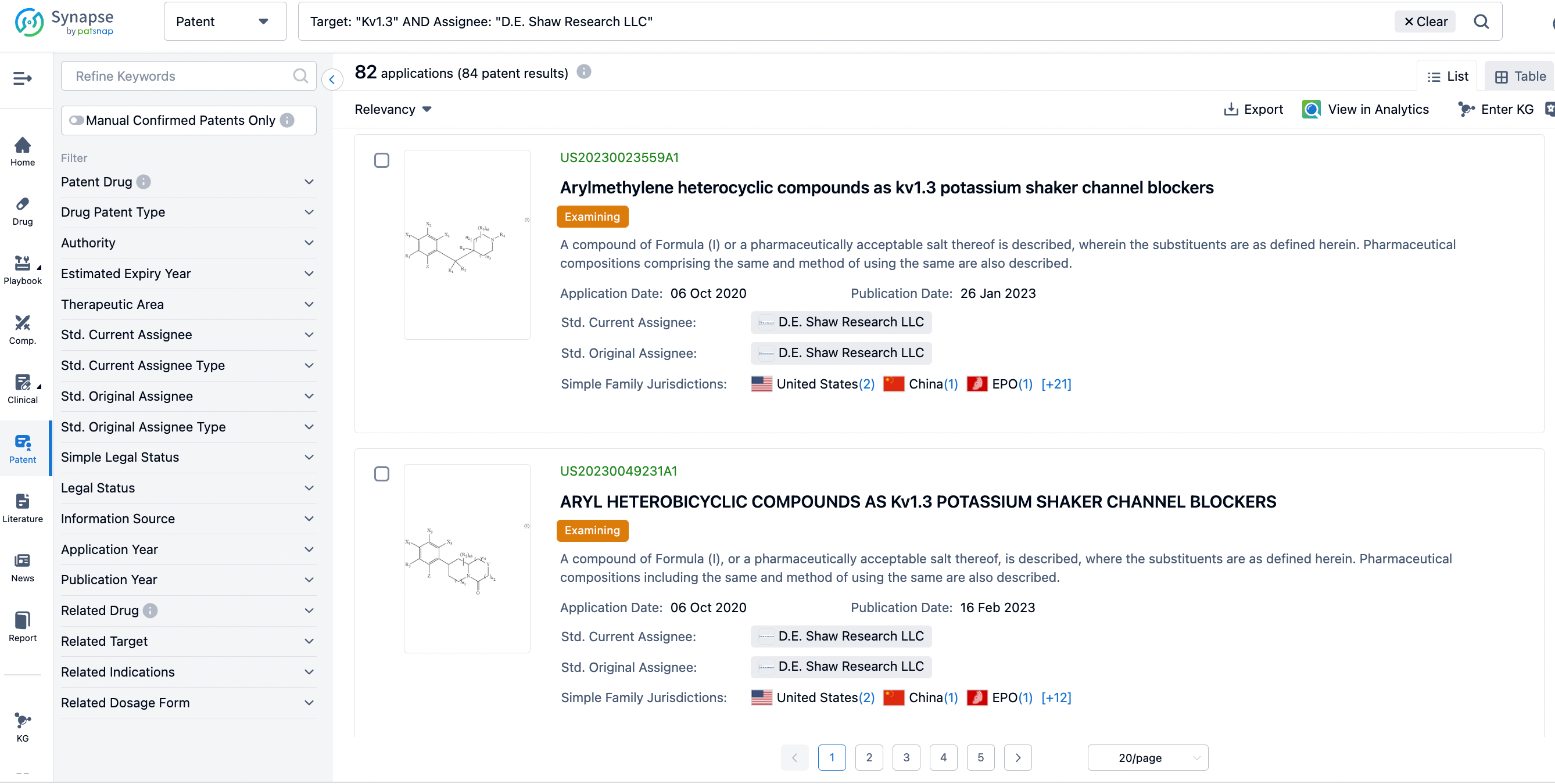
Related Patents of DES-7114
A total of 82 applications were found in the synapse database associated with D. E. Shaw Research and Kv1.3, with 11 INPADOC family applications, predominantly applied in 2022 (two applications in March and May), 2020 (five applications), 2021 (one application) and 2023 (two applications). Moreover, the DES-7114 entered phase I clinical trials in January 2022. As early as September 2013, D.E. Shaw Research had disclosed a method for screening voltage-gated proteins. The structure of the clinical molecule DES-7114 is not yet disclosed. Clues could be extracted from six INPADOC family applications in 2021 and 2020.
The six patents are: WO2022076285, WO2021071832, WO2021071812, WO2021071802, WO2021071803, and WO2021071821. The synthetic complexity of the structures in these patents is relatively low, although most of the compounds bear several chiral centers. Some fragments and core structures are relatively novel and worth attention.
However, most compounds disclosed in these patents only display IC50 data and hERG data regarding the inhibition of the Kv1.3 channel, and are only in ranges. Additionally, there is no selectivity data for other channels, such as Kv1.1 and Kv1.2, thus the inference of specific structures remains challenging.
Conclusion
Relay Therapeutics is a well-known drug discovery company in recent years, characterized by computational chemistry, with three drugs in its pipeline all from D.E. Shaw. Although two of Relay's current three clinical compounds have had some hiccups in clinical trials, its drug discovery platform characterized by molecular dynamics has greatly promoted drug development.
In the structural type exploration of the Kv1.3 channel blocker, it has been difficult for small molecules to achieve selectivity for Kv1.1 and Kv1.2 for more than 20 years. D.E. Shaw Research has extensive experience in differentiated targeting of ion channel protein subtypes. In addition to the Kv1.3 channel protein, there are also multiple published patents related to the TRPA1 cationic channel protein.
According to intelligence gathered from the Synapse database, Kv1.3 blockers are mainly used clinically for the treatment of autoimmune diseases. In order to develop safer therapeutic drugs, it is necessary to pay close attention to the compound's selectivity for Kv1X channel subtypes (such as the Kv1.1 channel and Kv1.2 channel).
Reference
1.https://seekingalpha.com/article/4620984-relay-therapeutics-stock-market-may-be-prematurely-dismissing-rly-2608.
2.Špela Gubič et.al, Discovery of KV1.3 ion channel inhibitors:Medicinal chemistry approaches and challenges.Med Res Rev. 2021;41:2423–2473.
3.Antonio Felipe et.al; Fighting rheumatoid arthritis: Kv1.3 as a therapeutic target.Biochemical Pharmacology 165 (2019) 214-220.