JAK1 Inhibitor - A rising star of small molecule targeted drugs in the field of autoimmunity
The JAK molecular family is a key kinase and central node in the cellular signaling pathway within organisms. JAK (Janus kinase) is an important family of non-receptor tyrosine kinases, which includes four subtypes: JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and TYK2. Its upstream regulators are various types of cell surface receptors of cytokines, and its downstream is signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT). Its main signaling pathway is: after extracellular cytokines bind to receptors, the JAK coupled with the receptor gets activated. The activated JAK enhances its kinase activity through autophosphorylation of tyrosine residues and phosphorylates downstream STAT. The activated STAT forms dimers and enters the cell nucleus to regulate the transcription process of relevant genes.
The JAK-STAT pathway is one of the core intracellular signaling pathways, extensively participating in cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and other physiological processes, and plays a significant role in immune regulation. JAK1 is closely related to inflammation, cancer, immunity, and other diseases. Among the members of the JAK family, JAK1 is the only subtype which can form heterodimers with all three types of JAKs. Dysfunction of JAK1 can lead to severe inflammation, autoimmune diseases, etc.
Therefore, JAK1 has received widespread attention in recent years. The range of diseases related to the signaling pathway is broad, and the potential for drug targets is considerable. The discoveries related to the JAK-STAT pathway not only help in understanding various autoimmune diseases, inflammatory diseases, hematological diseases, and tumors but also suggest the broad prospects of JAK as a drug target. Its specific mechanisms include, ① In autoimmune diseases, JAK inhibitors can mediate immune suppression and inhibit the increase of serum pro-inflammatory cytokines; ② In diseases induced by JAK mutations (such as myeloproliferative neoplasms), JAK inhibitors can have a therapeutic effect by inhibiting mutated JAKs.
Understanding the role of JAK1 has led to the development of targeted therapies that aim to modulate its activity for the treatment of various autoimmune and inflammatory diseases.
JAK1 Competitive Landscape
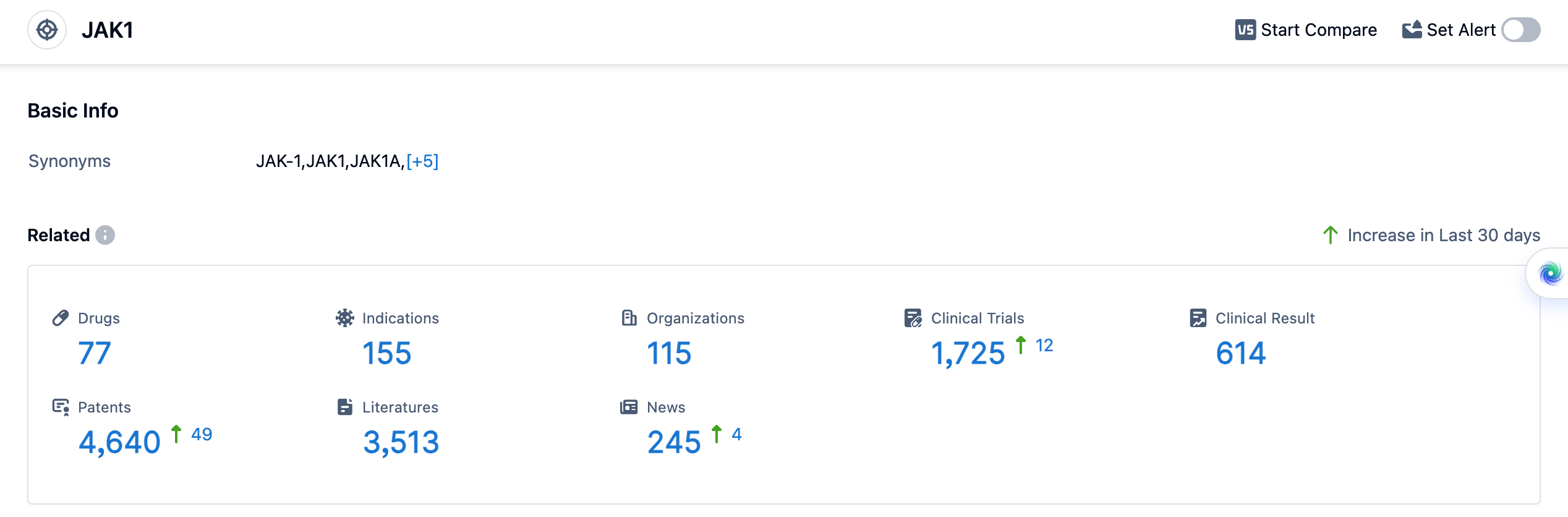
According to the data provided by Patsnap Synapse-Global Drug Intelligence Database: the following figure shows that as of 11 Sep 2023, there are a total of 77 JAK1 drugs worldwide, from 115 organizations, covering 155 indications, and conducting 1725 clinical trials.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or login directly if you have freemium accounts, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs , indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target.
Drugs under the target JAK1 have been approved for various indications. The indications include Rheumatoid Arthritis, Dermatitis, Atopic, Colitis, Ulcerative, Ankylosing Spondylitis, Arthritis, Psoriatic, Ulcerative colitis, active severe, Alopecia Areata, Primary Myelofibrosis, and Colonic Crohn's disease, active severe. The drug types progressing most rapidly under the current target JAK1 include Small molecule drugs and Chemical drugs. Small molecule drugs have the highest number of drugs in the Approved, Preclinical, and Inactive phases. Chemical drugs are in the Preclinical phase. China has made progress in the development of drugs under the target JAK1. It has drugs in the Approved, Preclinical, and Inactive phases. Overall, the target JAK1 presents a competitive landscape with multiple companies and a diverse range of indications and drug types.
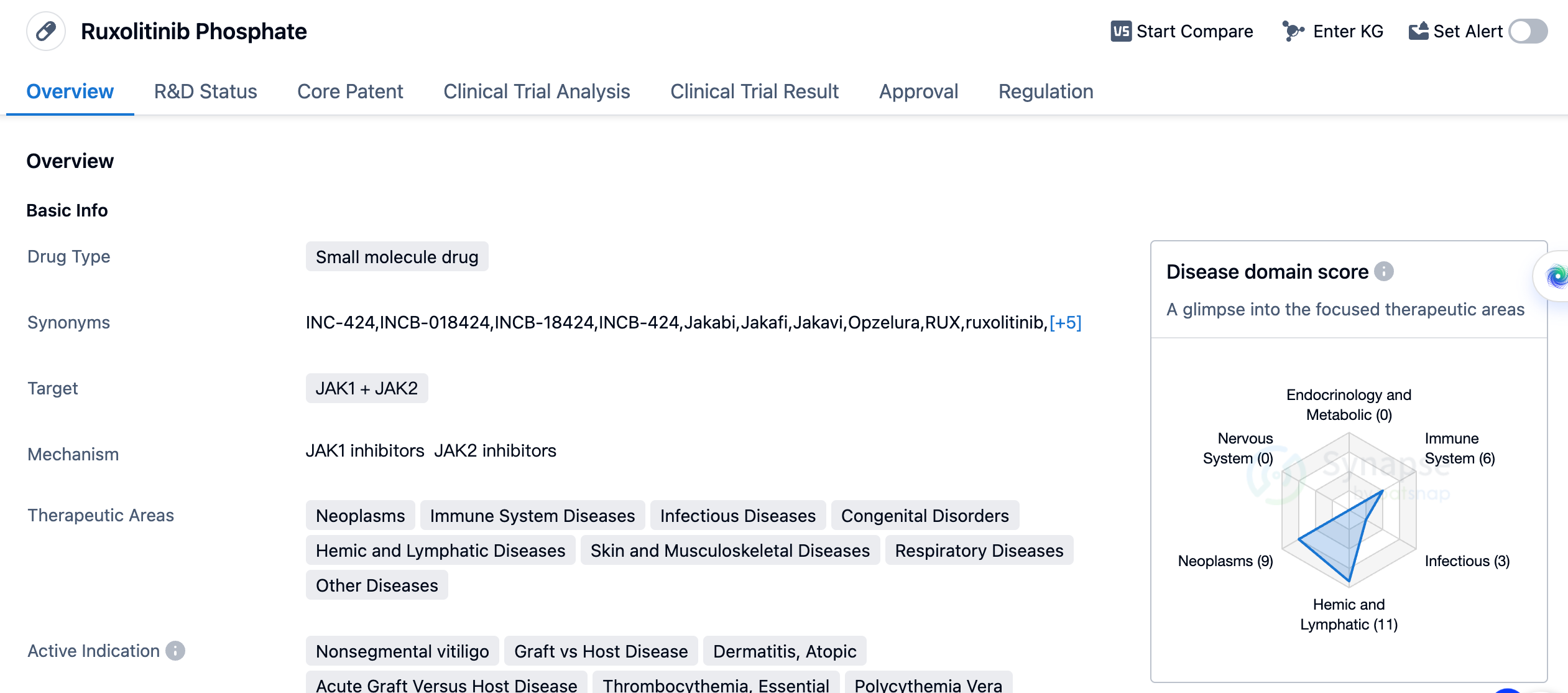
First-generation pan-JAK inhibitors:Ruxolitinib
Ruxolitinib Phosphate is a small molecule drug that targets JAK1 and JAK2. It has been approved for various therapeutic areas including neoplasms, immune system diseases, infectious diseases, congenital disorders, hemic and lymphatic diseases, skin and musculoskeletal diseases, respiratory diseases, and other diseases. The drug has shown efficacy in treating nonsegmental vitiligo, graft vs host disease, dermatitis, atopic, acute graft versus host disease, thrombocythemia, essential, polycythemia vera, primary myelofibrosis, osteomyelofibrosis, prurigo nodularis, SARS-CoV-2 acute respiratory disease, cytokine release syndrome, COVID-19, chronic eczema, lymphohistiocytosis, hemophagocytic, dermatitis, seborrheic, anemia, chronic myelogenous leukemia, bronchiolitis obliterans, head and neck neoplasms, breast cancer, leukemia, acute lymphoblastic leukemia, alopecia areata, B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia, thalassemia, cachexia, chronic myelomonocytic leukemia, and Hodgkin's lymphoma.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
The drug was first approved in the United States in November 2011 and has since received approval in other countries. It is developed by Incyte Corp., an originator organization in the pharmaceutical industry. Ruxolitinib Phosphate has reached the highest phase of development, which is approved, both globally and in China. This indicates that it has successfully completed clinical trials and demonstrated safety and efficacy in treating the indicated conditions.
In terms of regulation, Ruxolitinib Phosphate has undergone accelerated assessment and has been designated as an orphan drug. Accelerated assessment is a regulatory process that expedites the evaluation of drugs that address unmet medical needs. Orphan drug designation is granted to drugs that treat rare diseases, providing incentives for their development.
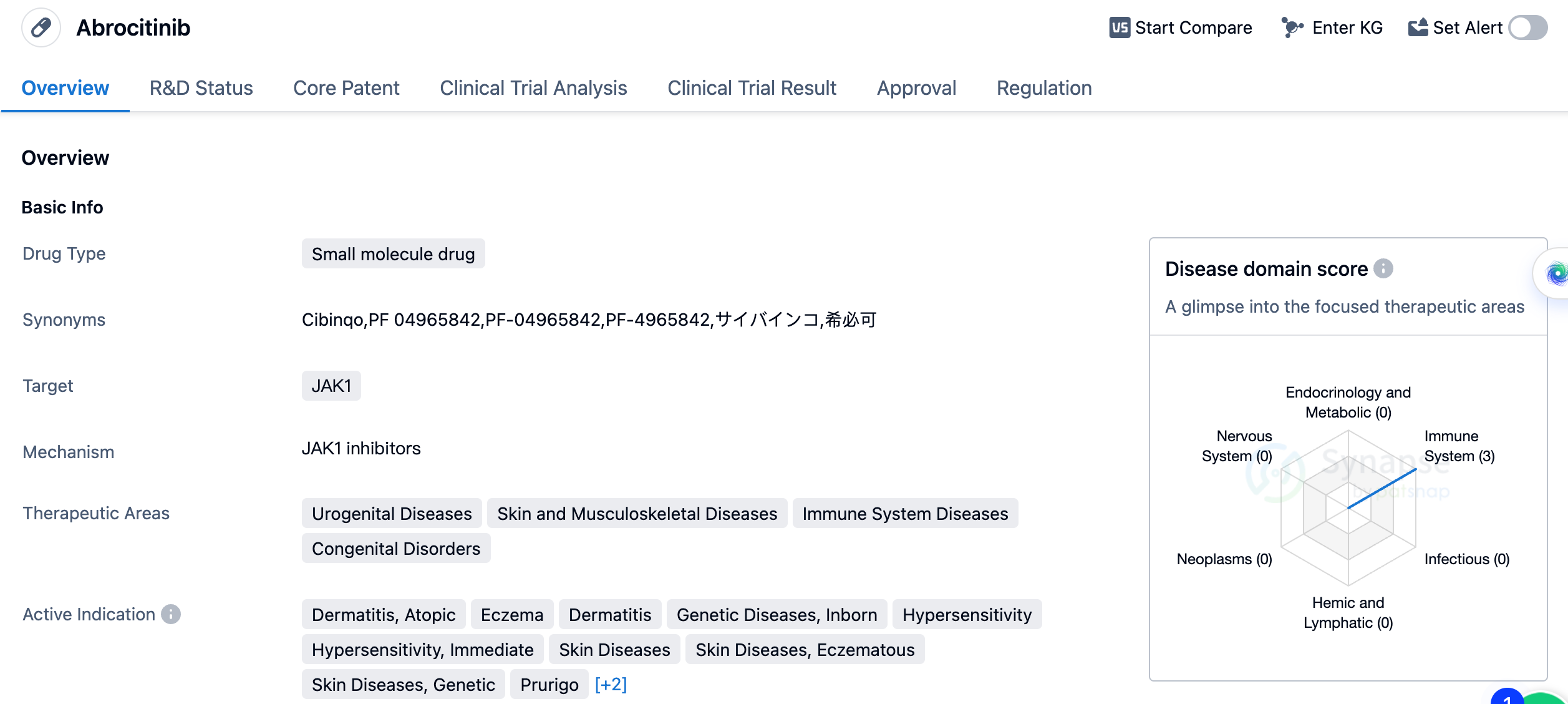
Second-generation Specific JAK1 Inhibitor:Abrocitinib
Abrocitinib is a small molecule drug that targets JAK1, a protein involved in various immune responses. It has been developed by Pfizer Inc., a leading pharmaceutical company. The drug has received approvals in both the global market and China, indicating its potential efficacy and safety. Abrocitinib is primarily indicated for the treatment of several urogenital diseases, skin and musculoskeletal diseases, immune system diseases, and congenital disorders. Specifically, it has shown positive results in the treatment of dermatitis, atopic eczema, genetic diseases, inborn dermatitis, hypersensitivity, immediate hypersensitivity, skin diseases, eczematous skin diseases, genetic skin diseases, prurigo, pruritus, and kidney diseases.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
The first approval of Abrocitinib was granted in the United Kingdom in September 2021, marking an important milestone for the drug. The drug has been evaluated under various regulatory pathways, including priority review, breakthrough therapy, and promising innovative medicine.
As a small molecule drug targeting JAK1, Abrocitinib offers a promising approach to modulating immune responses and treating a wide range of diseases. By inhibiting JAK1, the drug may help regulate the immune system and alleviate symptoms associated with urogenital diseases, skin and musculoskeletal diseases, immune system diseases, and congenital disorders. The drug's specific targeting of JAK1 and its broad range of indications make it a promising candidate for the treatment of various diseases. Further research and clinical studies will likely shed more light on the efficacy and safety profile of Abrocitinib, potentially expanding its applications and benefiting a larger patient population.