LEO Pharma Presents Temtokibart and Dupilumab Phase 2a Results in Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis at 2024 EADV Conference
LEO Pharma A/S, a prominent company in the field of medical dermatology, reported encouraging outcomes from the Phase 2a Mechanism of Action (MoA) study. This research evaluated the mechanistic effects of the investigational drugs temtokibart and dupilumab in individuals with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD). The findings were disclosed during a Late Breaker oral presentation at the 2024 EADV Annual Meeting.
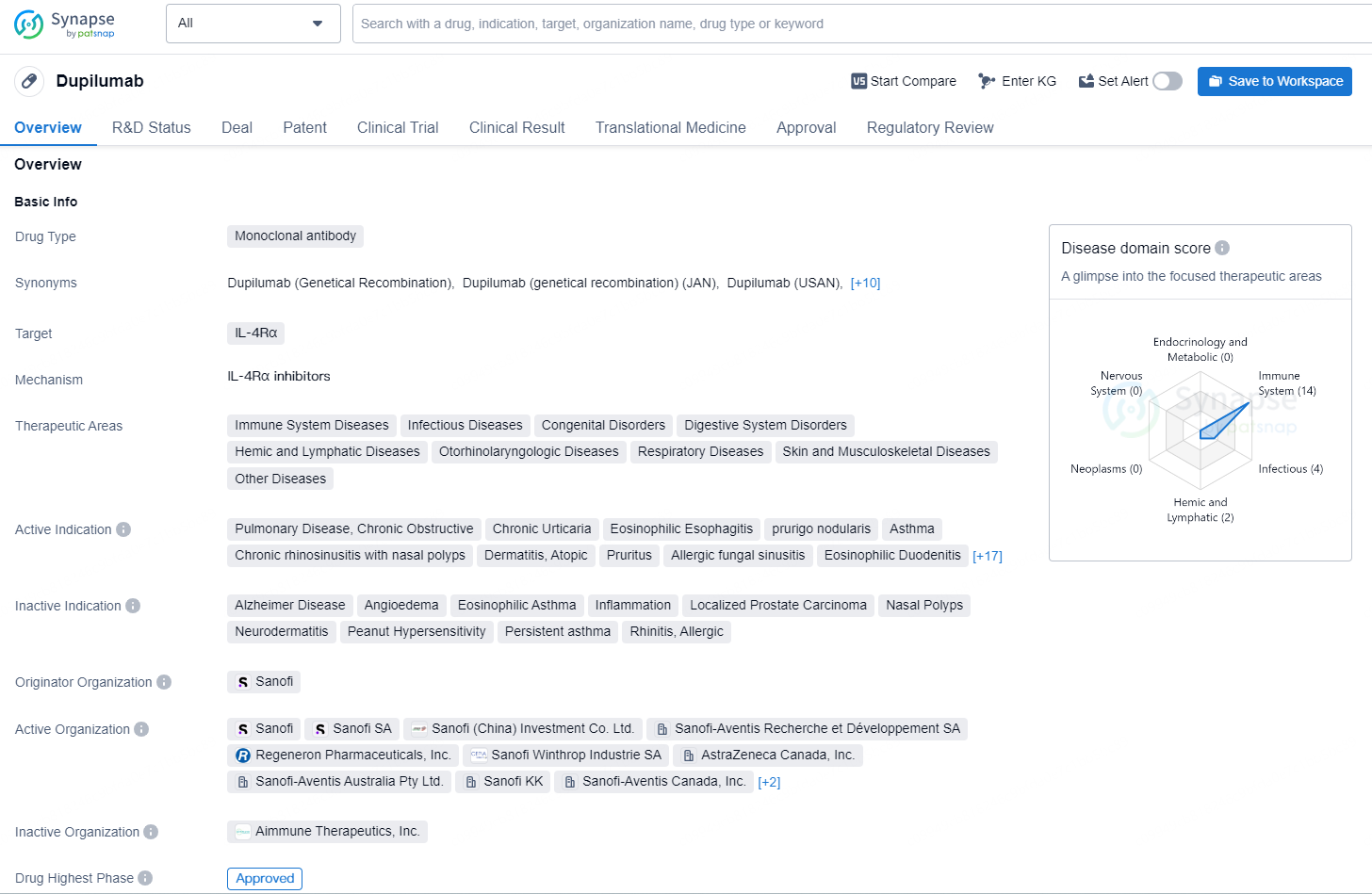
👇Discover comprehensive information about this drug, from its R&D status, core patents, clinical trials to approval status in global countries, by simply clicking on the image below. Dive deep into our drug database now.
The Phase 2a Mechanism of Action (MoA) trial examined the effects of inhibiting the interleukin-22 receptor subunit alpha 1 (IL-22RA1) or the interleukin 4 receptor alpha (IL-4Rα) on a mechanistic level in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD). The findings demonstrated that administering temtokibart 450 mg bi-weekly (Q2W, n=8) led to a more rapid and superior improvement in skin hydration compared to 300 mg of dupilumab Q2W (n=4). Importantly, temtokibart resulted in a significant enhancement in natural moisturizing factors PCA and UCA by the first week from baseline (p<0.0001).
Additionally, temtokibart treatment also showed subsequent improvements in barrier function metrics, including terminal differentiation markers and cell adhesion molecules. Aligning with its specific MoA, dupilumab was associated with a pronounced and consistent reduction in Type 2-associated inflammatory markers, notably in immune cells and fibroblasts. Clinical metrics such as EASI and itch NRS from baseline to Week 16 showed comparable improvements for both temtokibart and dupilumab. These findings suggest that while IL-22RA1 blockade does not directly impact skin immune cells, it can swiftly ameliorate barrier dysfunctions, indicating a potential novel MoA for individuals with moderate-to-severe AD.
"The results of this trial offer fresh insights into the pathophysiology of AD and impart a unique understanding of the mechanistic action of temtokibart," stated Dr. Christine Bangert, MD, the Head of the Allergology Task Force of the Austrian Society of Dermatology and Venereology, and Principal Investigator of the Phase 2a MoA trial. "These data indicate that the IL-22 pathway is integral to the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis, demonstrating that Type 2 inflammation is not the sole critical factor."
Temtokibart is an investigational monoclonal antibody currently in Phase 2 development for moderate-to-severe AD, functioning by blocking the IL-22RA1 receptor subunit and thereby inhibiting the interleukin-22 (IL-22) cytokine's effects. It also partially inhibits IL-20 and IL-24 signaling. A Phase 2b dose-finding trial is underway to assess the efficacy and safety of varying doses of temtokibart in adult patients with moderate-to-severe AD. Phase 2b recruitment is complete, with results anticipated in Q1 2025. LEO Pharma is also investigating applications beyond dermatology for temtokibart in conditions where the IL-22 pathway has a significant role.
"We are encouraged by the results of this AD trial, which explores how different mechanisms of action affect disease markers," said Kreesten Meldgaard Madsen, Chief Development Officer at LEO Pharma. "These results further elucidate the mechanism of action of temtokibart, suggesting it could meet unmet needs in other diseases where the IL-22 pathway is pivotal. LEO Pharma is also investigating temtokibart for inflammation-induced anemia."
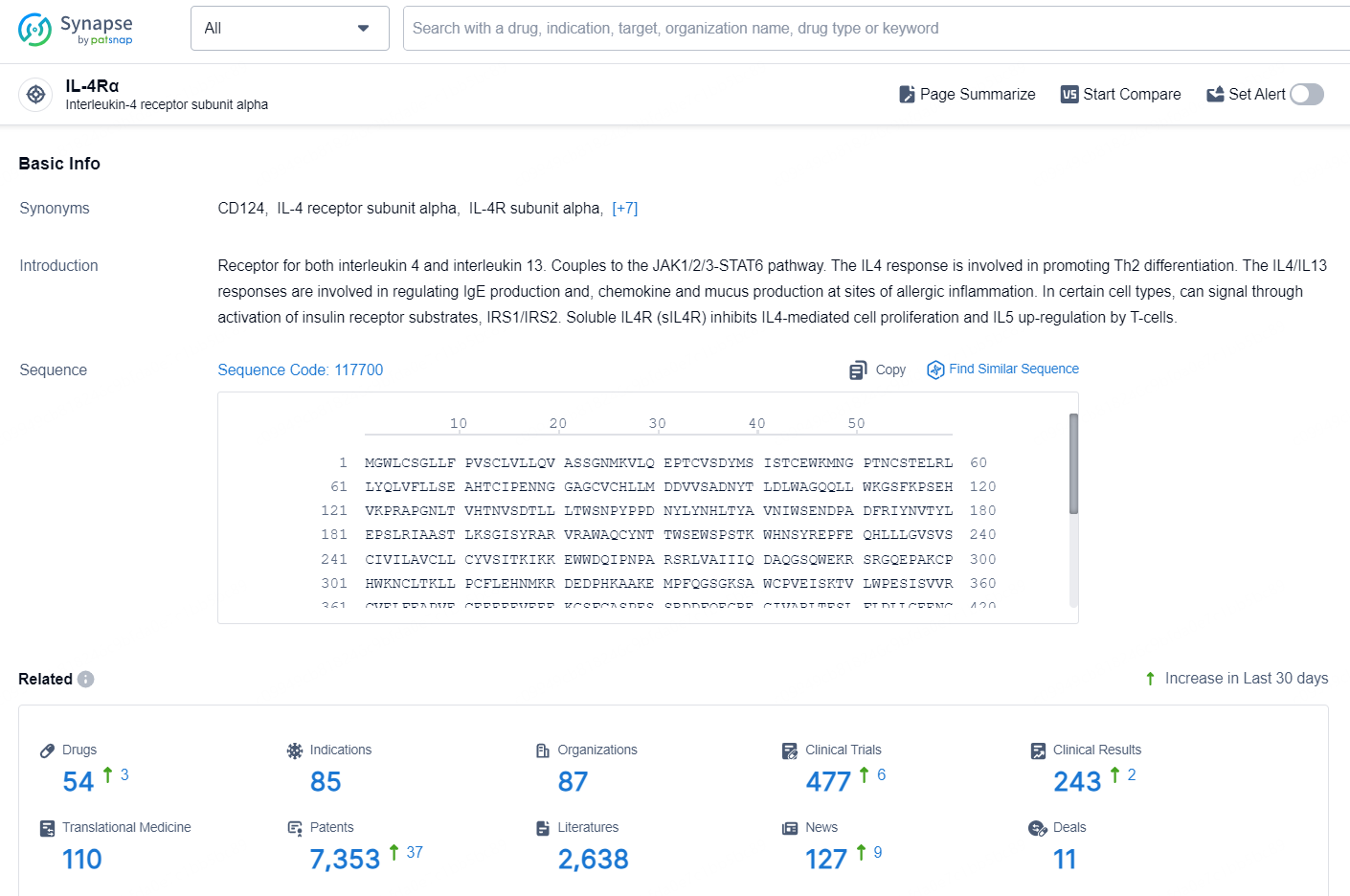
👇Explore the latest research progress on drug-related developments, indications, therapeutic organizations, clinical trials, results, and patents by clicking on the targeted picture link below. Unfold a world of comprehensive information on this target in just a click!
According to the data provided by the Synapse Database, As of September 29, 2024, there are 54 investigational drugs for the IL-4Rα targets, including 85 indications, 87 R&D institutions involved, with related clinical trials reaching 477, and as many as 7353 patents.
Dupilumab is a monoclonal antibody drug targeting IL-4Rα with a wide range of therapeutic indications across various disease areas. It has been approved in both the global and Chinese markets, with its first approval in the United States in 2017, and is regulated under priority review and breakthrough therapy designations, among others.