May 2025 Biotech Boom: $12B+ in Deals Reshape Next-Gen Therapies from AI to RNA Editing
In May 2025, a new wave of capital and technological resonance swept across the global biotechnology sector. Industry giants such as CSPC Pharmaceutical Group, Sanofi, and Eli Lilly accelerated their deployment of next-generation therapies through multibillion-dollar deals. From AI-driven targeted protein degradation (TPD) and RNA editing to in vivo CAR-T therapies, and from oral small-molecule drugs to non-opioid analgesics, the industry is fiercely competing around three central themes: “conquering previously undruggable targets,” “breaking traditional R&D bottlenecks,” and “reshaping the treatment paradigm for chronic diseases and cancer.”
1. CSPC Eyes $5 Billion Global Collaboration: EGFR-ADC Licensing and AI-Driven Drug Discovery Platform for Global Expansion
On May 30, 2025, CSPC Pharmaceutical Group announced that it is in discussions with several independent third parties regarding three potential transactions. These involve its self-developed epidermal growth factor receptor antibody-drug conjugate (EGFR-ADC) and other innovative therapeutics developed via its proprietary technology platform. The deals cover development, manufacturing, and commercialization rights, with a potential total value of up to $5 billion, including upfront payments, R&D milestone payments, and commercial milestone payments.
A key asset in the negotiations is CSPC’s EGFR-ADC, a drug built on precise conjugation of monoclonal antibodies and cytotoxic agents. EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) is overexpressed in various solid tumors, such as non-small cell lung cancer and colorectal cancer. The ADC specifically targets and binds to EGFR on tumor cell surfaces, delivering a highly potent payload (e.g., a topoisomerase or tubulin inhibitor) directly into the cancer cells to induce apoptosis. Compared to traditional chemotherapy, EGFR-ADC significantly reduces systemic toxicity while expanding the therapeutic window.
CSPC's technology platform also includes an AI-powered drug discovery system, which simulates target-ligand interactions to accelerate screening and optimization of small-molecule candidates, particularly for developing oral therapies for chronic diseases, such as autoimmune disorders.
Another licensed product, liposomal irinotecan injection, uses liposomal encapsulation to prolong drug half-life, increase local tumor concentration, and overcome resistance—offering new hope for hard-to-treat cancers like pancreatic cancer.
2. Sanofi Acquires DR-0201 for $1.9 Billion: Advancing Deep B Cell Depletion Therapy and Redefining Autoimmune Disease Treatment
On May 27, 2025, Sanofi announced the acquisition of DR-0201 (now renamed SAR448501) in a deal valued at $1.9 billion. DR-0201 is a bispecific myeloid cell engager (MCE) developed by clinical-stage biopharma company Dren Bio. The acquisition was executed through the purchase of Dren Bio’s affiliate Dren 0201, Inc. for an upfront payment of $600 million, with potential additional payments of up to $1.3 billion tied to development and commercialization milestones.
As a potential first-in-class therapy, DR-0201 is designed to achieve deep B cell depletion to treat autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), addressing the unmet need for patients resistant to current therapies. The transaction significantly strengthens Sanofi’s global leadership in immunology and adds a critical asset to its next-generation immunotherapeutics pipeline.
The core mechanism of DR-0201 lies in its dual-targeting design. One arm binds to phagocytic receptors (e.g., Dectin-1) on myeloid cells such as dendritic cells and macrophages, while the other targets the CD20 antigen on B cells. This bispecific configuration activates myeloid cell phagocytosis to induce deep clearance of B cells. Unlike conventional CD20 monoclonal antibodies, DR-0201 targets multiple B cell subtypes, including plasma cells, offering more comprehensive suppression of pathogenic B-cell-driven immune responses.
In autoimmune diseases, B cells not only produce autoantibodies but also exacerbate inflammation via antigen presentation and cytokine secretion. DR-0201’s deep depletion of B cells helps reset the adaptive immune system, providing durable remission for patients with refractory disease. Preclinical and Phase I trials have shown promising safety and efficacy across indications such as non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, Sjögren’s syndrome, and polymyositis, without inducing cytokine release syndrome or neurotoxicity—common side effects seen with other immunotherapies.
This acquisition is strategically significant for Sanofi:
First, DR-0201 substantially enhances Sanofi’s immunology pipeline, particularly in autoimmune indications. Although Sanofi’s flagship drug Dupixent leads the market, its core patents will expire in 2031, and new-generation therapies are urgently needed to maintain leadership. DR-0201 is well-positioned to become the "next immunology blockbuster" for difficult-to-treat diseases like lupus, while also paving the way for label expansions into COPD, chronic spontaneous urticaria, and more.
Second, by acquiring Dren Bio’s platform technology, Sanofi reinforces its capabilities in developing myeloid cell-targeting agonists and phagocytosis-based therapies—with applications in oncology, infectious diseases, and metabolic disorders. Maintaining Dren Bio as an independent entity promotes synergy in pipeline development (e.g., selective pathogenic cell clearance programs) and accelerates translational research.
For Dren Bio, this deal provides strong financial backing ($600M upfront + $1.3B in milestones) to focus on other candidates, such as novel bispecifics or small molecules targeting myeloid cells. Additionally, Sanofi’s global commercialization infrastructure and clinical development expertise will support efficient advancement of DR-0201 into Phase II/III trials and beyond.
3. Eli Lilly Acquires SiteOne for $1 Billion to Advance Non-Opioid Pain Therapies and Accelerate Pipeline Diversification
On May 27, 2025, Eli Lilly and Company announced the completion of its $1 billion acquisition of clinical-stage biotech firm SiteOne Therapeutics. The deal centers on SiteOne’s lead asset STC-004, a non-opioid oral analgesic targeting the Nav1.8 sodium ion channel, which is currently in Phase II clinical trials. The transaction includes an upfront payment estimated at $300–400 million, with an additional $700 million tied to regulatory and commercial milestones.
This acquisition marks a strategic expansion of Lilly’s pain management portfolio and reflects its intent to reduce dependency on its blockbuster diabetes and obesity franchise (e.g., GLP-1 receptor agonist tirzepatide) by capturing opportunities in the rapidly growing non-opioid analgesics market.
STC-004 is a highly selective Nav1.8 inhibitor, designed to modulate voltage-gated sodium channels (VGSCs) involved in pain transmission. Nav1.8 is predominantly expressed in nociceptive neurons of the peripheral nervous system (e.g., dorsal root ganglia), playing a critical role in transmitting pain signals. Unlike traditional opioids, which act on central nervous system (CNS) receptors and are associated with addiction and respiratory depression, STC-004 blocks the sodium ion influx via Nav1.8, effectively interrupting pain signaling at the peripheral level—providing relief without CNS-related risks.
Compared to Vertex Pharmaceuticals’ approved Nav1.8 inhibitor Journavx (suzetrigine), which was authorized for acute pain but showed limited superiority over opioids in Phase III trials, STC-004 offers key advantages: greater selectivity, oral convenience, and reduced resistance risk. Its optimized molecular structure enhances Nav1.8 targeting while minimizing off-target effects, potentially expanding its therapeutic window.
Beyond STC-004, SiteOne's platform also includes other sodium channel inhibitors (e.g., Nav1.7, Nav1.9), laying the groundwork for multi-target pain therapies in the future.
4. AI-Driven Molecular Glue Discovery: VantAI Expands Collaboration with Blueprint Medicines to Target “Undruggable” Proteins
On May 20, 2025, VantAI and Blueprint Medicines announced an expanded partnership, building on their initial 2022 collaboration. The extended agreement focuses on developing induced proximity therapeutics, including molecular glues and heterobifunctional degraders, aimed at modulating historically undruggable targets. This effort will leverage VantAI’s new AI foundation model Neo-1 to accelerate rational molecular design.
Under the terms, VantAI is eligible to receive up to $1.67 billion in potential milestone payments, including $1.4 billion in commercial milestones and $270 million in R&D/regulatory milestones, along with tiered royalties on future product sales.
This collaboration deepens both companies' positions in the targeted protein degradation (TPD) space and demonstrates how AI can overcome traditional drug discovery constraints.
For VantAI, the deal validates its integrated AI drug discovery platform, combining NeoLink’s structural proteomics with the Neo-1 foundation model. The partnership provides long-term financial support and accelerates real-world application of VantAI’s AI in drug design. The launch of Neo-1 represents a paradigm shift—transforming molecular glue development from serendipitous discovery to rational design. Blueprint’s reputation lends credibility to VantAI’s technology, while collaboration around undruggable targets will help build data and experience critical for VantAI’s internal pipeline, including proprietary glue programs.
For Blueprint Medicines, this marks a pivotal extension of its precision medicine strategy. By integrating VantAI’s AI capabilities, Blueprint can rapidly identify and optimize molecular glue candidates for complex disease drivers, dramatically shortening development timelines. The companies plan to focus on oncology and hematology targets, such as transcription factors and key signaling nodes—areas where Blueprint's current pipeline (e.g., Kisqali, Ayvakit) leaves strategic gaps.
The partnership will also advance engineered protein-protein interface (PPI) technologies, enabling Blueprint to differentiate its TPD programs from competitors like Arvinas and C4 Therapeutics. Long-term, this alliance positions Blueprint to build a next-generation pipeline for undruggable targets, strengthening its global leadership in oncology and rare disease therapeutics.
5. AstraZeneca Acquires EsoBiotec for $1 Billion: Transforming In Vivo CAR-T Therapy and Accelerating the “Third Wave” of Cell Therapy
On May 20, 2025, AstraZeneca announced the acquisition of EsoBiotec, a pioneering in vivo cell therapy company, in a transaction valued at $1 billion. AstraZeneca will pay $425 million upfront, with additional milestone payments of up to $575 million tied to development and regulatory achievements.
At the core of the deal is EsoBiotec’s proprietary Engineered Nanobody Lentiviral Platform (ENaBL), which uses highly targeted lentiviral vectors to deliver gene payloads directly to immune cells such as T cells inside the patient’s body, enabling in vivo reprogramming without ex vivo manipulation. This technology could address major limitations of conventional CAR-T therapies, including long manufacturing cycles, high costs, and safety concerns—opening a new frontier in treating cancer and autoimmune diseases.
The ENaBL platform leverages lentiviral vector-mediated gene delivery. Its mechanism includes:
·Targeted cell recognition via engineered nanobodies displayed on the lentivirus surface (e.g., anti-CD3, anti-CD8, or anti-TCR nanobodies), ensuring precise binding to T cells;
·Efficient gene integration, with viral payloads encoding chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) or immune modulators that integrate into host T cell genomes, enabling stable long-term expression;
·Functional T cell activation in vivo, allowing patients’ T cells to express CARs and actively target tumor or autoreactive cells.
Unlike traditional CAR-T therapies, which require leukapheresis, genetic editing, and reinfusion, ENaBL enables systemic administration via intravenous injection. Additionally, the platform incorporates features such as CD47 gene insertion (to evade macrophage clearance) and MHC-I knockout (to reduce immunogenicity), improving both efficacy and safety.
This approach can reduce the treatment timeline from weeks to minutes, significantly lower production costs, and eliminate the need for lymphodepletion preconditioning—a key advantage in expanding access to cell therapy.
6. Eli Lilly Invests $1.3 Billion in Rznomics: Advancing RNA Editing for Genetic Hearing Loss
On May 15, 2025, South Korea–based Rznomics announced a global R&D collaboration and licensing agreement with Eli Lilly, valued at over $1.3 billion, including undisclosed upfront payments and future milestone-based and revenue-sharing components.
The collaboration focuses on developing RNA editing therapies for hereditary sensorineural hearing loss, using Rznomics’ proprietary trans-splicing ribozyme platform. Rznomics will lead early-stage research, while Lilly will oversee late-stage development and global commercialization. The deal marks Lilly’s strategic expansion into RNA editing therapeutics, aiming to address unmet needs in hearing loss and beyond.
Rznomics’ platform is based on group I intron-derived trans-splicing ribozymes, which enable precise RNA editing via two consecutive transesterification reactions. The mechanism includes:
·Target recognition and cleavage, where the ribozyme’s Internal Guide Sequence (IGS) forms a complementary P1 helix with the target RNA (5′-GN′N′N′N′N′-3′), and an exogenous guanosine acts as a nucleophile to cleave at the 5′ splice site, exposing a 3′-OH uridine;
·RNA replacement and ligation, in which the ribozyme undergoes conformational change, and its conserved ωG residue replaces the exogenous guanosine to ligate a therapeutic RNA sequence to the cleaved target RNA;
·Dynamic regulation and safety, enabled by RNA-sensing riboswitches, which balance therapeutic gene expression with endogenous RNA levels, avoiding overexpression.
Additionally, the use of DNA vectors allows for stable and durable RNA modulation without genomic integration, minimizing genotoxic risk.
The platform offers three distinct advantages:
·A dual-function, single-molecule system (silencing pathogenic RNA while promoting therapeutic gene expression),
·Dynamic expression control (for personalized therapy),
·Long-lasting safety profile (no genome editing required).
While currently in preclinical development for genetic hearing loss, the technology holds potential across metabolic, neurological, and genetic disorders.
This collaboration represents a transformational milestone for Rznomics, marking its emergence from a domestic biotech into a global RNA therapeutics leader. The $1.3 billion deal, including milestones, ensures robust funding for platform development and clinical translation. Eli Lilly’s involvement provides high-level validation, strengthening Rznomics’ credibility in capital markets and with potential partners, and attracting future investment.
Lilly’s commercialization capabilities are expected to accelerate time to market, with the hearing loss therapy potentially becoming the first RNA editing drug based on trans-splicing ribozymes to receive approval—possibly before 2030.
7. Novo Nordisk and Septerna Enter $2.2 Billion Collaboration to Redefine Oral Weight Loss Drug Development
On May 14, 2025, Novo Nordisk, a global leader in pharmaceuticals, announced an exclusive worldwide collaboration and licensing agreement with U.S.-based biotechnology company Septerna, with a total deal value of up to $2.2 billion. The partnership focuses on the development of oral small-molecule drugs targeting obesity, type 2 diabetes, and other cardiometabolic diseases.
The deal includes over $200 million in upfront and near-term milestone payments, with the remaining value to be realized through development, commercialization milestones, and royalties on product sales. The collaboration will initiate four discovery programs, targeting key G protein–coupled receptor (GPCR) pathways, including GLP-1, GIP, and glucagon receptor (GCGR). By combining Novo Nordisk’s scientific leadership in metabolic diseases with Septerna’s proprietary GPCR drug discovery platform, the companies aim to accelerate the development of next-generation oral weight management therapies. Novo Nordisk will lead global development and commercialization post-IND, while Septerna will co-lead early-stage research and share in global profits for selected programs.
At the core of Septerna’s innovation is its Native Complex Platform™, which overcomes longstanding challenges in GPCR drug discovery. This proprietary technology isolates GPCRs from cellular membranes and reconstitutes them into native-like complexes, incorporating ligands, signaling proteins, and lipid bilayers that mimic the natural membrane environment. This approach preserves the native structure, function, and dynamics of GPCRs, addressing the common issue of receptor instability in traditional in vitro assays.
Leveraging this platform, Septerna can screen billions of small molecules to identify precise binding sites on validated targets such as GLP-1 and GIP receptors—including novel allosteric pockets. The platform supports multiple pharmacological modes of action, including agonists, antagonists, and allosteric modulators, enabling comprehensive control over GPCR signaling. The resulting oral small-molecule candidates offer high selectivity, potency, and favorable drug-like properties, directly modulating GPCR pathways to regulate metabolism, energy balance, and appetite—offering long-acting therapeutic options for obesity and diabetes.
Summary
The global surge in biotechnology financing in May 2025 underscores three major industry trends: breakthrough technologies are reigniting investor interest, therapeutic paradigms are rapidly evolving, and global competition is reshaping industry alliances.
Amid this wave, Eli Lilly’s strategic expansion into non-opioid analgesics and RNA editing therapies reflects a dual-track approach toward chronic and rare diseases, while Novo Nordisk’s investment in oral small molecules complements its GLP-1-based franchise and exemplifies a broader industry shift toward multi-target, multi-mechanism, and multimodal strategies, especially as companies approach patent cliffs.
Meanwhile, China’s innovation-driven biotech firms, such as CSPC, are increasingly entering strategic partnerships and acquisition agreements with Western pharmaceutical giants like Novo Nordisk and Sanofi. These moves signal a transition from “point-to-point competition” to a deeper integration of technology sovereignty and ecosystem alliances, reshaping the global biotechnology landscape.
How to get the latest progress on drug deals?
If you would like to access the latest transaction event information, you can click on the 'Deal' module from the homepage of the Synapse database. Within the Deal module, you can search for global pharmaceutical transaction information using labels such as Drugs, Organization, Target, Drug Type, Deal Date.
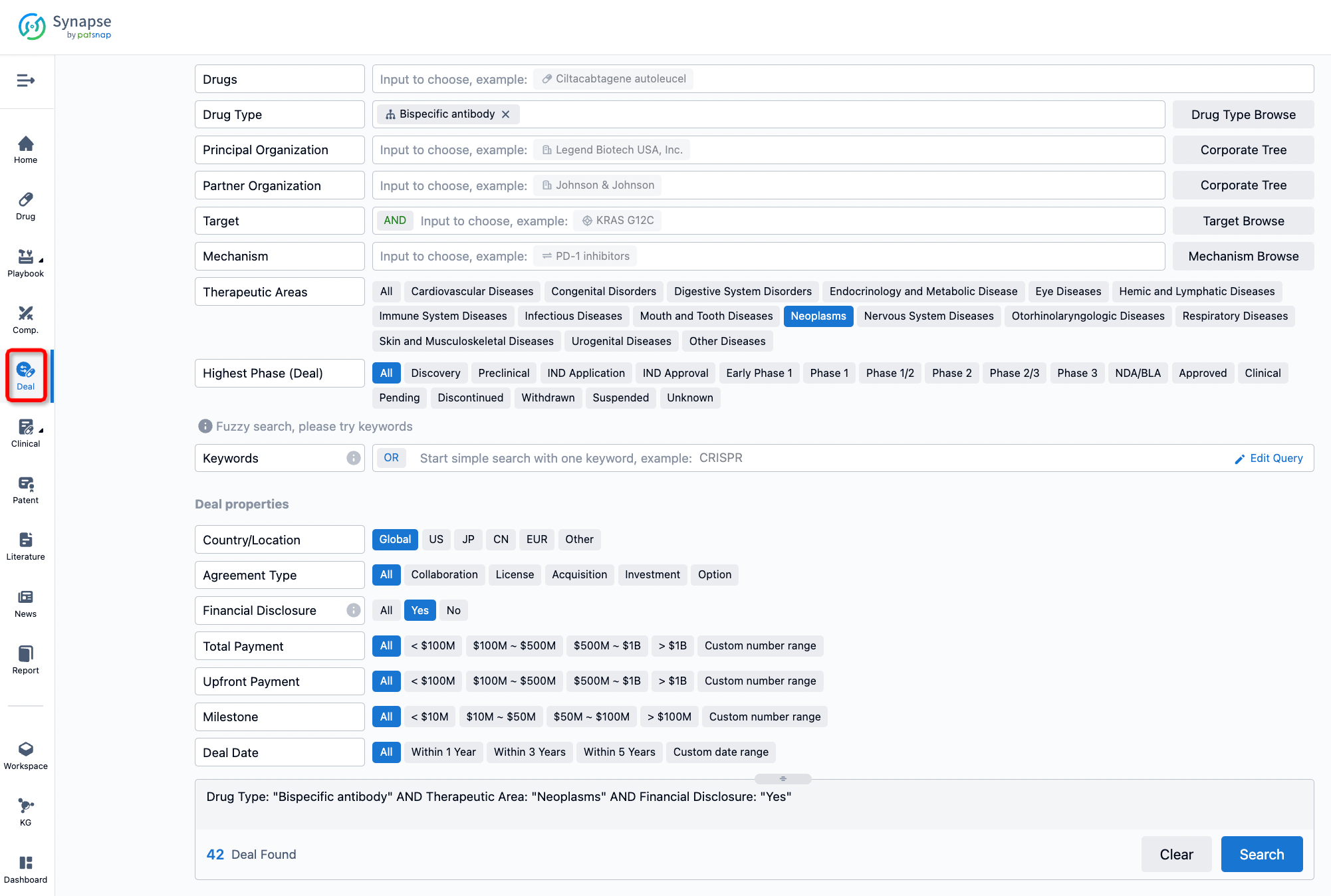
Furthermore, you can obtain the original link to the transaction coverage by clicking on the "Deal Name."
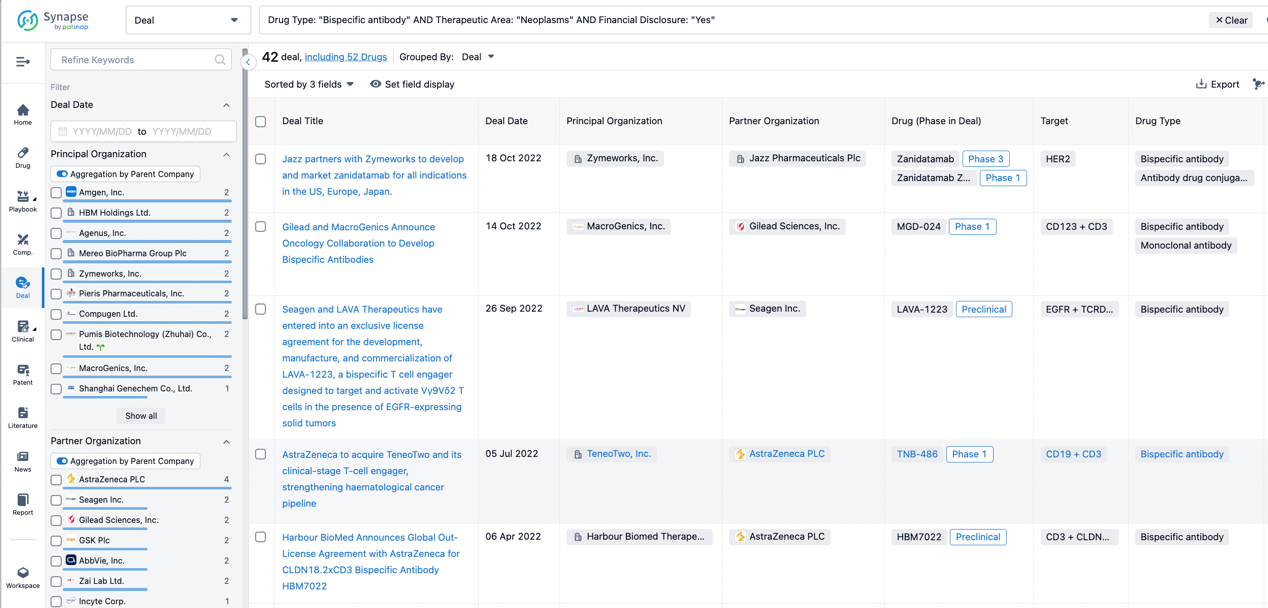
In the analysis view, you can see the most active assignors, assignees, popular targets, and other dimensions of analysis, as well as the distribution of research and development statuses at the time of the transaction, to help you better understand the search results.
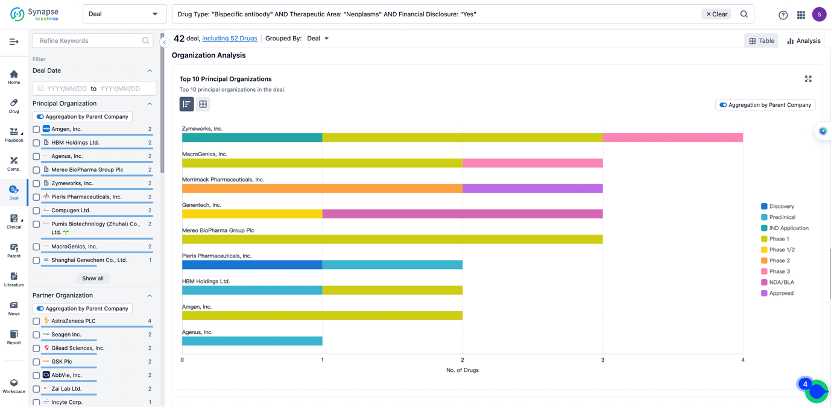
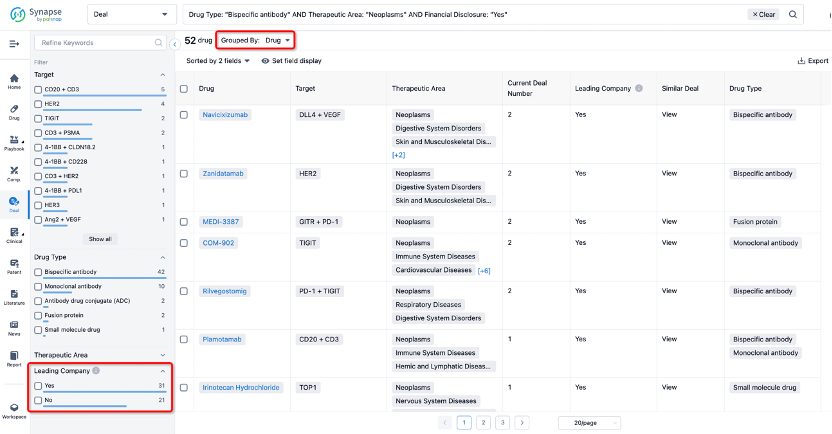
The Synapse database also supports the ability to view current transactions from the dimension of "drugs" (by selecting "drugs" from the "Adjust Dimension" dropdown menu above). Targeting transactions involving renowned pharmaceutical companies that are of interest to the industry, such as Merck, Roche, etc., Synapse has identified a group of "leading companies" through drugs that have achieved global sales exceeding 1 billion US dollars in 2022. Transactions involving drugs from these leading companies can be filtered by clicking on the "Leading Company" tag on the left-hand side.
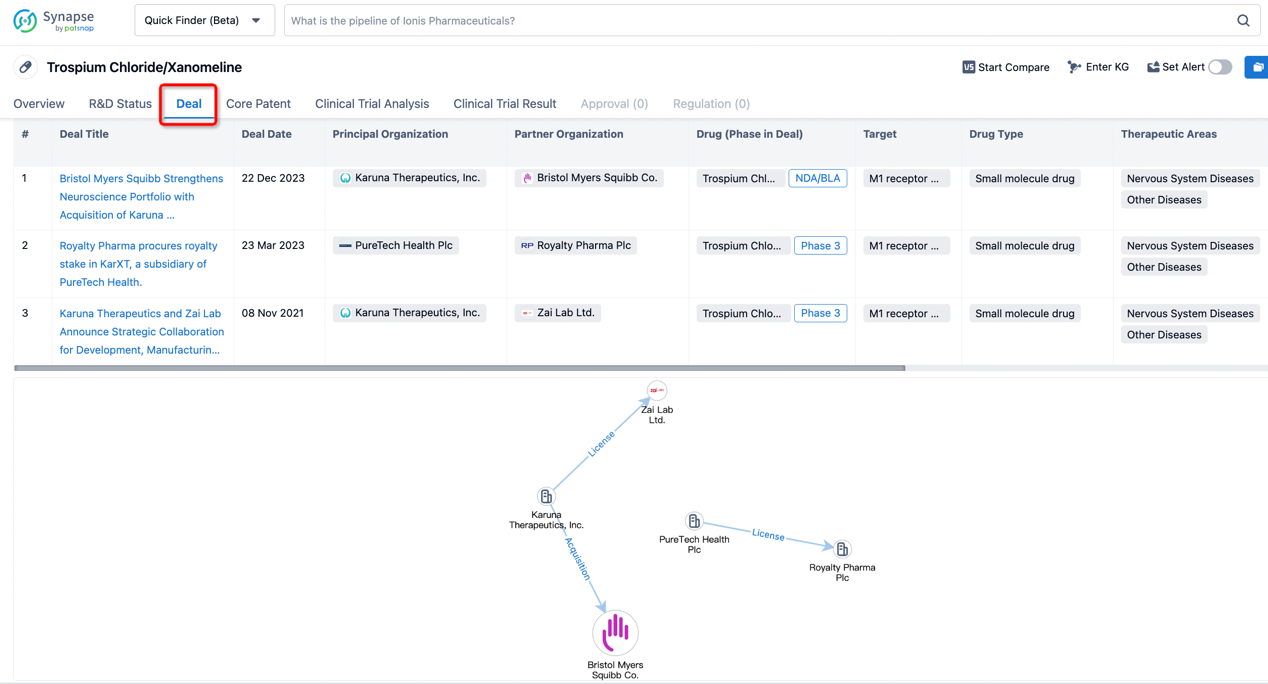
In addition to the drug transaction module, you can also view related transaction history on the drug detail page and the institution detail page.
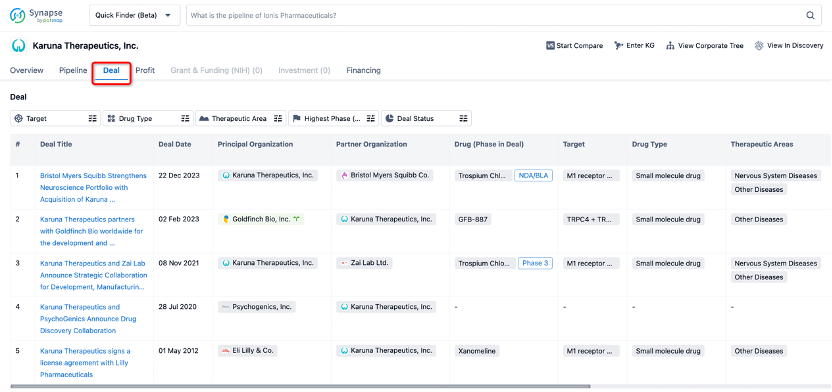
Click on the image below to explore new pharmaceutical funding transactions!