Pharmaceutical Insights: Silodosin's R&D Progress
Silodosin's R&D Progress
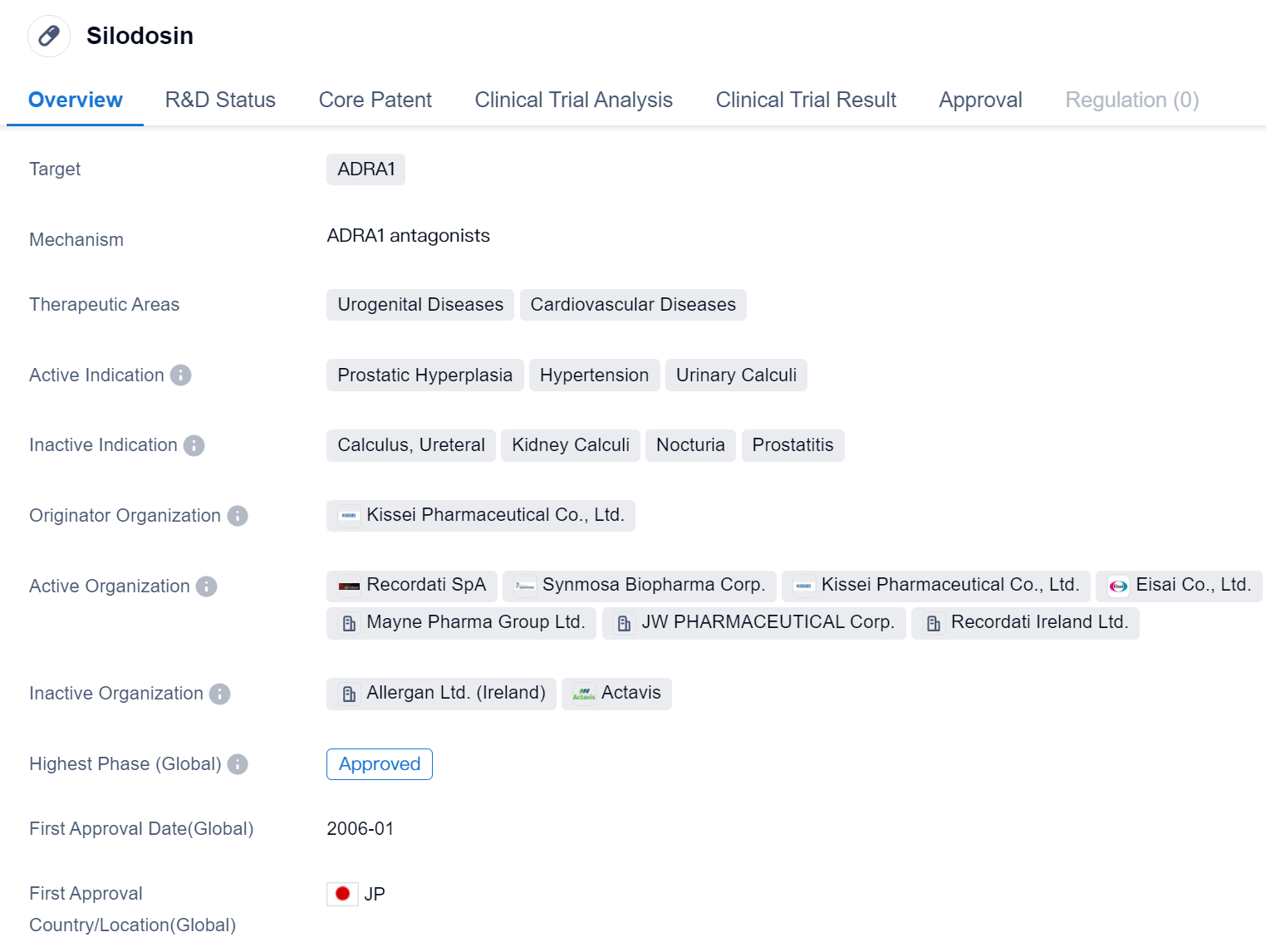
Silodosin is a small molecule drug that falls under the therapeutic areas of urogenital diseases and cardiovascular diseases. It primarily targets the ADRA1 receptor. The drug has been approved for the treatment of prostatic hyperplasia, hypertension, and urinary calculi.
Silodosin was developed by Kissei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., a pharmaceutical organization based in Japan. It received its first approval in Japan in January 2006, the drug has also obtained approval in other countries globally.
Prostatic hyperplasia, also known as an enlarged prostate, is a condition commonly found in older men. It is characterized by the enlargement of the prostate gland, leading to urinary symptoms such as frequent urination, weak urine flow, and difficulty in emptying the bladder. Silodosin has been approved for the treatment of this condition, providing relief to patients suffering from these symptoms.
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a prevalent cardiovascular disease that affects a significant portion of the global population. Silodosin has also been approved for the treatment of hypertension, offering an additional option for patients to manage their blood pressure levels.
Urinary calculi, commonly referred to as kidney stones, are solid masses that form in the urinary tract. These stones can cause severe pain and discomfort and may require medical intervention for their removal. Silodosin has been approved for the treatment of urinary calculi, potentially aiding in the management and dissolution of these stones.
As a small molecule drug targeting the ADRA1 receptor, Silodosin exhibits its therapeutic effects by selectively blocking the receptor. This action helps relax the smooth muscles in the prostate, blood vessels, and urinary tract, leading to improved symptoms and outcomes in patients with prostatic hyperplasia, hypertension, and urinary calculi.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Silodosin: ADRA1 antagonists
ADRA1 antagonists are a type of drugs that act as antagonists at the alpha-1 adrenergic receptors. Alpha-1 adrenergic receptors are a subtype of adrenergic receptors found in various tissues throughout the body, including smooth muscle cells in blood vessels, the heart, and the urinary bladder.
By antagonizing or blocking these receptors, ADRA1 antagonists inhibit the binding of norepinephrine and epinephrine (stress hormones) to the receptors. This leads to a decrease in the activation of the receptors and subsequent physiological responses mediated by these receptors.
In the context of biomedicine, ADRA1 antagonists have various clinical applications. They are primarily used for the treatment of conditions such as hypertension (high blood pressure), benign prostatic hyperplasia (enlarged prostate), and certain cardiovascular disorders. By blocking the alpha-1 adrenergic receptors, these drugs help to relax smooth muscles, dilate blood vessels, and reduce peripheral vascular resistance, ultimately leading to a decrease in blood pressure.
It's important to note that ADRA1 antagonists can have side effects, including dizziness, orthostatic hypotension (a drop in blood pressure upon standing up), and reflex tachycardia (increased heart rate). Therefore, their use should be carefully monitored and prescribed by healthcare professionals.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Silodosin
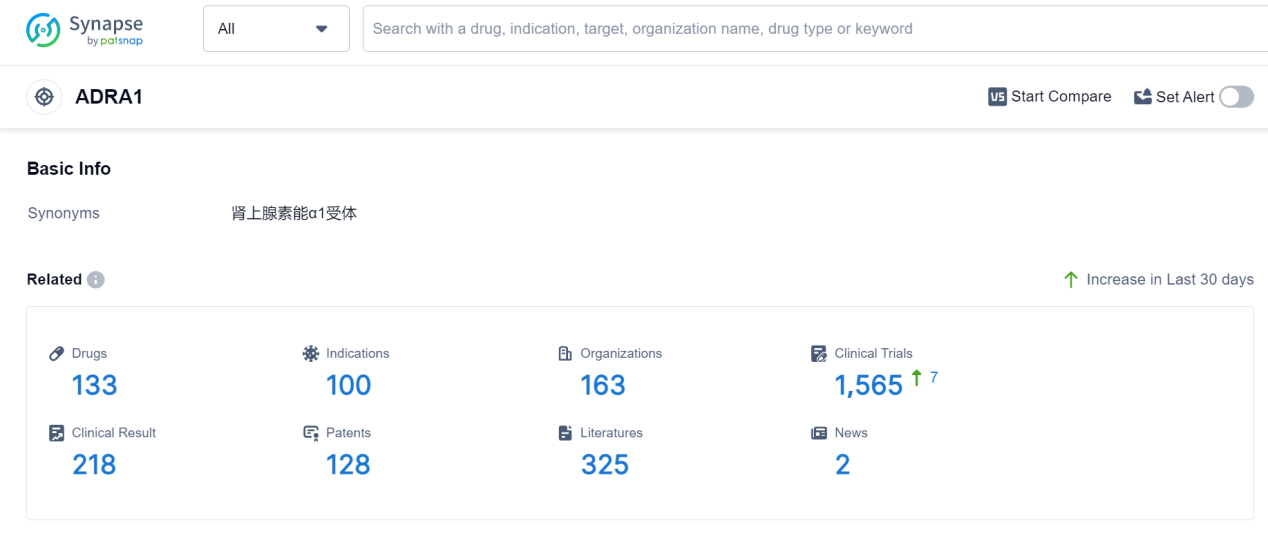
ADRA1, or alpha-1 adrenergic receptors, play a crucial role in the human body. These receptors are found in various tissues and organs, including the smooth muscles of blood vessels, urinary bladder, and prostate gland. Activation of ADRA1 receptors leads to vasoconstriction, which helps regulate blood pressure. Additionally, ADRA1 receptors are involved in the contraction of smooth muscles in the urinary bladder and prostate, contributing to urinary control. Understanding the role of ADRA1 receptors is essential in the development of drugs targeting these receptors, which can be used to treat conditions such as hypertension, benign prostatic hyperplasia, and urinary incontinence.
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 7 Sep 2023, there are a total of 133 ADRA1 drugs worldwide, from 163 organizations, covering 100 indications, and conducting 1565 clinical trials.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Silodosin is a small molecule drug developed by Kissei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. It has been approved for the treatment of prostatic hyperplasia, hypertension, and urinary calculi. With its ability to target the ADRA1 receptor, Silodosin offers potential benefits in managing urogenital and cardiovascular diseases. Its approval in Japan in 2006.