Progress in the Research and Development of METTL3 Drug Targets
METTL3 is an RNA methyltransferase that catalyzes the methylation of RNA at N6-adenosine, making it a key player in this process. Abnormal expression of METTL3 can lead to various diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disorders, and neurodegenerative diseases. Therefore, finding inhibitors of METTL3 could help further our understanding of the biological functions of this enzyme and aid in the development of new treatments.
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is one of the most common and abundant covalent modifications in messenger RNA. First discovered in bacterial and eukaryotic RNA back in 1958, approximately 0.1% to 0.5% of mRNA adenines are modified by m6A. In vitro data suggests that m6A modifications affect fundamental biological processes of mRNA, including expression, splicing, localization, and translation. The occurrence of m6A modifications demonstrates tissue specificity, with significant variations observed between healthy and diseased tissues.

Timeline of m6A Discovery
The METTL3, an RNA methyltransferase, is one of the primary enzymes catalyzing m6A modification of RNA, but not the only one. It coexists with METTL14 and Wilms Tumor 1 Associated Protein (WTAP) in the form of a heterotrimeric complex. METTL3 possesses catalytic activity, transferring methyl groups from cofactor S-adenosylmethionine to substrate RNA, while METTL14 facilitates the binding of the substrate RNA. WTAP locates the complex at a specific nuclear region and positions the RNA substrate onto the complex.
METTL3 plays roles in various aspects of cancer development. Knocking out the METTL3 gene in lung cancer cell lines and Hela cells results in decreased growth, survival, and invasion of human lung cancer cells. In human bladder, the expression of METTL3 is significantly upregulated, and the knockout of METTL3 significantly reduces the proliferation, invasion, in vitro survival, and in vivo tumorigenicity of bladder cancer cells.
Competitive Landscape
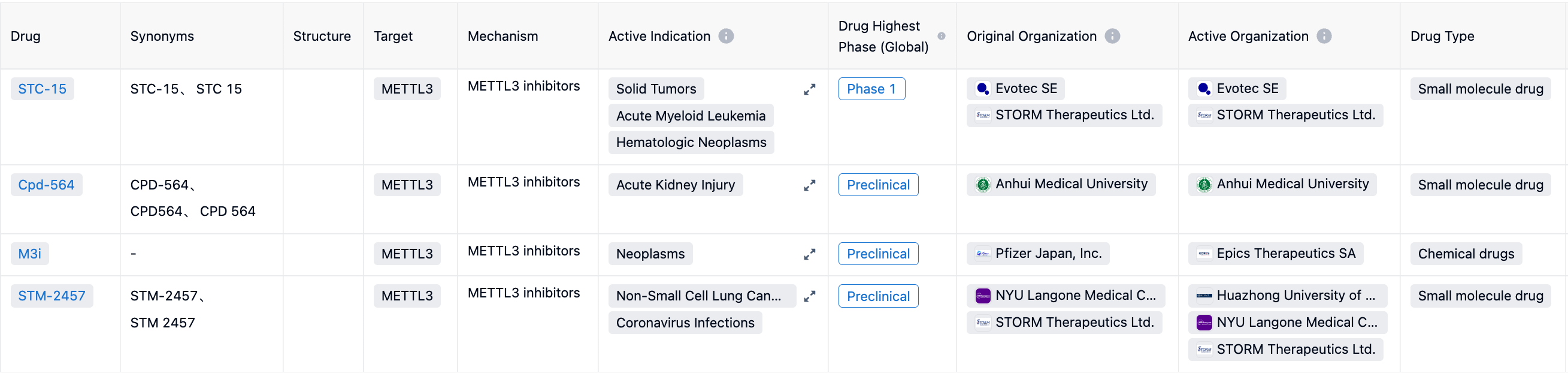
By entering "Mettl3" into the Synapse database, the clinically relevant molecule STC-15 can be found. In addition, a batch of molecules is in the preclinical research stage, including SAM binding pocket inhibitors, conformation inhibitors, natural products, and adenine analogs.
According to a review summarized by Professor Qidong You in "Drug Discovery Today", the binding pattern of METTL3-METTL14 with inhibitors can be divided into three parts: part A is the aromatic ring, part B is the connecting chain, part C is the amino hydrophobic chain. Furthermore, the available cocrystal structures of METTL3-METTL14 and its inhibitors can help rationally design new molecules. To achieve this goal, analyzing the cocrystal structures of METTL3-METTL14 and conformation inhibitors will provide new ways for the development of new tools and potential drugs.
Accent Therapeutics, which is in the same field, was established in 2017 and has attracted attention from several capitals, and has had strong development momentum in recent years. The company announced in April 2020 that it completed a $63 million B round of financing to advance new precise cancer treatments for RNA modification proteins (including METTL3 and ADAR1). At present, the company has received more than $100 million in financing. In June of the same year, Accent announced a partnership with pharmaceutical giant AstraZeneca.
Key Drug
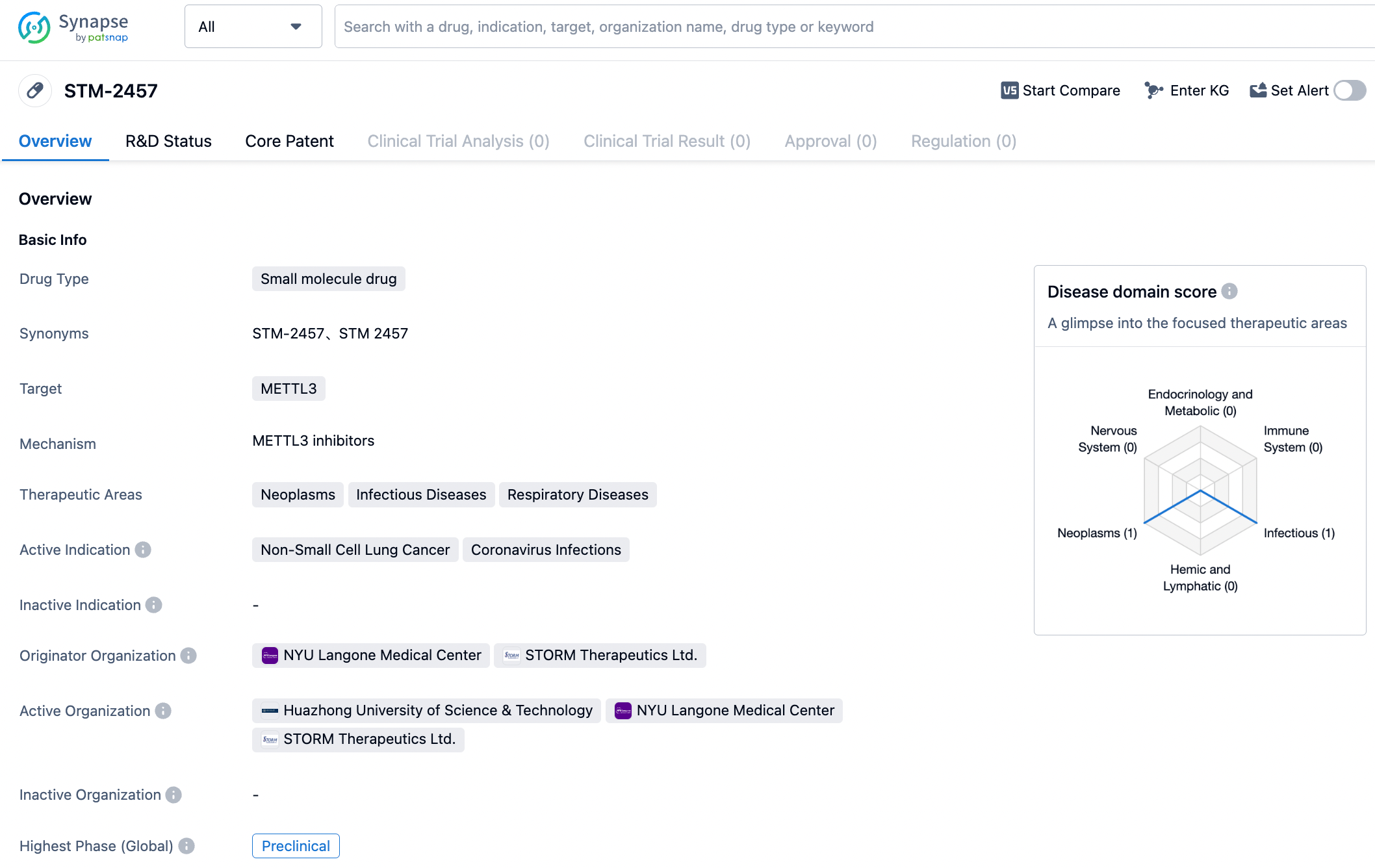
STM2457 is the first METTL3 class small molecule inhibitor developed by the UK pharmaceutical company STORM THERAPEUTICS. Unlike other RNA methyltransferases, STM2457 has high specificity for METTL3 (IC50=51.7 μM). It can induce apoptosis in cells of AML patients and mouse AML models, but it does not induce apoptosis in normal non-leukemic hematopoietic cells. After treatment, it can reduce the number of human CD45 cells in the bone marrow and spleen of mice. STORM THERAPEUTICS had raised £30 million in its Series A financing and began human clinical trials for the latest generation METTL3 inhibitor, STC-15, on November 15, 2022. The study's indication is for advanced solid tumors.
This study is a phase I, multi-center, open-label study with a 3+3 cohort design, expecting to recruit 66 patients. The aim is to evaluate the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of STC-15 in multiple escalating daily oral doses in the Q3W treatment cycle, with dose levels determined by the modified Fibonacci algorithm. The study aims to systematically assess the safety, tolerance, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of STC-15 in adult patients with advanced malignant tumors. The dose levels further evaluated in the expanded cohort will be selected based on available PK, pharmacodynamics, target activity, efficacy, safety, and tolerability data, including long-term safety data beyond Dose Limiting Toxicity (DLT).
As METTL3 is a SAM-dependent methyltransferase, the earliest prototypes of METTL3 inhibitors were structural analogues of SAM. We are still in the early stage of discovering potent and selective METTL3 inhibitors, and many biological questions about the mechanism and function of the METTL3-METTL14 complex remain unanswered. STC-15 is the only drug that has entered the clinical stage. Interruption of METTL3-METTL14 activity could potentially lead to damage to fundamental physiological processes, resulting in harmful outcomes. To thoroughly validate METTL3-METTL14 as a manageable drug target, a multi-disciplinary approach is required to further elucidate its biological function in a broader context of epitranscriptomics.