The Application of 5-HT1A Agonists in the Treatment of Psychoneurological Disorders
The 5-HT system is a significant neurotransmitter system in the human brain, with 5-HT receptors widely distributed throughout it. Its functions primarily comprise vegetative nerve regulation, behavioral and emotional states, sleep, and pain, among others such as cognition. Among these receptors, the most studied is the 5-HT1A receptor, since it is closely tied to neuronal development and plasticity, stress, and immunity. It is also closely associated with several neuropsychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia, depression, anxiety, substance abuse, dementia, etc. More importantly, the 5-HT1A receptor can also regulate the function of neurons and other receptors and is closely related to various behaviors.
The 5-HT1A receptor is one of the most widely distributed 5-HT receptors, present on the cell bodies and dendrites of 5-HT neurons, situated in the raphe nucleus and the terminal location of 5-HT release. The 5-HT1A receptor is the only 5-HT receptor on the presynaptic dendritic membrane, and it feeds back to diminish neural impulse transmission and decrease 5-HT release, thereby regulating the activity of 5-HT neurons. Electrophysiological studies have indicated that 5-HT1A agonists could suppress the firing of rat 5-HT neurons located in the raphe nucleus, while 5-HT1A antagonists can counteract this effect. In vitro experiments also discovered that 5-HT1A agonists could inhibit the excitability of 5-HT neurons in various brain regions. It was formerly assumed that presynaptic 5-HT1A receptors primarily regulate the activity of 5-HT neurons. Still, current research suggests that postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptors also play a role in the mediation of 5-HT neuron activity.
Dysfunction of the 5-HT1A receptor has been implicated in various psychiatric disorders, including depression, anxiety disorders, and schizophrenia. Understanding the role of the 5-HT1A receptor is essential for the development of novel therapeutic interventions targeting these conditions.
5-HT1A receptor Competitive Landscape
According to the data provided by Patsnap Synapse-Global Drug Intelligence Database: the following figure shows that as of 4 Sep 2023, there are a total of 223 5-HT1A receptor drugs worldwide, from 229 organizations, covering 132 indications, and conducting 1527 clinical trials.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or login directly if you have freemium accounts, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs , indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target.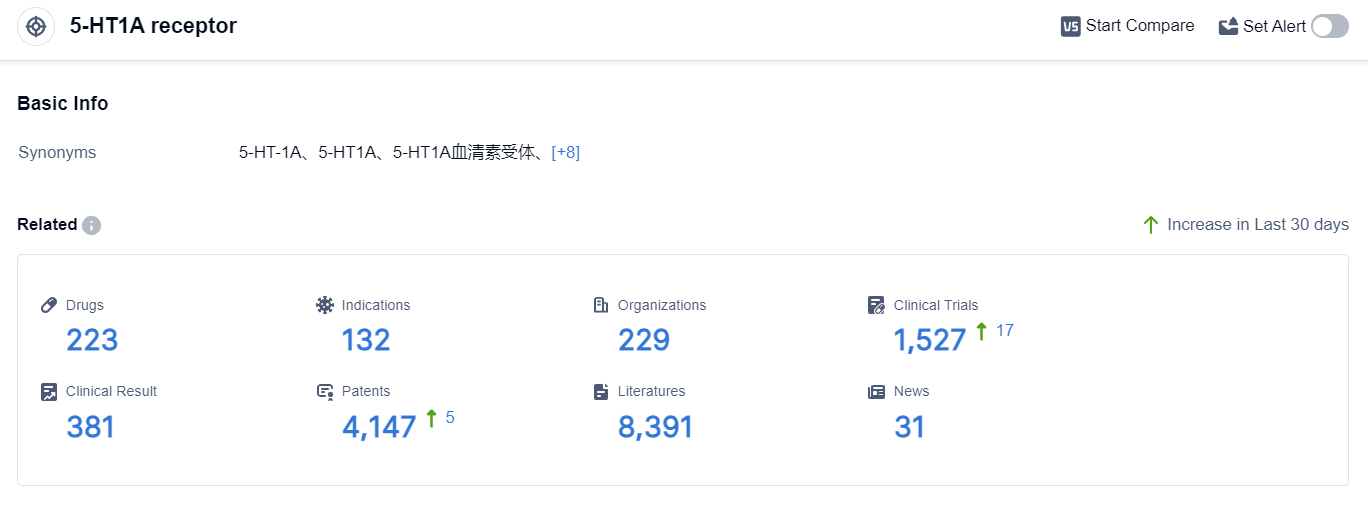
The analysis of the target 5-HT1A receptor reveals that Otsuka Holdings Co., Ltd., AbbVie, Inc., and Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd. are the companies growing fastest in this field. These companies have made significant progress in the R&D of drugs targeting the 5-HT1A receptor.
The most common indications for approved drugs include Depressive Disorder, Major, Schizophrenia, and Depressive Disorder. Small molecule drugs are progressing rapidly, indicating a focus on developing innovative drugs.
The United States, China, and the European Union are the countries/locations developing fastest in this field, with China showing notable progress. Overall, the competitive landscape for the target 5-HT1A receptor is dynamic, with potential for future development and innovation in the pharmaceutical industry.
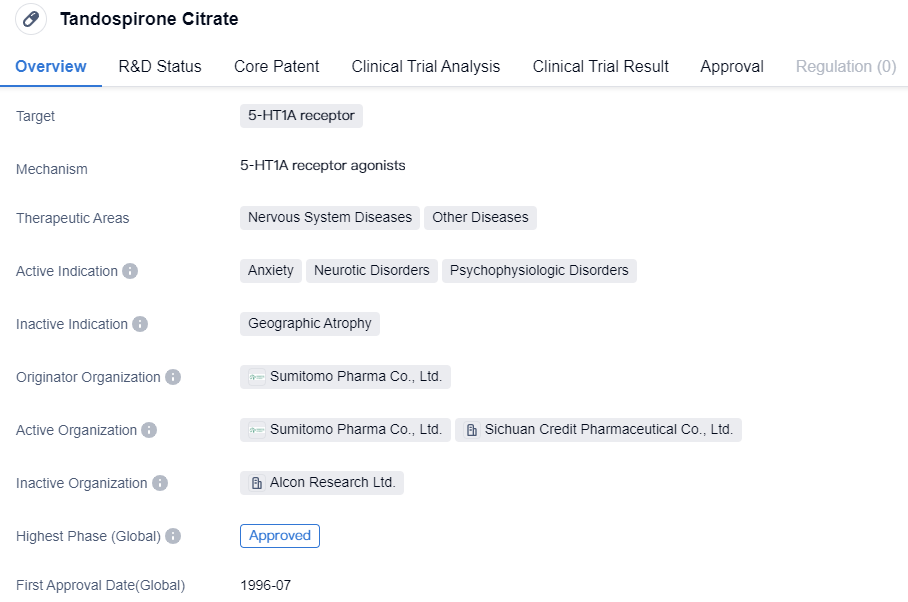
Key Drug: Tandospirone Citrate
Tandospirone Citrate is a small molecule drug that targets the 5-HT1A receptor. It has been approved for the treatment of anxiety, neurotic disorders, and psychophysiologic disorders. Developed by Sumitomo Pharma Co., Ltd., the drug has a long history since its first approval in Japan in 1996. Its approval in multiple countries and therapeutic areas indicates its potential as a reliable and effective treatment option in the field of biomedicine.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Tandospirone Citrate is a highly selective agonist for 5-HT1A receptors, possessing unique pharmacological characteristics. On one hand, Tandospirone Citrate binds with presynaptic membrane 5-HT1A receptors, causing early desensitization of the receptor and allowing the neuron to maintain the normal release of 5-HT, thus accelerating the time to onset of action. On the other hand, it can stimulate postsynaptic membrane 5-HT1A receptors, maintaining normal nerve impulses and producing an anti-anxiety effect. Tandospirone Citrate, due to its unique pharmacological attributes and confirmed clinical data, combined use of Tandospirone Citrate could enhance efficacy and shorten time to onset. In addition to improving anxiety symptoms, it also improves symptoms of depression, somatic symptoms, cognitive functions and sexual performance, among many other advantages. Research also indicates that Tandospirone Citrate does not lead to dependency, making it suitable for long-term use in patients.
The approval of Tandospirone Citrate in multiple countries suggests its efficacy and safety profile. It has undergone rigorous clinical trials and demonstrated positive results in treating anxiety, neurotic disorders, and psychophysiologic disorders. The drug's small molecule nature allows for easy absorption and distribution in the body, enhancing its therapeutic effects.
The therapeutic areas of nervous system diseases and other diseases indicate the potential for Tandospirone Citrate to be used in a wide range of conditions beyond anxiety-related disorders. However, further research and clinical trials may be required to explore its efficacy in these areas.