The latest phase II clinical research by Innovent Biologics on Mazdutide, a GLP-1R/GCGR dual agonist, has been released, showing significant weight loss effects
Recently, Innovent Biologics announced that after reaching the primary endpoint of the phase II clinical trial (ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT04904913) in obese Chinese subjects for the higher dose of 9 mg of the GLP-1R/GCGR dual agonist, Mazdutide, the 48-week treatment phase has been completed. The results showed a reduction in body weight of 18.6% compared to a placebo at 48 weeks for Mazdutide 9mg, and a significant increase in the proportion of subjects with weight reductions of over 15%/20% compared to 24 weeks. Innovent plans to initiate a phase III clinical trial of Mazdutide 9mg in obese Chinese subjects by the end of 2023.
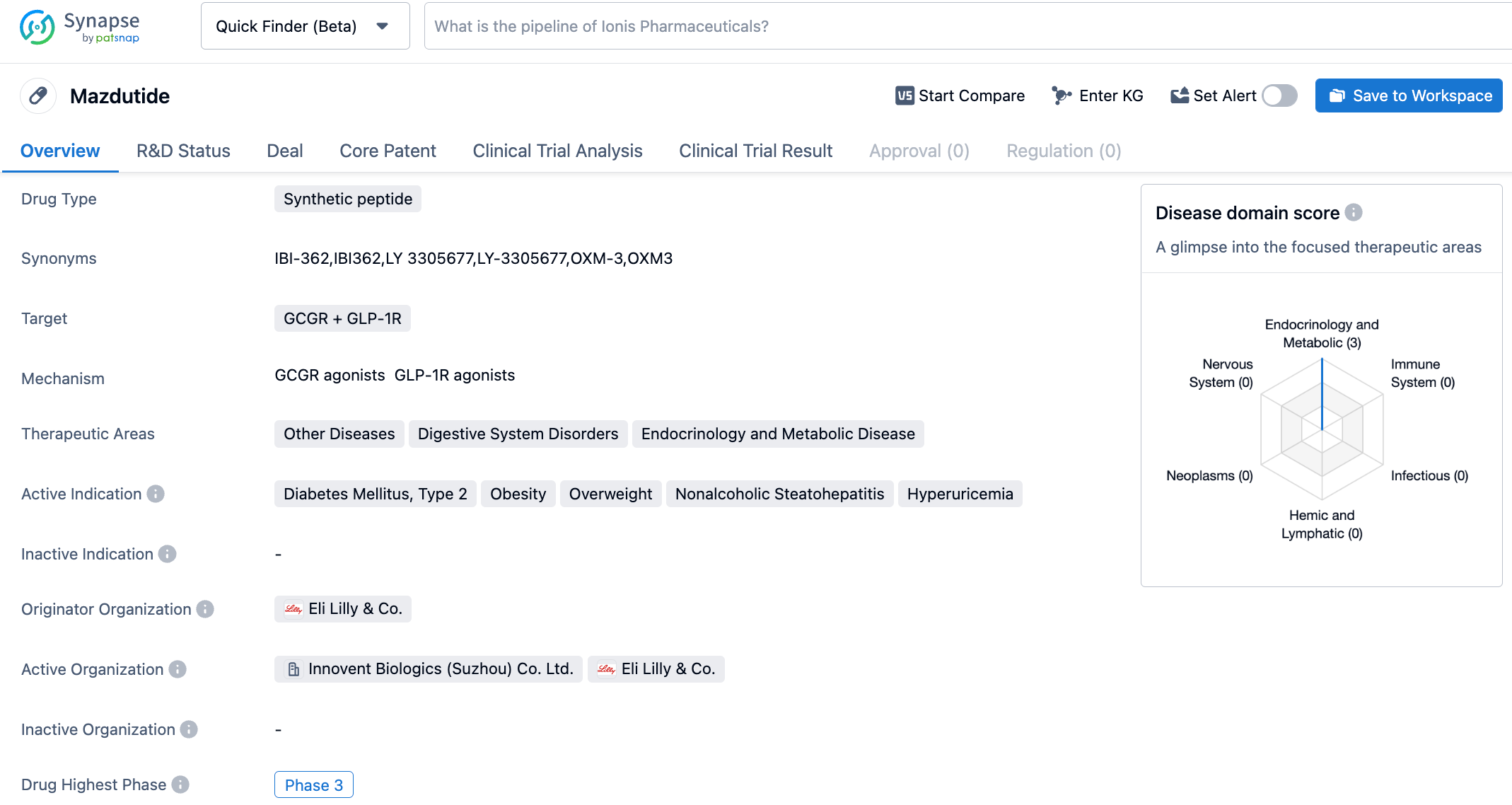
Mazdutide, an innovative compound regulating gastric acid secretion introduced by Innovent in 2019 from Eli Lilly, is a long-acting synthetic peptide similar to mammalian gastric acid-regulatory polypeptides. Mazdutide binds and activates the GLP-1 receptor (GLP-1R) and the glucagon receptor (GCGR). The main function of GLP-1R is to promote the release of insulin, increase the regeneration of beta cells, inhibit the apoptosis of beta cells, and decrease the release of glucagon. In tissues such as the gastrointestinal tract, GLP-1R can inhibit gastric motility and gastric juice secretion, delay gastric emptying, and increase satiety by binding with its agonist. In addition to promoting insulin secretion, reducing blood glucose levels and reducing body weight, Mazdutide, by activating GCGR, can increase energy expenditure and improve hepatic fat metabolism, exhibiting excellent performance against comparator products in clinical trial data. In a hyperuricemic rat model, different doses of Mazdutide and allopurinol, a first-line treatment for hyperuricemia, significantly reduced blood uric acid levels by about 50%, while semaglutide did not have a similar effect. Improvements were also observed in both the Mazdutide and allopurinol groups in blood creatinine and urea nitrogen levels, with a statistically significant difference compared to the hyperuricemic control group. Only a downward trend was observed in the semaglutide group, with a non-significant difference. Furthermore, the Mazdutide group showed some improvement in oxidative stress and renal pathology markers, which merits further study and validation.
This is a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase II clinical trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of Mazdutide 9mg, carried out in Chinese obese subjects with a baseline Body Mass Index (BMI) of 34.3 kg/m2. A total of 80 subjects were included and randomly received either Mazdutide 9mg or a placebo on a 3:1 ratio once a week. The main endpoint of the study was the percentage change in body weight relative to the baseline after 24 weeks of treatment, compared to a placebo. Subsequently, as an extension study, subjects who volunteered to continue the treatment were extended to 48 weeks. After 48 weeks of treatment with Mazdutide 9mg, a strong weight loss effect of 18.6% compared to a placebo was achieved, equivalent to metabolic surgery; this is currently the greatest weight reduction achieved by GLP-1 category drugs in the obese Chinese population compared to a placebo.
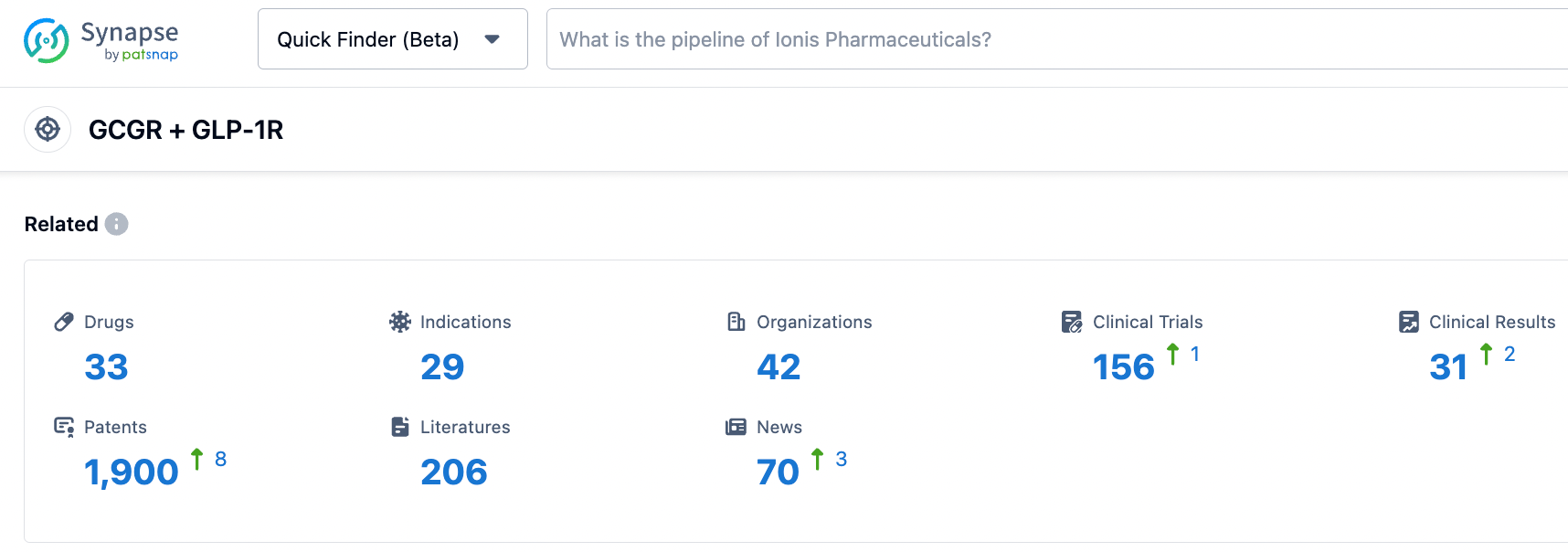
According to information disclosed by the synapse database, as of October 31, 2023, there were 33 drug candidates targeting GIPR + GLP-1R, including 28 indications, 42 research institutions involved, 156 related clinical trials, and up to 1900 patents. Both single-target and multi-target GLP-1R drugs have huge market potential in the treatment of endocrine diseases such as lowering blood sugar levels, losing weight, and reducing blood uric acid. We look forward to more new drugs emerging in this field.