The novel Aβ-targeting drug Donanemab by Eli Lilly is applying for market authorization in China to treat Alzheimer's disease
Recently, the official website of the CDE shows that the marketing authorization application for Eli Lilly's new Alzheimer's medication, donanemab, has been accepted. Earlier, the NMPA had granted Donanemab breakthrough therapy designation for the treatment of early symptomatic Alzheimer's disease, including mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer's and mild Alzheimer's disease.
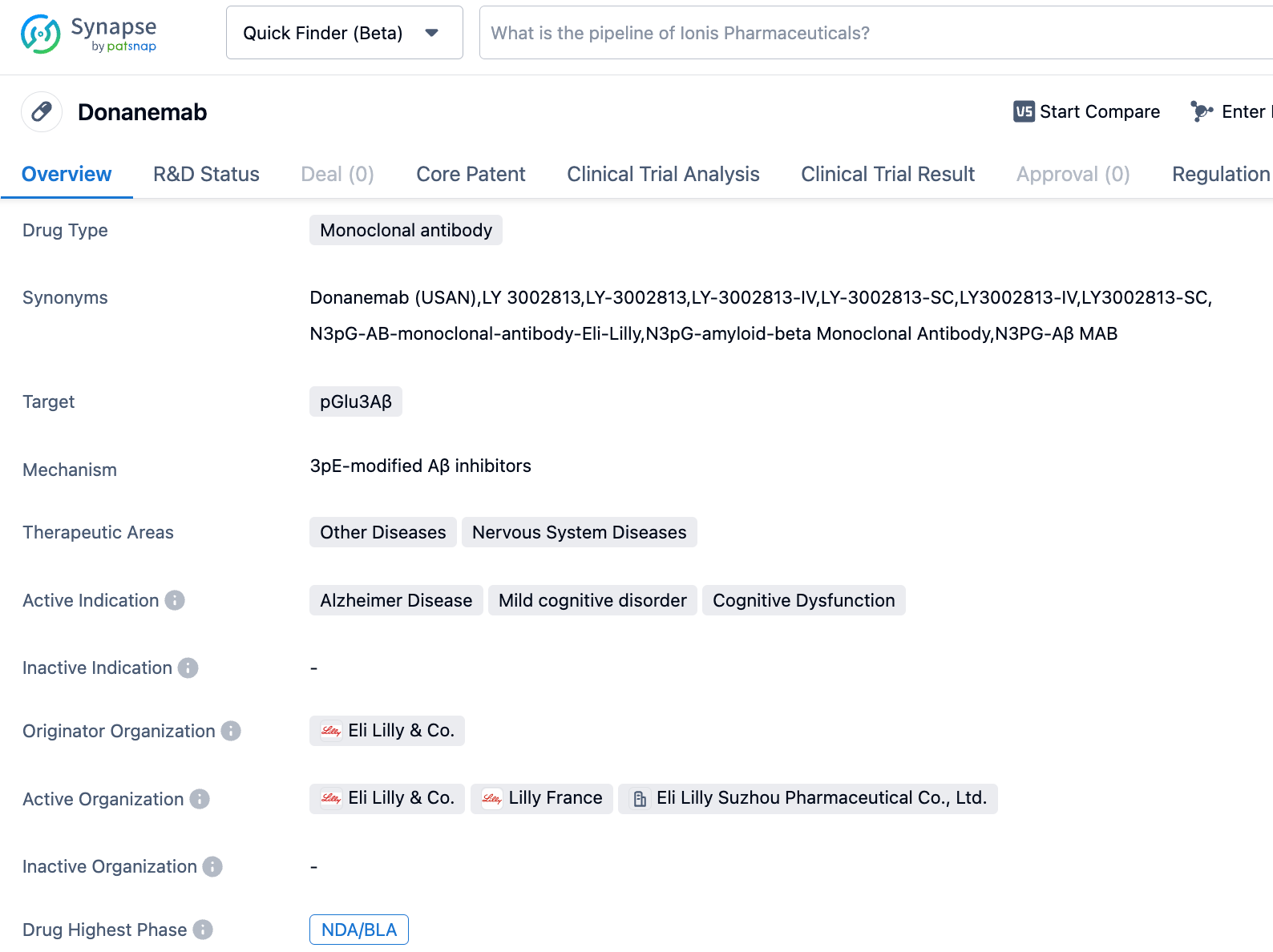
Donanemab (also known as monoclonal antibody) is a drug under research by Eli Lilly. This drug binds to the N3pG subtype of β-amyloid protein (3pE-modified Aβ), which aids in the elimination of β-amyloid plaques in the brains of Alzheimer's patients, thus improving their symptoms and signs and slowing the progression of the disease. In May this year, Eli Lilly announced that the phase III TRAILBLAZER-ALZ 2 study of Donanemab in treating early symptomatic Alzheimer's disease (AD) patients reached its primary endpoint. The results showed that Donanemab significantly slowed cognitive decline in early symptomatic AD patients, with nearly half of the subjects (47%) not experiencing disease progression (defined as no decline in the clinical dementia rating) within a year, compared to 29% for the placebo group. Eli Lilly submitted a marketing authorization application for Donanemab to the FDA in the second quarter, seeking accelerated approval.
TRAILBLAZER-ALZ 2 is a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled Phase III clinical trial. The primary population (n=1182) consists of patients with an average tau protein level and evident AD clinical symptoms. The primary endpoint is the change in the score of the AD Composite Scale (iADRS) from baseline to 18 months, which assesses the patient's cognitive ability and daily living skills. Key secondary endpoints include the baseline and 18-month Clinical Dementia Rating Scale (CDR-SB), which assesses the patient's cognitive ability, the AD Collaborative Study Daily Living Skills Scale (ADCS iADL), and the AD cognition scale (ADAS-Cog13). The results showed that, compared with the placebo group, the rate of decline in the iADRS scores of patients treated with Donanemab slowed by 35% (p<0.0001); at 18 months, the CDR-SB scores of the Donanemab group decreased by 36% slower than those of the placebo group (p<0.0001); the ADCS iADL scores showed that at 18 months, the rate of disease progression in the Donanemab group was delayed by 40% (p<0.0001). Furthermore, Donanemab reduced the risk of the disease progressing to the next stage by 39% (HR=0.61; p<0.001).
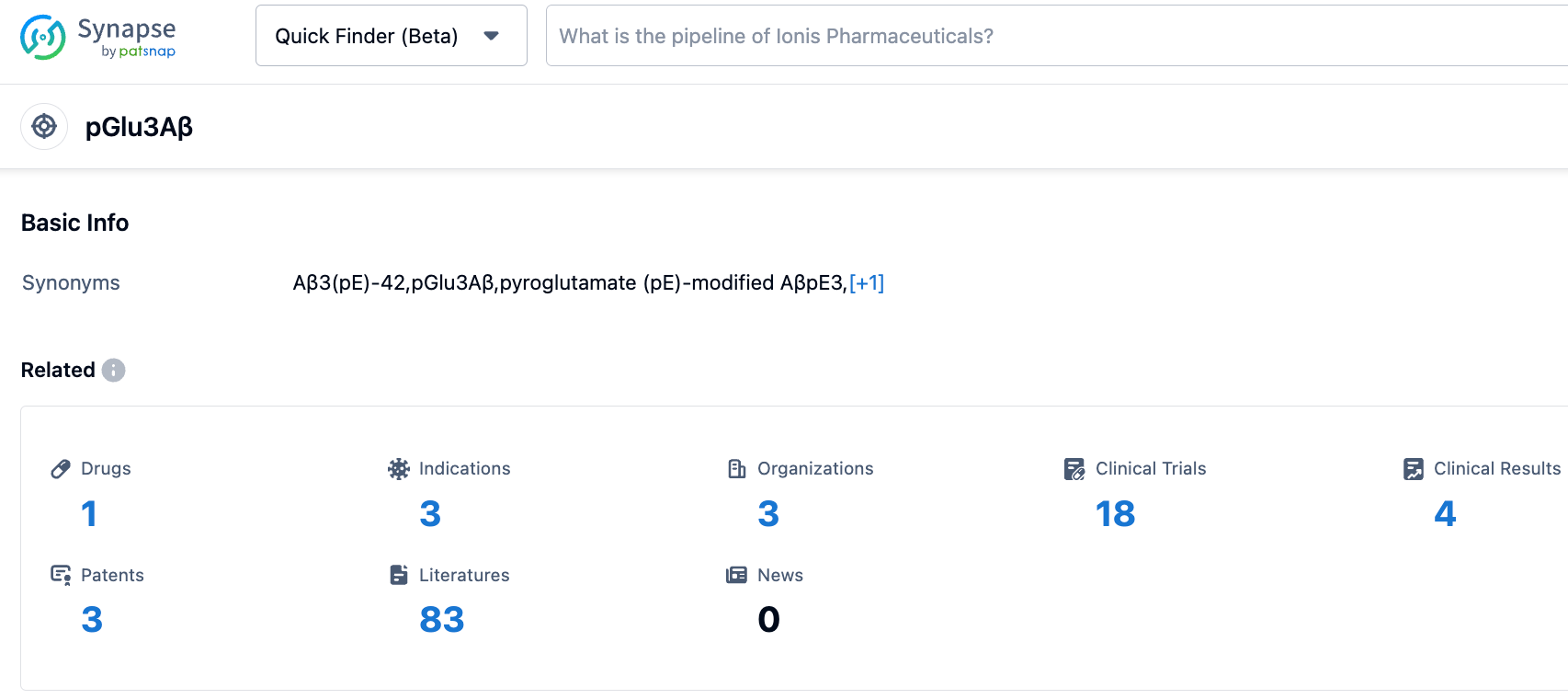
According to information disclosed by the synapse database, as of November 1, 2023, there is one 3pE-modified Aβ targeted drug under investigation, with three expected indications, researched by three organizations, involved in 18 clinical trials, and covered by three patents. New GLP-1 class drugs and Donanemab are the core pillars supporting Eli Lilly's market value of $500 billion. Donanemab has significantly slowed cognitive and functional declines in early symptomatic Alzheimer's disease patients who are β-amyloid positive and reduced the risk of disease progression. Once approved, this drug is expected to be a blockbuster.