What are CD38 inhibitors and how do you quickly get the latest development progress?
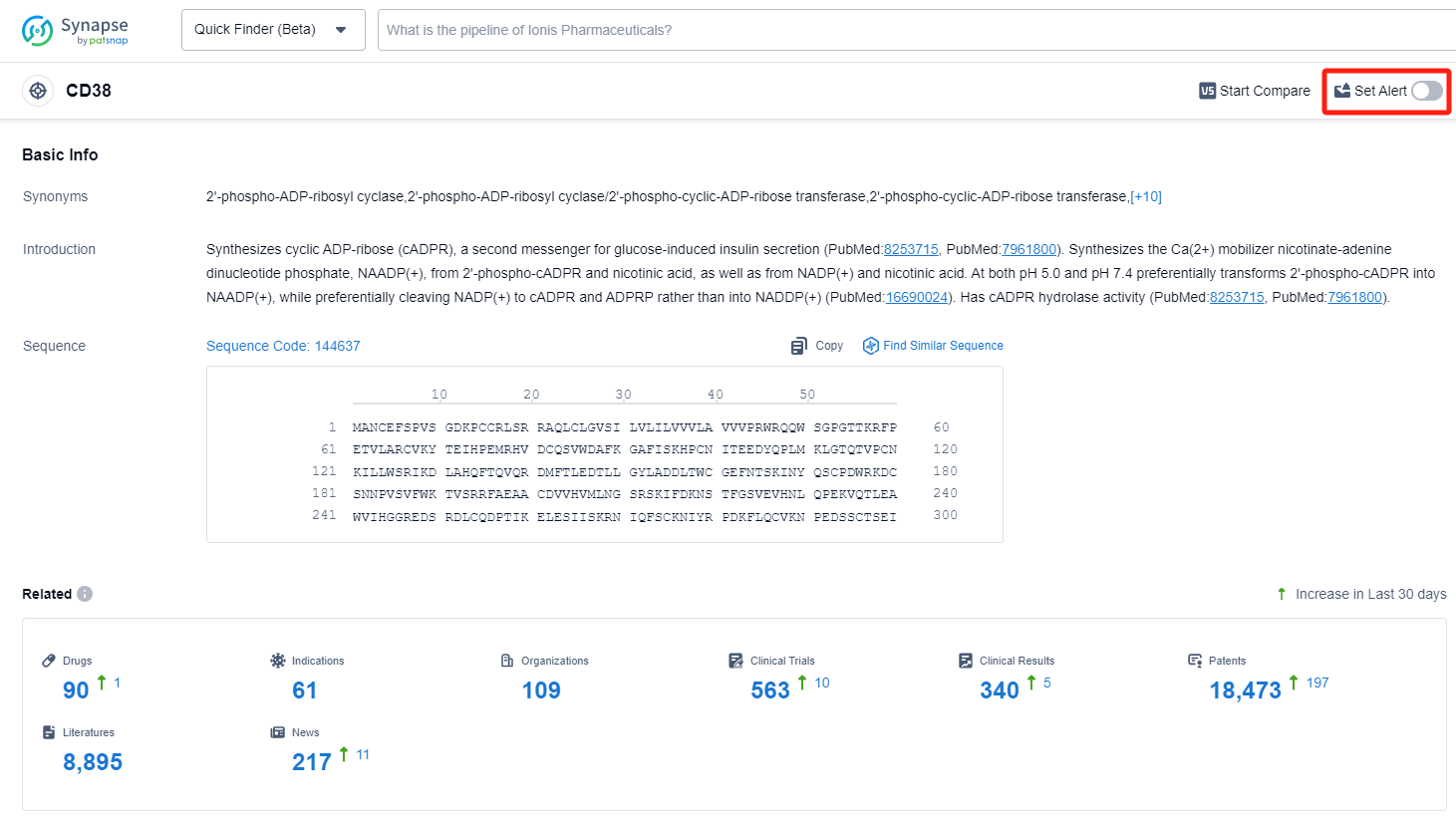
CD38 is a multifunctional enzyme found on the surface of various cells in the human body. It plays a crucial role in regulating calcium signaling and cell adhesion, as well as in the metabolism of NAD+ and cADPR. CD38 is particularly important in immune responses, as it is involved in the activation and differentiation of immune cells, such as T and B lymphocytes. Additionally, CD38 has been identified as a therapeutic target in certain diseases, including multiple myeloma and autoimmune disorders. Understanding the role of CD38 provides valuable insights into its potential as a target for drug development and treatment strategies.
The current competitive landscape of target CD38 is characterized by the presence of multiple companies, including Johnson & Johnson, Sanofi, Halozyme Therapeutics, Inc., I-MAB Biopharma Co., Ltd., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and others, actively involved in the research and development of drugs targeting CD38. Johnson & Johnson, Sanofi, and Halozyme Therapeutics, Inc. have drugs in the Approved phase, indicating successful development and regulatory approval. The R&D progress of these companies varies, with drugs in different phases of development.
Overall, the current competitive landscape of target CD38 is dynamic, with multiple companies and countries actively involved in the research and development of drugs targeting CD38. The future development of target CD38 holds promise, with ongoing R&D efforts and the potential for new indications and drug types.
How do they work?
A CD38 inhibitor is a type of drug that specifically targets and inhibits the activity of the CD38 protein. CD38 is a cell surface receptor and enzyme that is involved in various cellular processes, including immune regulation and cell signaling. In the context of biomedicine, CD38 inhibitors are primarily used in the treatment of certain types of cancer, such as multiple myeloma.
By inhibiting CD38, these drugs can interfere with the growth and survival of cancer cells. CD38 inhibitors work by blocking the enzymatic activity of CD38 or by preventing its interaction with other molecules. This can help to reduce the proliferation of cancer cells and enhance the effectiveness of other cancer treatments.
In addition to their anti-cancer properties, CD38 inhibitors also have potential therapeutic applications in other conditions, such as autoimmune diseases and certain inflammatory disorders. These drugs are typically administered through intravenous infusion or oral administration, and their usage is closely monitored by healthcare professionals to ensure optimal dosage and minimize potential side effect.
List of CD38 Inhibitors
The currently marketed CD38 inhibitors include:
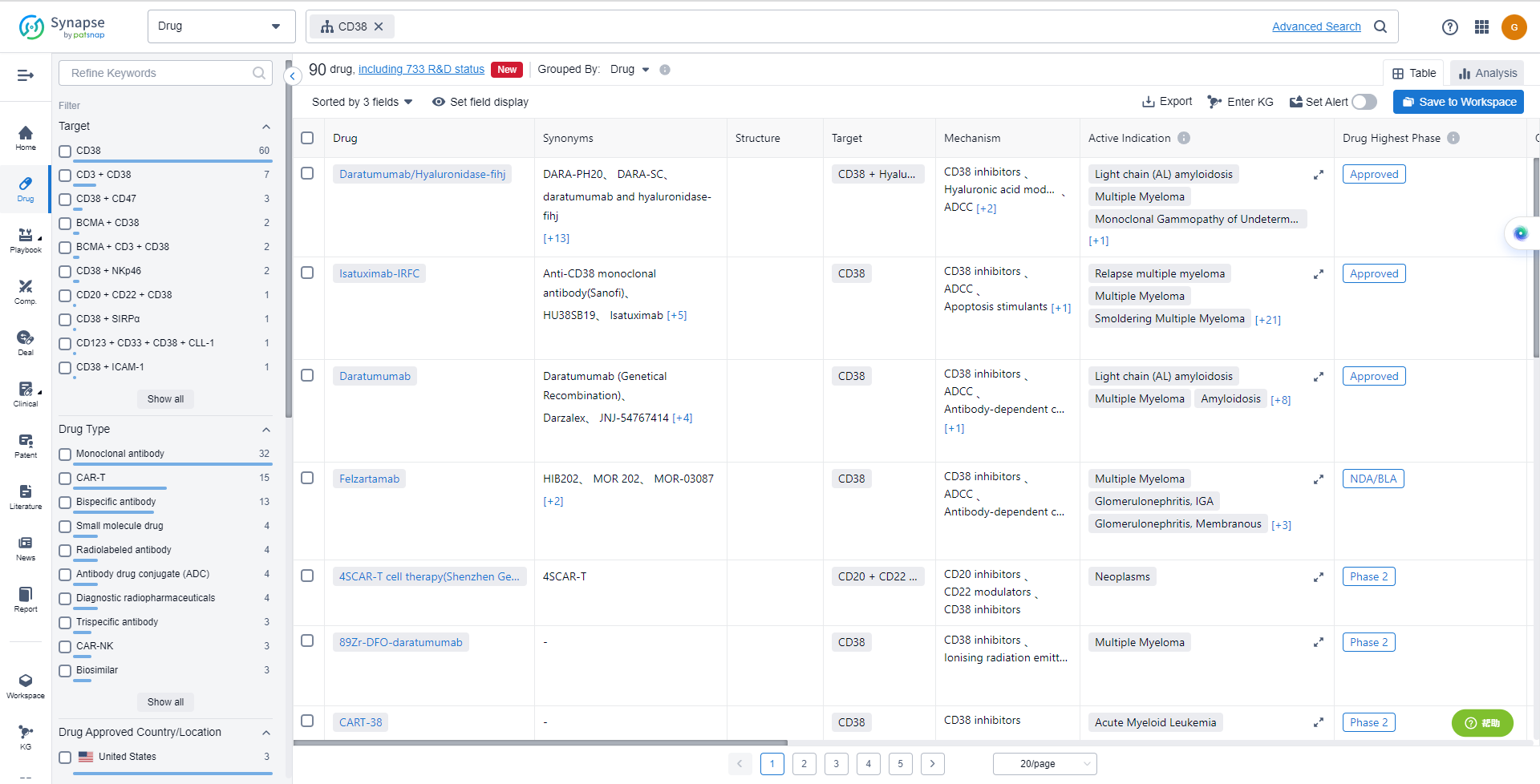
- Daratumumab/Hyaluronidase-fihj
- Isatuximab-IRFC
- Daratumumab
- Felzartamab
- 89Zr-DFO-daratumumab
- CART-38
- KP-1237
- Mezagitamab
- Modakafusp Alfa
- GEN-3014
For more information, please click on the image below.
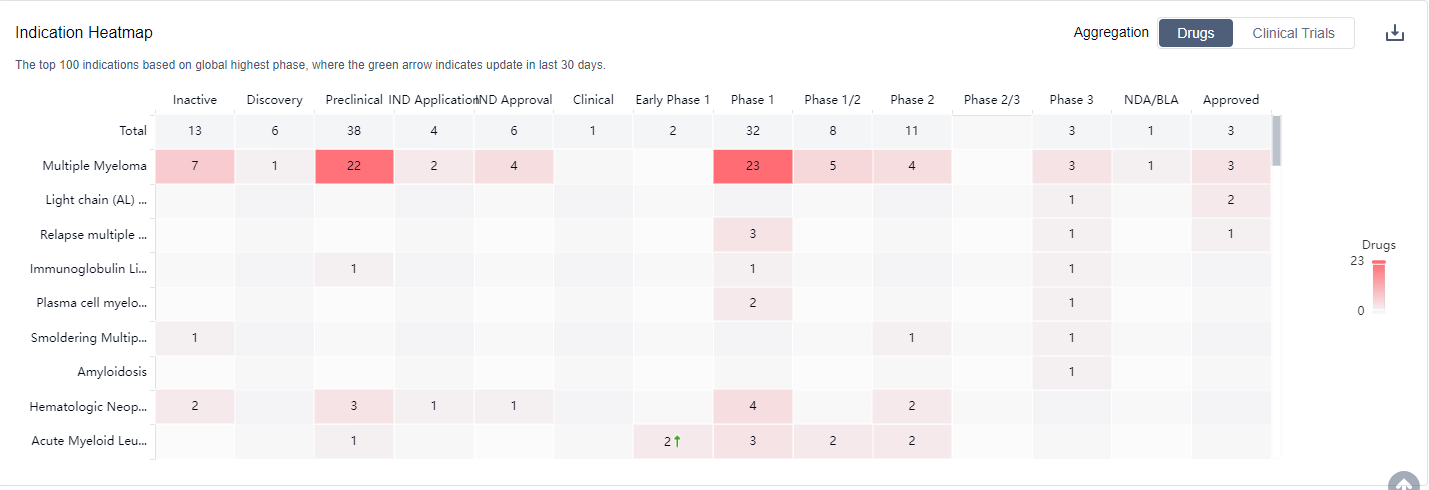
What are CD38 inhibitors used for?
CD38 inhibitors are primarily used in the treatment of certain types of cancer, such as multiple myeloma. For more information, please click on the image below to log in and search.
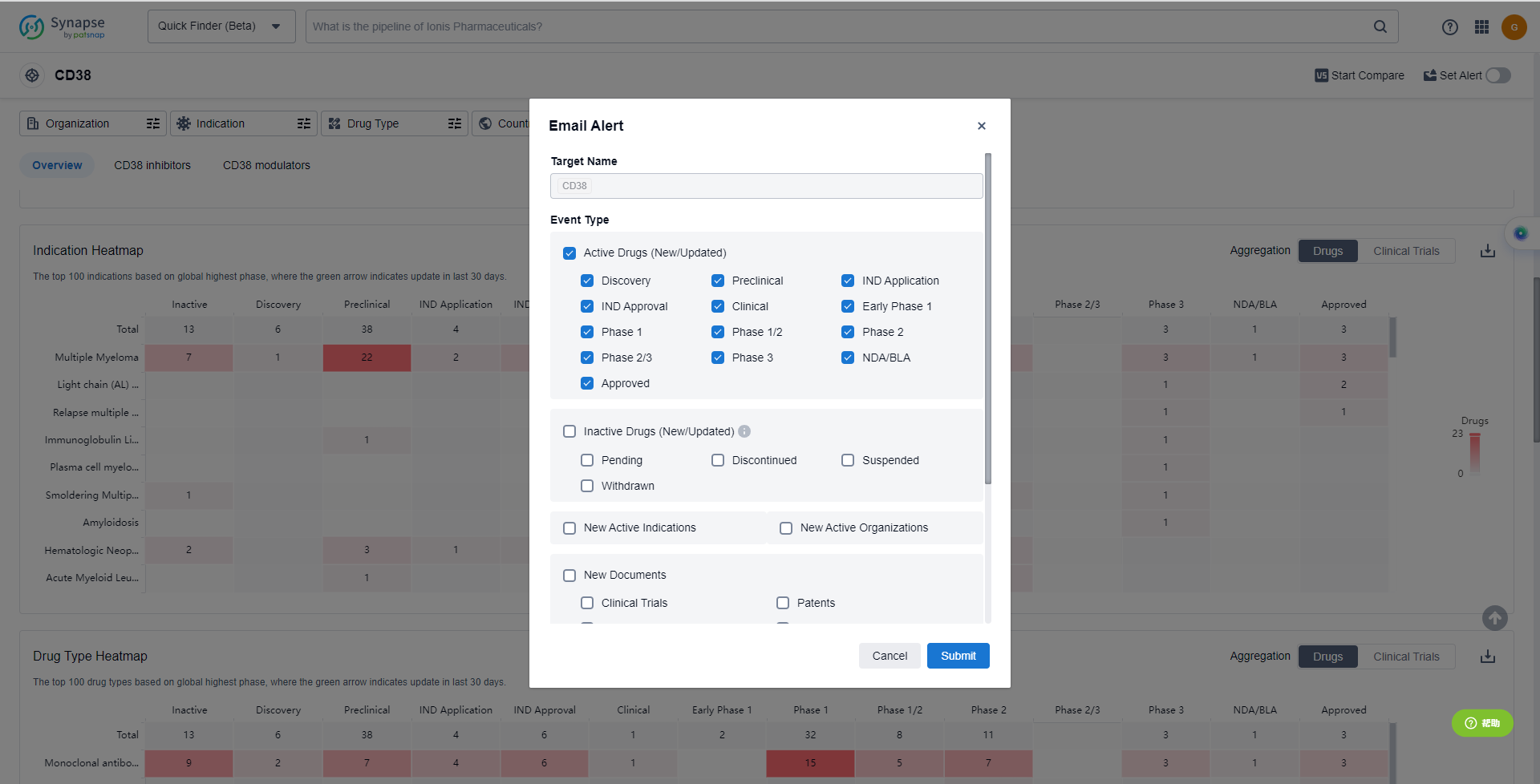
How to obtain the latest development progress of CD38 inhibitors?
In the Synapse database, you can keep abreast of the latest research and development advances of CD38 inhibitors anywhere and anytime, daily or weekly, through the "Set Alert" function. Click on the image below to embark on a brand new journey of drug discovery!