What are Nrf2 inhibitors and how do you quickly get the latest development progress?
Nrf2, or nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2, is a transcription factor that plays a crucial role in the human body's defense against oxidative stress and inflammation. It regulates the expression of various antioxidant and detoxification genes, promoting cellular protection and maintaining redox homeostasis. Nrf2 activation is essential for combating harmful free radicals and reactive oxygen species, which can lead to various diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and cardiovascular conditions. Understanding and harnessing the potential of Nrf2 signaling pathways have become a significant focus in pharmaceutical research, aiming to develop novel therapeutic interventions for oxidative stress-related diseases.
Due to the biological characteristics of tumors, multidrug resistance (MDR) is a major cause of chemotherapy failure. Studies have shown that high expression of Nrf2 is found in different types of cancer cells (bladder cancer, lung cancer, pancreatic cancer, liver cancer, and head and neck cancer). Nrf2 can activate the transcription of more than 500 genes in the human genome, most of which have cell protective functions, enhancing the detoxification and excretion of harmful substances and toxic metals, thereby leading to tumor resistance to chemotherapy drugs. Therefore, the development of Nrf2 inhibitors is considered an important strategy to overcome chemotherapy drug resistance. The use of Nrf2 inhibitors as sensitizers in combination with anticancer drugs will reverse tumor resistance and significantly improve the efficacy of chemotherapy drugs.
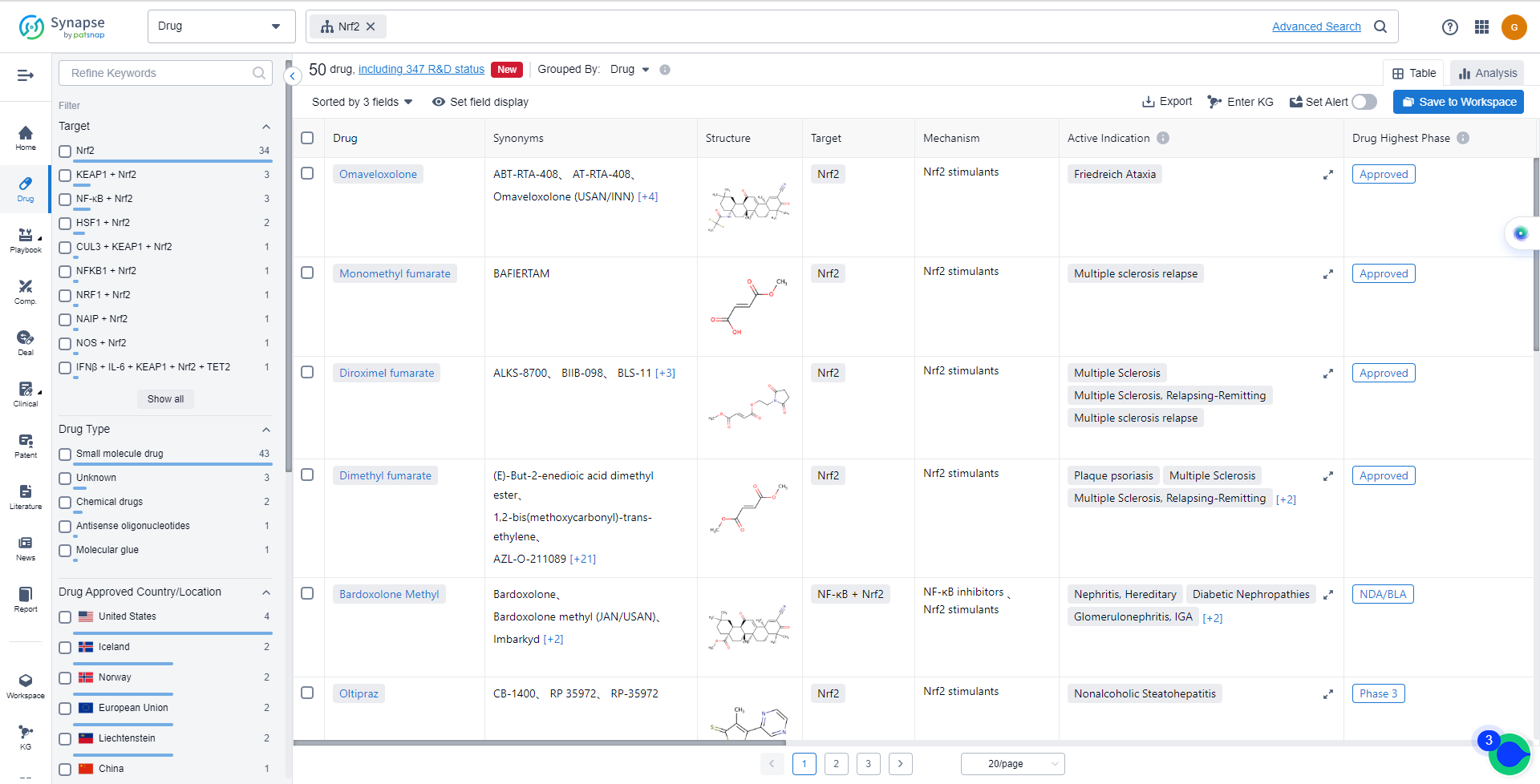
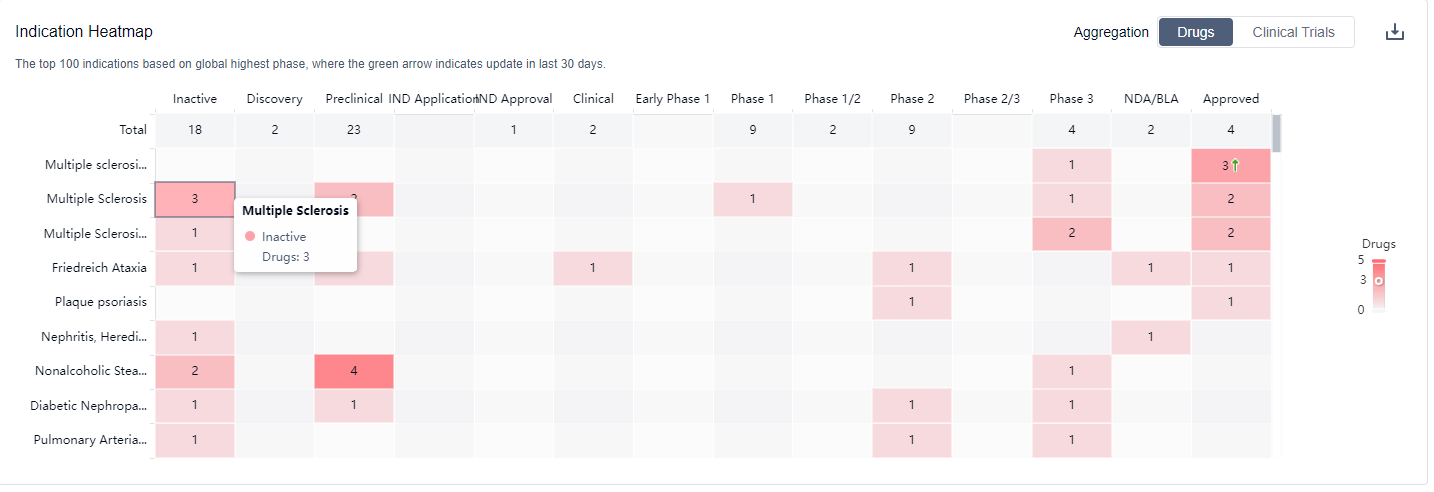
The analysis of the target Nrf2 in the pharmaceutical industry reveals a competitive landscape with companies like Biogen, Inc., Reata Pharmaceuticals, Inc., and Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. leading the way in R&D progress. Multiple drugs targeting Nrf2 have been approved for indications such as Multiple Sclerosis and Friedreich Ataxia. Small molecule drugs are progressing rapidly, with biosimilars indicating intense competition. The United States is at the forefront of development, followed by the European Union, China, and other countries. The future development of target Nrf2 holds promise for the treatment of various indications and requires continued research and investment in innovative drug development.
How do they work?
Nrf2 inhibitors are a class of compounds or drugs that specifically target and inhibit the activity of the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2). Nrf2 is a transcription factor that plays a crucial role in regulating the expression of genes involved in antioxidant response and cellular defense against oxidative stress.
From a biomedical perspective, Nrf2 inhibitors are of interest because they have the potential to modulate the Nrf2 pathway and alter the cellular response to oxidative stress. By inhibiting Nrf2, these compounds can prevent the activation of antioxidant genes and disrupt the cellular defense mechanisms against oxidative damage.
Nrf2 inhibitors have been studied in various biomedical contexts, including cancer research. In some cancer cells, Nrf2 is overexpressed, leading to increased antioxidant capacity and resistance to chemotherapy or radiation therapy. By inhibiting Nrf2, researchers aim to sensitize cancer cells to treatment and enhance the effectiveness of anticancer therapies.
Moreover, Nrf2 inhibitors have also been investigated as potential therapeutic agents for other conditions associated with oxidative stress, such as neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and inflammatory disorders. By modulating the Nrf2 pathway, these inhibitors may offer a way to restore redox balance and mitigate the detrimental effects of oxidative stress in these conditions.
It is important to note that the development and use of Nrf2 inhibitors require careful consideration of their potential side effects and impact on normal cellular functions. While inhibiting Nrf2 may be beneficial in certain disease contexts, it may also disrupt the physiological antioxidant defense mechanisms and have unintended consequences. Therefore, further research and clinical trials are necessary to fully understand the therapeutic potential and safety profile of Nrf2 inhibitors.
List of Nrf2 Inhibitors
The currently marketed Nrf2 inhibitors include:
- Omaveloxolone
- Monomethyl fumarate
- Diroximel fumarate
- Dimethyl fumarate
- Bardoxolone Methyl
- Oltipraz
- 10-Nitrooleic acid
- ALZ-001
- ALZ-002
- APPA
For more information, please click on the image below.
What are Nrf2 inhibitors used for?
Nrf2 inhibitors have been studied in various biomedical contexts, including cancer research. For more information, please click on the image below to log in and search.
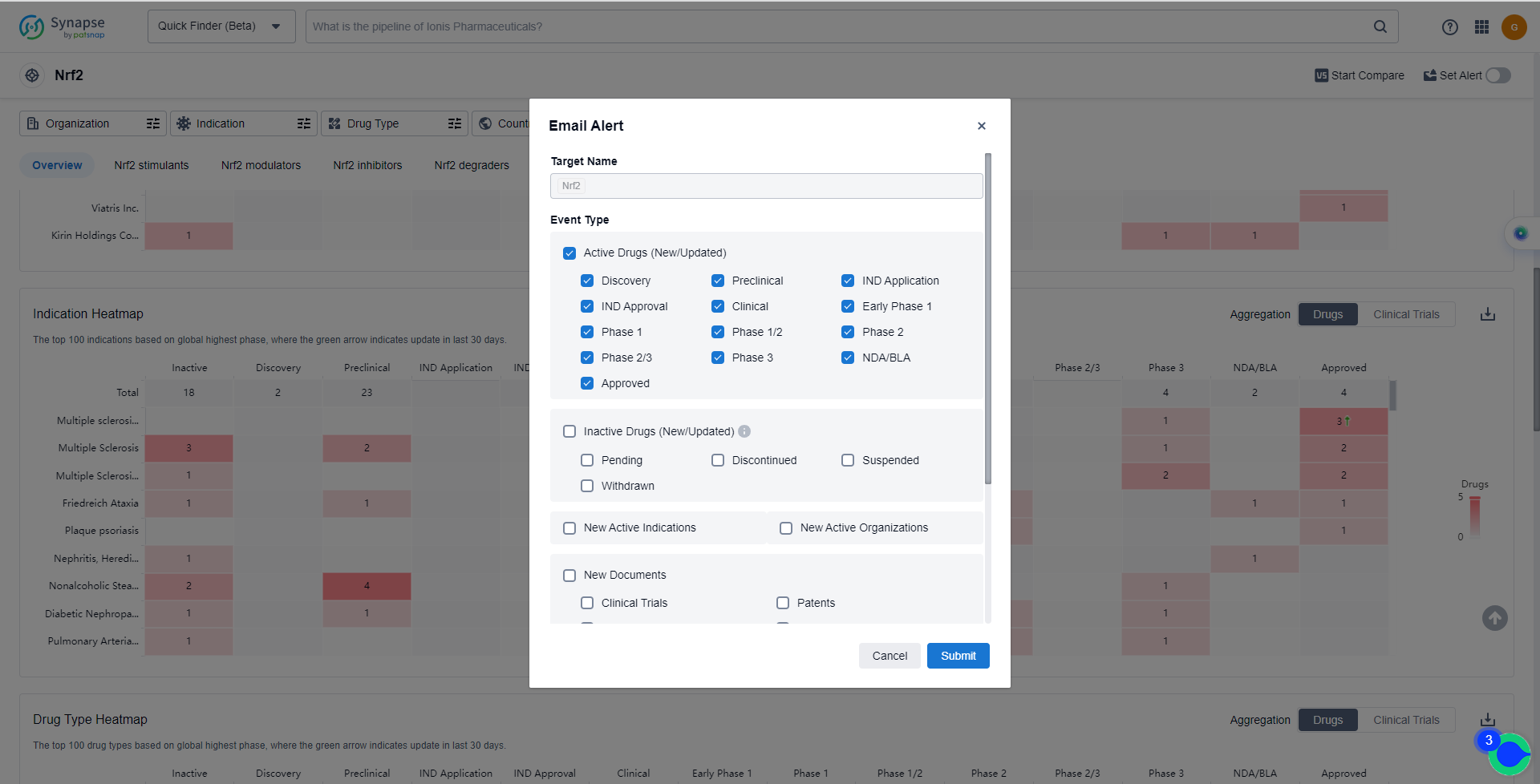
How to obtain the latest development progress of Nrf2 inhibitors?
In the Synapse database, you can keep abreast of the latest research and development advances of Nrf2 inhibitors anywhere and anytime, daily or weekly, through the "Set Alert" function. Click on the image below to embark on a brand new journey of drug discovery!