Request Demo
Last update 08 May 2025
Osteoradionecrosis
Last update 08 May 2025
Basic Info
Synonyms Osteonecrosis caused by ionising radiation, Osteonecrosis caused by ionizing radiation, Osteoradionecroses + [15] |
Introduction Necrosis of bone following radiation injury. |
Related
1
Drugs associated with OsteoradionecrosisTarget- |
Mechanism Cell differentiation modulators [+1] |
Active Org. |
Originator Org. |
Active Indication |
Inactive Indication |
Drug Highest PhasePhase 2 |
First Approval Ctry. / Loc.- |
First Approval Date20 Jan 1800 |
37
Clinical Trials associated with OsteoradionecrosisRBR-6tnqpjm
Prevention of Osteoradionecrosis of the jaw with the drug combination of Pentoxifylline and Tocopherol: randomized clinical trial - PENTO Pentoxifylline and tocopherol
Start Date15 Jun 2024 |
Sponsor / Collaborator |
ChiCTR2400085145
Effect of nutritional status on rapid recovery of patients with skull base osteonecrosis after radiotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Start Date01 Jun 2024 |
Sponsor / Collaborator |
NCT06055257
Combination Therapy: Hyperbaric Oxygen and PENTOCLO for Treatment of Osteoradionecrosis of the Mandible, a Pilot Randomized Control Trial
Radiation is commonly used to treat cancer in the head and neck, however, this can lead to a serious complication called osteoradionecrosis (ORN), where there is necrotic (dead) open bone inside or outside of the mouth. This complication is difficult to treat, involves large healthcare costs, and can have devastating effects on quality of life.
Two common adjuncts used in treatment of ORN are hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT), which may requires up to 60 treatments at a specialized clinic where patients are treated with high concentrations of oxygen using special chambers, and a less complex option called PENTOCLO which involves treating patients with several antibiotics followed by a combination of other oral medications taken for at least 1 year.
This pilot study will be guide the design of a definitive trial to examine if the combination of HBOT and a modified PENTOCLO protocol together is better than the current standard treatment of HBOT alone. Outcomes will include pain, side effects and the need for surgery in patients with ORN. Specifically, the results of this small, pilot study will help to inform the design of a future larger study.
Two common adjuncts used in treatment of ORN are hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT), which may requires up to 60 treatments at a specialized clinic where patients are treated with high concentrations of oxygen using special chambers, and a less complex option called PENTOCLO which involves treating patients with several antibiotics followed by a combination of other oral medications taken for at least 1 year.
This pilot study will be guide the design of a definitive trial to examine if the combination of HBOT and a modified PENTOCLO protocol together is better than the current standard treatment of HBOT alone. Outcomes will include pain, side effects and the need for surgery in patients with ORN. Specifically, the results of this small, pilot study will help to inform the design of a future larger study.
Start Date01 May 2024 |
Sponsor / Collaborator |
100 Clinical Results associated with Osteoradionecrosis
Login to view more data
100 Translational Medicine associated with Osteoradionecrosis
Login to view more data
0 Patents (Medical) associated with Osteoradionecrosis
Login to view more data
2,532
Literatures (Medical) associated with Osteoradionecrosis01 Jun 2025·International Dental Journal
Establishment of an Osteoradionecrosis Model and its Mechanism Via Single Ionizing Radiation Exposure
Article
Author: Wang, Yuetong ; Wang, Xian ; Liu, Zhiqing ; Li, Yuetao ; Wang, Daiyou ; Mo, Dongqin ; Lu, Haoyu
01 Jun 2025·Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology and Oral Radiology
Reply to Letter to the Editor regarding “Osseointegrated dental implants that will undergo radiotherapy. Does risk of osteoradionecrosis exist? A scoping review.”
Letter
Author: Somoza-Martin, José Manuel ; García-Carnicero, Tamara ; García-García, Abel ; Prado-Pena, Irene Beatriz ; Blanco-Carrión, Andrés ; Lorenzo-Pouso, Alejandro I ; Gándara-Vila, Pilar ; Pérez-Sayáns, Mario ; Sanmartín-Barragáns, Valeria
01 Jun 2025·Radiotherapy and Oncology
Externally validated digital decision support tool for time-to-osteoradionecrosis risk-stratification using right-censored multi-institutional observational cohorts
Article
Author: Garden, Adam S ; Canahuate, Guadalupe ; Watson, Erin ; Phan, Jack ; Kaffey, Zaphanlene ; Wentzel, Andrew ; Urbano, Teresa Guerrero ; van Dijk, Lisanne V ; Mohamed, Abdallah S R ; Zhang, Xinhua ; Aponte-Wesson, Ruth ; Wahid, Kareem A ; Rosenthal, David ; Otun, Adegbenga O ; Spier, Kyle B ; Lai, Stephen Y ; Lee, Anna ; Morrison, William H ; Hutcheson, Katherine A ; Brock, Kristy K ; He, Renjie ; Naser, Mohamed A ; Chen, Melissa M ; Schaefer, Andrew J ; Marai, G Elisabeta ; Frank, Steven J ; Patel, Vinod ; Chambers, Mark ; Fuller, Clifton D ; Rigert, Jillian ; Spiotto, Michael T ; Hope, Andrew ; Kamel, Serageldin ; Hosseinian, Seyedmohammadhossein ; Moreno, Amy C ; Abdelaal, Moamen ; West, Natalie A ; Humbert-Vidan, Laia ; Sandulache, Vlad C
2
News (Medical) associated with Osteoradionecrosis18 Apr 2023
LITT allows for the prompt cessation of steroids and alleviates symptom burden in brain metastasis patients
with radiation necrosis as supported by evidence from 90 patients treated with NeuroBlate laser ablation
MINNETONKA, Minn. , April 18, 2023 /PRNewswire/ -- Monteris Medical announced today that a new publication on laser interstitial thermal therapy (LITT) using the NeuroBlate® System to treat patients with radiation necrosis (RN) has been published in the journal, Neuro-Oncology Advances. The largest prospectively-gathered dataset, collected through the company's LAANTERN (Laser Ablation of Abnormal Neurological Tissue Using Robotic NeuroBlate System) multi-center study and comprised of 90 patients with biopsy-proven RN, showed that LITT with NeuroBlate is a safe and highly effective minimally invasive option for the treatment of RN. The evidence also demonstrated that following the NeuroBlate procedure, patients tapered corticosteroid use rapidly, showed excellent symptom control and continued systemic cancer treatments, allowing for maximal survival benefit.
The evidence gathered from this large cohort of pure RN continues to support the utilization of NeuroBlate LITT for the treatment of RN, an inflammatory process that can occur following stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS).
These data showed that patients rapidly discontinued steroid use post-LITT (median time of 13 days), an important benefit, given steroid use may worsen survival rates, particularly for those on immunotherapy. Patients in the study who were undergoing chemotherapy and/or immunotherapy experienced little to no interruption in their treatments post-LITT. This is in contrast to craniotomy, which generally requires that patients pause systemic treatments to facilitate wound healing and recovery time.
"LITT compares favorably to historical efficacy of craniotomy and resection yet has a degree of versatility when faced with deeper lesions or with those close to eloquent brain," said Dr. Michael D. Chan, lead author and professor of radiation oncology at Atrium Health Wake Forest Baptist in Winston-Salem, NC. "Compared to historical expectations with craniotomy, LITT has demonstrated favorable hospitalization times and favorable risk profile. It seems that LITT has truly carved itself a role in the management of post-SRS radiation necrosis alongside other tools including steroids, bevacizumab and open resection. I look forward to results of the ongoing prospective studies meant to validate the present findings."
The use of stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) has significantly expanded in recent years as brain metastases have become more common. This is due in part to advances in systemic therapy that enable the long-term control of extracranial disease. The growing use of radiotherapy has also resulted in the proliferation of post-SRS imaging changes, which may represent either RN or tumor growth, a diagnostic question best confirmed via biopsy. Laser interstitial thermal therapy with biopsy offers patients an immediate diagnostic confirmation of the disease process and is a highly effective treatment for RN with respect to local control and symptom management.
"We are grateful to our investigators for their continued work to generate clinical proof that supports NeuroBlate as a surgical tool for early intervention for those patients with progressive brain metastases," said Martin J. Emerson, president and chief executive officer of Monteris. "As the leader in the LITT space, Monteris remains uniquely committed to delivering high quality evidence that physicians need when making critical patient care decisions. With more than 1,100 patients enrolled, our prospective LAANTERN study continues to demonstrate a distinct position for NeuroBlate as an evidenced-based, mainstay technology for brain tumors, radiation necrosis, and drug-resistant epilepsy."
About LAANTERN
LAANTERN (Laser Ablation of Abnormal Neurological Tissue Using Robotic NeuroBlate System) is a post-market study designed to evaluate the performance and utilization of the NeuroBlate® System in the standard of care, "real-world" setting. This is the first prospective multicenter laser ablation study. All sites operate under an IRB-approved protocol and undergo rigorous data management and monitoring practices to ensure data quality and consistency. The registry will follow up to 3,000 patients for five years evaluating safety, quality of life, health economics and procedural outcomes, including survival and seizure freedom.
About Monteris and the NeuroBlate System
Monteris Medical is a privately held company that develops and markets innovative MR-guided ablation systems to perform minimally invasive, robotically controlled brain surgery, commonly referred to as laser ablation, LITT (Laser Interstitial Thermal Therapy) or SLA (Stereotactic Laser Ablation). The Monteris NeuroBlate System is the only minimally invasive system that enables a robotic interface for the precise and safe delivery of laser energy. The Monteris Medical NeuroBlate System is a neurosurgical tool and is intended for ablating intracranial soft tissue, including brain structures such as brain tumors, radiation necrosis, and epileptic foci (as identified by non-invasive and invasive neurodiagnostic testing, including imaging). For more information, visit monteris.com.
Radiation TherapyImmunotherapy
10 Oct 2022
Monteris Medical recently raised $35 million as it continues to advance its minimally invasive robotic brain surgery system.
The Minnetonka, Minnesota–based company reported a $13.5 million raise in an SEC Form D filed on Sept. 15. But in an article published yesterday in the Star Tribune of Minneapolis, CFO Jim Erickson said the equity financing range was actually $35 million.
“The first half of this year was more challenging than the year before. It took longer than we would have hoped,” Erickson told the Star Tribune. He later added that the life sciences space is proving to be a durable investment space, even amid the present economic hurdles.
Monteris Medical is among a host of companies big and small that are seeking to innovate in a surgical robotics space that has long been dominated by Intuitive. [Intuitive CEO Gary Guthart will deliver a keynote at DeviceTalks West, Oct. 19–20, 2022, in Santa Clara, California. Register here.]
Monteris designed its NeuroBlate minimally invasive surgical robot system for controlled laser thermotherapy, known as laser interstitial thermal therapy (LITT). More than 80 hospitals across the U. S. and Canada have used the NeuroBlate System since its market release in 2013.
NeuroBlate uses MRI-guided laser light to ablate (destroy) brain lesions or unwanted tissue. Patients treated with NeuroBlate have had conditions including epilepsy, gliomas, brain metastases and radiation necrosis.
New clinical trial kicks off for Monteris Medical
Also in September, Monteris Medical announced the first patient enrolled in its REMASTer (Recurrent Brain Metastases After Stereotactic Radiosurgery [SRS] Trial) clinical trial.
Researchers designed the randomized controlled study to investigate NeuroBlate-System-delivered LITT as an early intervention for radiographically progressive brain metastases. The goal of REMASTer is to provide Level I evidence to guide treatment. The company described the patient population in the space as complex.
Analysis
Perform a panoramic analysis of this field.
login
or
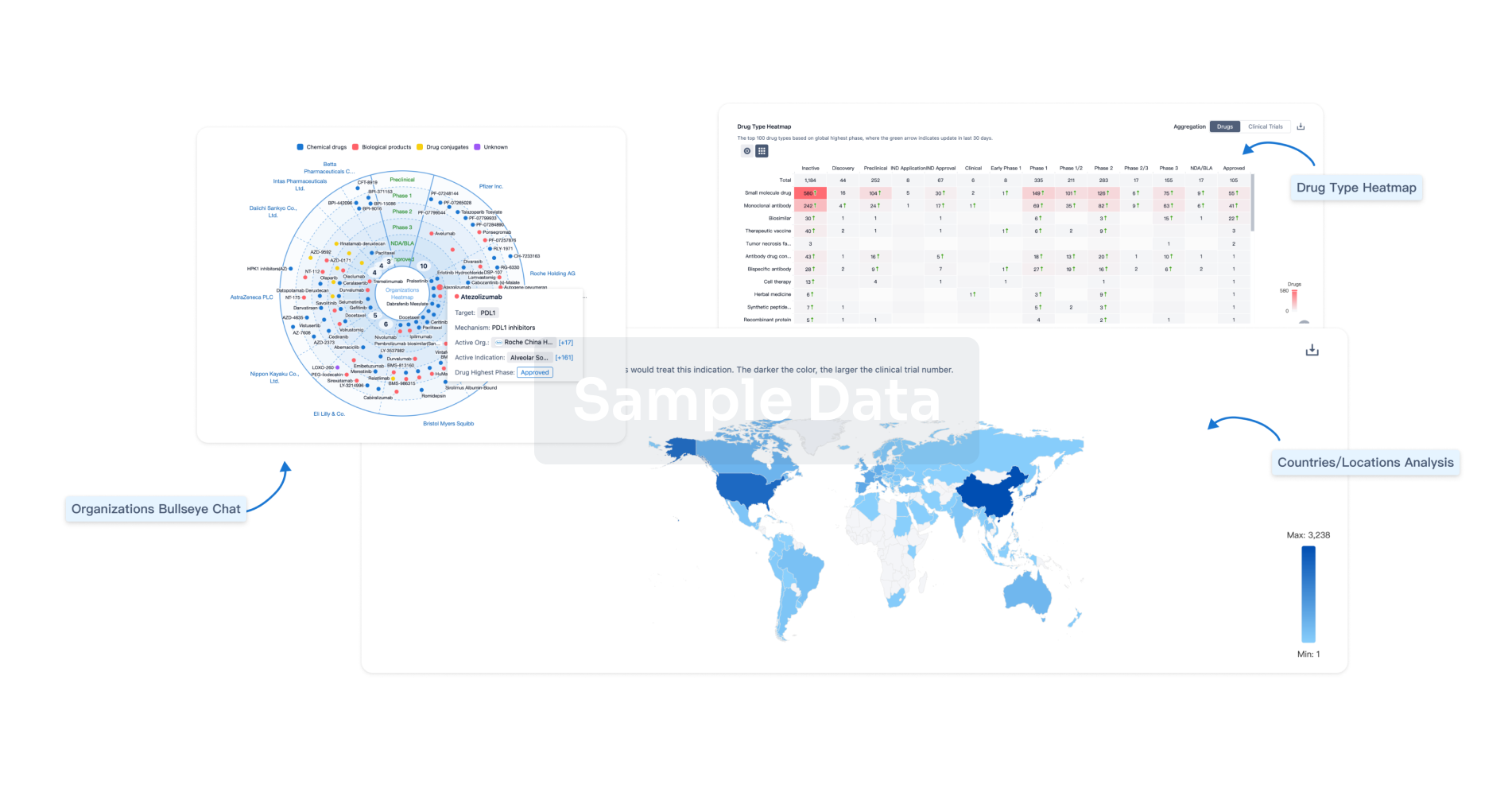
AI Agents Built for Biopharma Breakthroughs
Accelerate discovery. Empower decisions. Transform outcomes.
Get started for free today!
Accelerate Strategic R&D decision making with Synapse, PatSnap’s AI-powered Connected Innovation Intelligence Platform Built for Life Sciences Professionals.
Start your data trial now!
Synapse data is also accessible to external entities via APIs or data packages. Empower better decisions with the latest in pharmaceutical intelligence.
Bio
Bio Sequences Search & Analysis
Sign up for free
Chemical
Chemical Structures Search & Analysis
Sign up for free


