31
Clinical Trials associated with Brompheniramine Maleate/Phenylephrine Hydrochloride / Active, not recruitingNot ApplicableIIT Effects of Schroth-Based Three-Dimensional Exercise Program on Angle of Kyphosis, Muscle Strength, Balance, Pain, and Quality of Life in Patients With Postural Hyperkyphosis With Chronic Neck Pain
Our study is a randomized controlled trial designed to evaluate the effects of Schroth-based three-dimensional exercise program on kyphosis angle, trunk muscle strength, balance parameters, pain and quality of life in individuals with postural hyperkyphosis with chronic neck pain. The aim of our study was to investigate the effects of Schroth 3 dimensional exercise program and posture corrective exercises on kyphosis angle, trunk extensor muscle strength, endurance, and balance in adults with postural kyphosis. The inclusion criteria are as follows; individuals aged 20-50 years with a thoracic kyphosis angle greater than 40 degrees, have neck pain for more than 3 months, participants with a visual analog scale value of 3 and above, no treatment for postural kyphosis in the last 6 months, individuals who do not have a systemic disorder will be included. Exclusion criteria; Participants with a history of trauma or surgery in the spine joints, rheumatologic and metabolic disorders, congenital postural deformity and scoliosis will not be included in the study. In our study, participants will be randomized into two groups using a computer program as Schroth-based three-dimensional exercise group and control group. Our study was planned as a Schroth-based three-dimensional exercise group and a control group for 8 weeks. Both groups will receive a total of 20 sessions of electrotherapy and exercise in the first 4 weeks. At the end of the 4th week, after the electrotherapy sessions are completed, exercise sessions will continue 3 days a week for the next 4 weeks. The study group will receive electrotherapy treatment (hot pack, ultrasound, tens) to the cervical and thoracic region for 30 minutes in each session. In the study group, kyphotic posture correction exercises will be applied. Patients to be included in the control group will receive electrotherapy treatment (ultrasound, tens, hotpack) to the neck area for 30 minutes in each session. Corrective exercises for posture will be applied to participants in the control group. Participants will be evaluated before the treatment, at the end of the 4th week and at the end of the treatment (at the end of the 8th week) by the physiotherapist performing the study.
/ Not yet recruitingNot ApplicableIIT The CNS AE of Lorlatinib in Patients with ALK-positive Advanced NSCLC
The goal of this study is to investigate the incidence and risk factors of central nervous system adverse events of Lorlatinib in patients with ALK-positive advanced non-small cell lung cancer.
/ CompletedNot ApplicableIIT The Effect of Selective Dorsal Rhizotomy Surgery on Walking in Children With Ambulatory Cerebral Palsy in Turkey
Cerebral Palsy (CP) is a motor disorder that develops during fetal brain development or due to non-progressive damage to the developing infant brain. These movement and posture disorders are classified as Spastic Type, Dyskinetic Type, Ataxic Type and Mixed Type (Rosenbaum, 2007). Spastic type CP accounts for 20% of all CP cases. Spastic type CP is divided into three groups: diparetic (38%), hemiparetic (39%) and quadriparetic (23%) (Novak et al., 2014).
Lower extremity involvement is more common in diparetic cerebral palsy (DCP) (Donker et al., 2008). 98% of DCP cases vary between GMFS levels I and III. Walking rates are between 86-91% (Novak et al., 2014). Children with DCP can usually walk until the age of 4 (Cottalorda, 1998). However, these walks are often; Due to spasticity, muscle weakness, involuntary co-contraction, deficiencies in selective motor control, balance problems, structural changes of soft tissue and compensatory mechanisms (Manca, 2014), it can lead to musculoskeletal system problems and gait pathologies. Although the cerebral lesion that causes is static, children with spastic diplegia increase in height with age, and they may lose their ability to walk because bone length cannot be accompanied by muscle length at the same rate (Miller, 2020).
Selective Dorsal Rhizotomy (SDR) surgery is an effective method for spasticity management in children with spastic DCP (Novak et al., 2014). The positive effect of SDR on function and mobility has been proven (Novak et al., 2020).
It has been stated that SDR surgery applied to carefully selected candidates may be beneficial on gait quality in individuals with ambulatory CP (Chen, 2019). SDR surgery has been found to improve walking as a result of information collected from patients through a survey (Park, 2021). The aim of our study is to reveal the effect of SDR surgery performed in Turkey on gait function in children with CP using evaluation scales.
Start Date01 May 2024 |
Sponsor / Collaborator- |
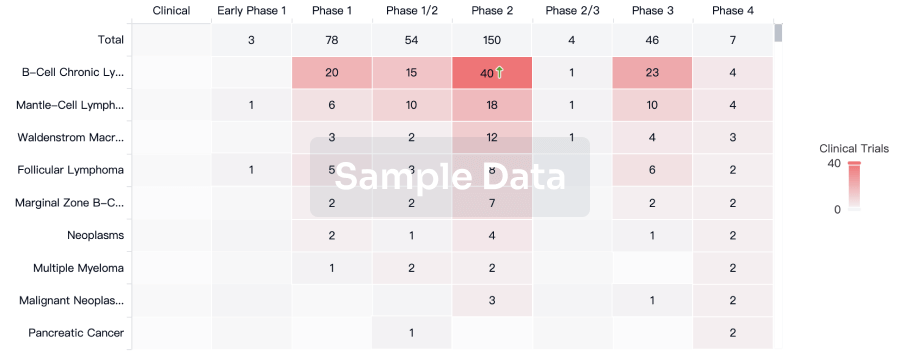
100 Clinical Results associated with Brompheniramine Maleate/Phenylephrine Hydrochloride
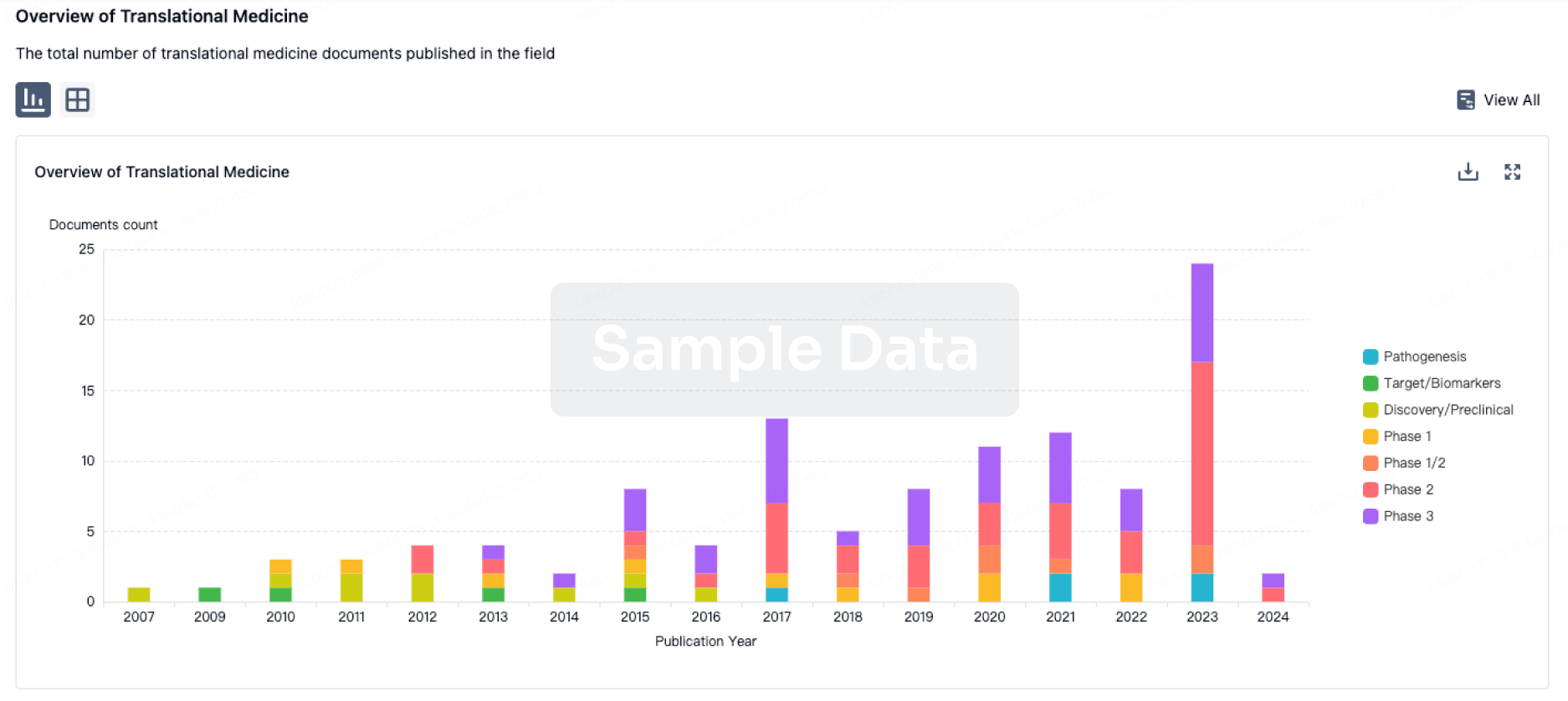
100 Translational Medicine associated with Brompheniramine Maleate/Phenylephrine Hydrochloride
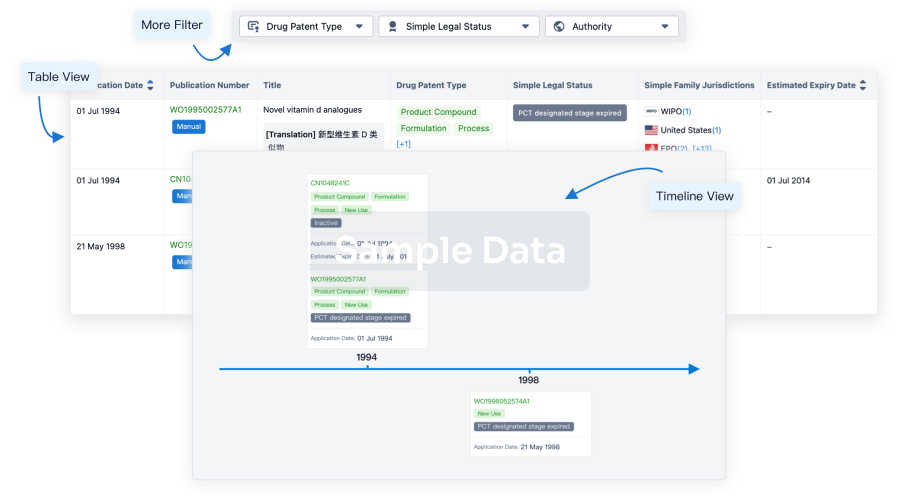
100 Patents (Medical) associated with Brompheniramine Maleate/Phenylephrine Hydrochloride
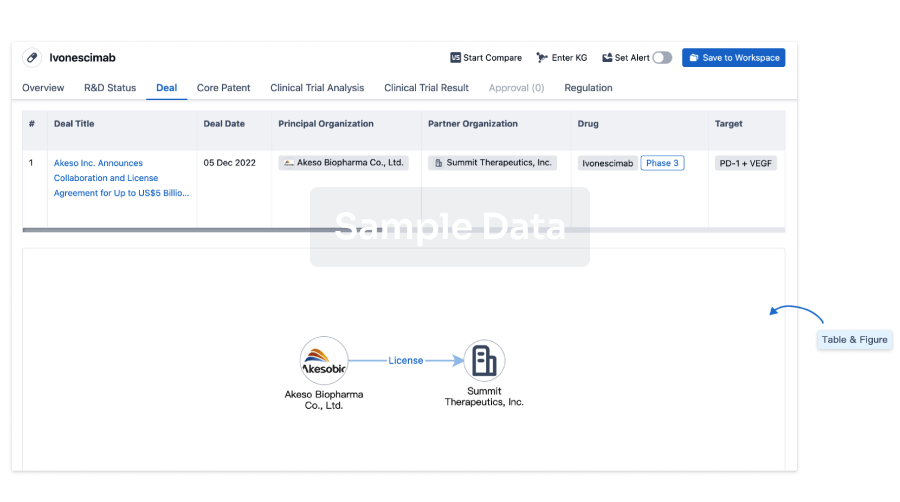
100 Deals associated with Brompheniramine Maleate/Phenylephrine Hydrochloride