Three Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis Studies Explore the Use of Traditional Chinese Medicine for Various Diseases
26 Jan 2024
XI'AN, China, Jan. 26, 2024 /PRNewswire/ -- Despite demonstrating significant clinical efficacy against various diseases, the widespread use of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) is still limited. This is mainly due to the complexity in their formulation and lack of sufficient pharmacological and safety-related data.
To address this gap, a new issue of the Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis presents three independent studies which assessed the potency of TCM-based compounds for various human diseases, along with their molecular mechanisms of action.
Continue Reading
Preview
Source: PRNewswire
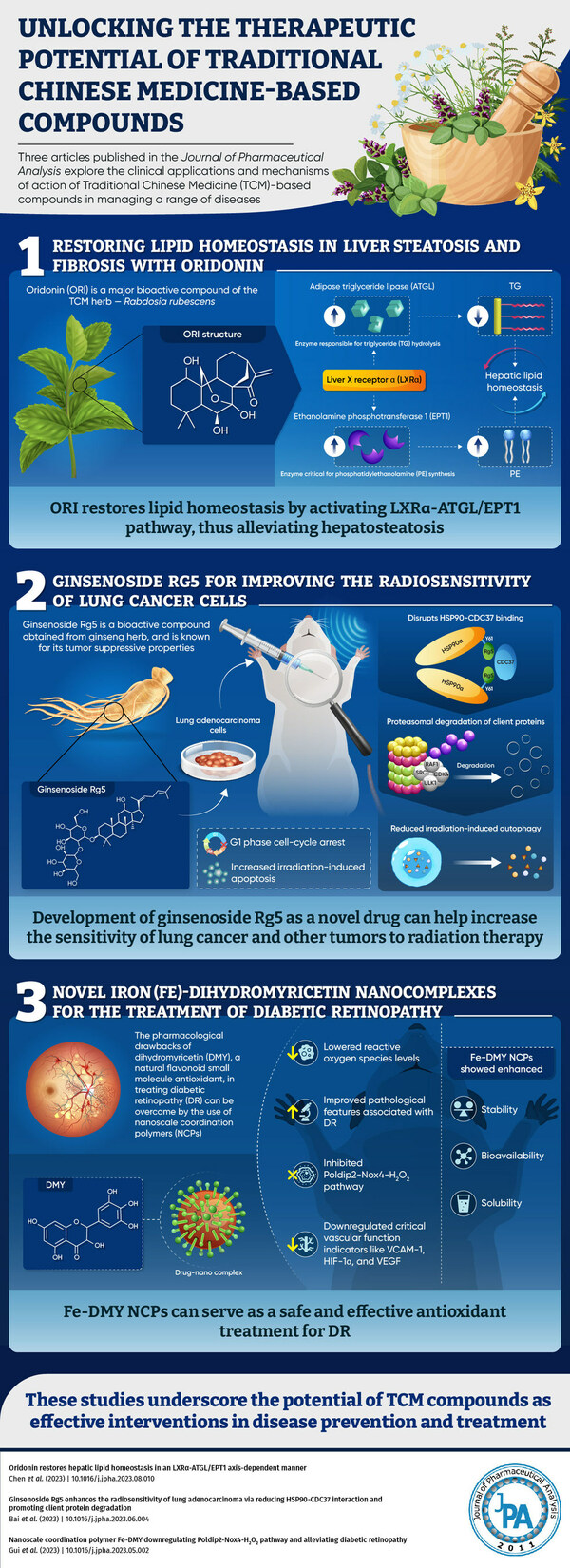
Latest research unveils the potential of Traditional Chinese Medicine compounds for the treatment of human diseases
The accumulation of excess fat in the liver leads to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Oridonin (ORI), a TCM derived from the Chinese herb Rabdosia rubescens, exhibits anti-inflammatory effects. An article available online on 21 August 2023 and published in Volume 13, Issue 11 of the journal in November 2023, now reveals that ORI regulates lipid homeostasis in the liver by maintaining the balance between triglyceride (TG) and phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), through modulation of adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL) and ethanolamine phosphotransferase 1 (EPT1) expression via the liver X receptor alpha (LXRα) signaling pathway. "When the TG-PE lipid balance is disturbed, the seesaw tilts towards TG, increasing the risk of NAFLD. Restoring lipid homeostasis using compounds like oridonin can alleviate lipid accumulation and liver cytotoxicity," explains Professor Lan Tang.
Tumor heterogeneity compromises the efficacy of radiotherapy for treating lung cancer. Radiosensitizers help prime tumor cells and improve their response to radiation. Now, in an article available online on 7 June 2023 and published in Volume 13, Issue 11 of the journal in November 2023, researchers found that ginsenoside Rg5 induced cell-cycle arrest and enhanced radiation-induced cell death. Ginsenoside Rg5 interacts with heat shock protein alpha (HSP90α) with high affinity and reduces the binding between HSP90 and cell division cycle 37 (CDC37), promoting HSP90-CDC37 client protein degradation. "Ginsenoside Rg5 can be potentially developed into a new drug for improving the sensitivity of lung cancer and other types of tumors to radiation therapy," the authors explain.
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is characterized by the activation of oxidative stress pathways in response to high glucose. In a study available online on 12 May 2023 and published in Volume 13, Issue 11 of the journal in November 2023, researchers synthesized a polymeric drug complex by combining a natural flavonoid antioxidant known as dihydromyricetin (DMY) with iron (Fe) ions in nano-coordinated polymer particles (NCPs). Fe-DMY NCPs can alleviate glucose-induced oxidative damage and reverse the pathological features of DR by decreasing the expression of key proteins involved in microvascular dysfunction. Fe-DMY NCPs could also inhibit the activation of Poldip2-Nox4-H2O2 signaling pathway and down-regulate important vascular function indicators such as VCAM-1, HIF-1α, and VEGF. Explaining its applications, the authors say, "We report for the first time the synthesis and validation of ultra-small Fe-DMY NCPs. Fe-DMY complexes bear the potential to alleviate the impact of DR on vision, thus improving the quality of life of affected individuals."
These studies provide a scientific basis for the development of TCM-based compounds into effective targeted therapies for various diseases.
Reference
Titles of original papers:
Oridonin restores hepatic lipid homeostasis in an LXRa-ATGL/EPT1 axis-dependent manner
Ginsenoside Rg5 enhances the radiosensitivity of lung adenocarcinoma via reducing HSP90-CDC37 interaction and promoting client protein degradation
Nanoscale coordination polymer Fe-DMY downregulating
Poldip2-Nox4-H2O2 pathway and alleviating diabetic retinopathy
Journal name: Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpha.2023.08.010
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpha.2023.06.004
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpha.2023.05.002
Media contact
Mengjie Wang
[email protected]
Xi'an, China
+86-(0)29-88960092
SOURCE Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis
For more details,please visit the original website
The content of the article does not represent any opinions of Synapse and its affiliated companies. If there is any copyright infringement or error, please contact us, and we will deal with it within 24 hours.
Organizations
-Drugs
Chat with Hiro
Hot reports
Get started for free today!
Accelerate Strategic R&D decision making with Synapse, PatSnap’s AI-powered Connected Innovation Intelligence Platform Built for Life Sciences Professionals.
Start your data trial now!
Synapse data is also accessible to external entities via APIs or data packages. Empower better decisions with the latest in pharmaceutical intelligence.


