/ CompletedNot Applicable Is Respiratory Rate Derived From Capnography Can Prevent Adverse Events Occurred in Sedated Patients.
Although appropriate sedation is recommended during colonoscopy, patients are at risk for adverse events e.g hypoventilation and hypoxemia due to inadvertent oversedation. The aim of this study was to evaluate the benefit of additional quantitative capnography monitoring ( respiratory rate )in management of patient undergoing colonoscopy under sedation in preventing or reducing the incidence of adverse events and also determine when to start the procedure and when to give and not to give increments of sedative drugs during the procedure.
/ CompletedNot Applicable Efficacy of Ultrasound-Guided Erector Spinae Plan Block on Postoperative Pain After Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Under General Anesthesia. Randomized, Controlled Trial
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is a widely employed procedure in ambulatory surgery. Pain after laparoscopic cholecystectomy arises significantly from port site incisions in the anterior abdominal wall. Innervation of the anterior abdominal wall is segmentally supplied by pain afferents in the plane of fascia between transversus abdominis and the internal oblique muscles. Opioids analgesia is used to control postoperative pain, but it carries the risk of increased nausea and vomiting, ileus and sedation that may delay hospital discharge.
Several techniques have been tried as.neuroaxial narcotics, intraperitoneal lavage of local anesthetic and transversus abdominis plan (TAP) block and successfully reduced opioid use and improve postoperative analgesia.
The ultrasound-guided erector spinae plan(ESP) block is a recently described technique which produces reliable unilateral analgesia at thoraco-lumbar dermatomes. ESP block carries the advantages of being simple, safe, easily recognizable by ultrasound, and a catheter can be threaded to extend the duration of analgesia.
Few case series reported the efficacy of (US)-guided ESP blocks in reducing postoperative pain and opioids consumption.
Because of that, the investigators aimed to test the hypothesis that US-guided ESP blocks can decrease opioid consumption during the first 24 h after of laparoscopic cholecystectomy in comparison with the conventional systemic analgesia.
/ CompletedNot Applicable Efficacy of Midazolam Addition to Local Anesthetic in Peribulbar Block. Randomized, Controlled Trial
Regional eye blocks are usually preferred for ophthalmic procedures. Peribulbar block (PBB) is a safe alternative for patients undergoing cataract surgery. Many studies tried to solve this issue by means of prolonging the duration of action of the local anesthetics used. Several drugs were tried as adjuncts to local anesthetics, and their effects have been studied. Midazolam added to the list of adjuvant used in the subarachnoid or epidural block can produce analgesia, probably mediated by the benzodiazepine-Gamma Amino-Butyric Acid(GABA) receptor complex.
The investigators hypothesized that the addition of midazolam to lidocaine will improve the quality of the peribulbar block; fasten the onset and prolonging its anesthetic and analgesic duration.
100 Clinical Results associated with Al Jedaani Group of Hospitals
0 Patents (Medical) associated with Al Jedaani Group of Hospitals
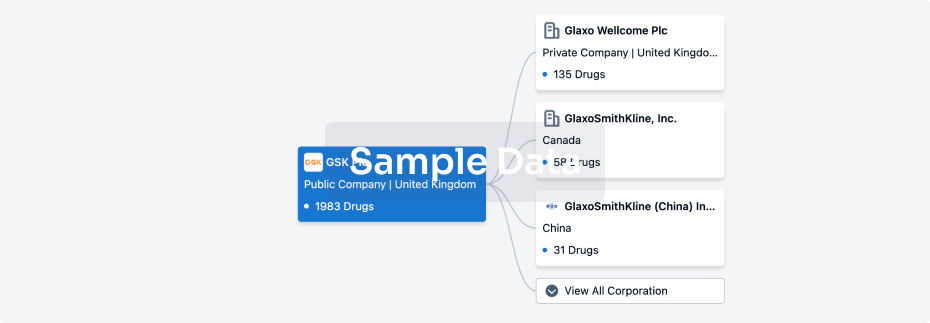
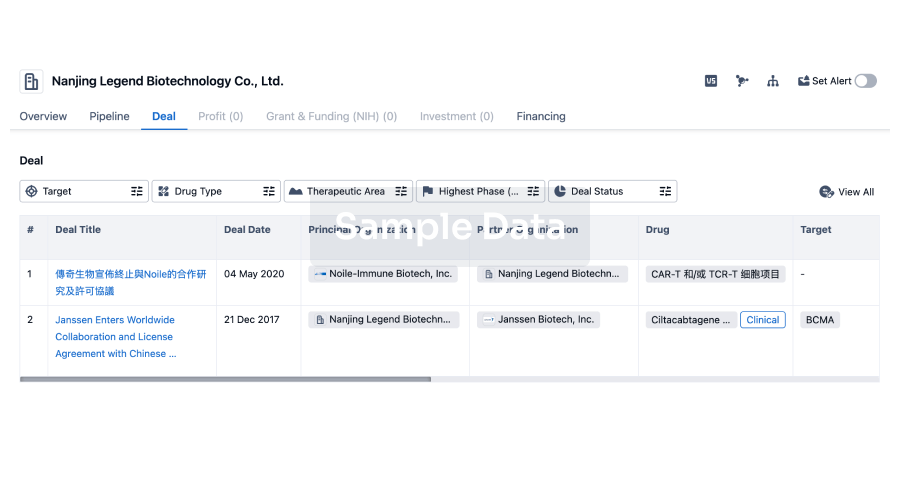
100 Deals associated with Al Jedaani Group of Hospitals
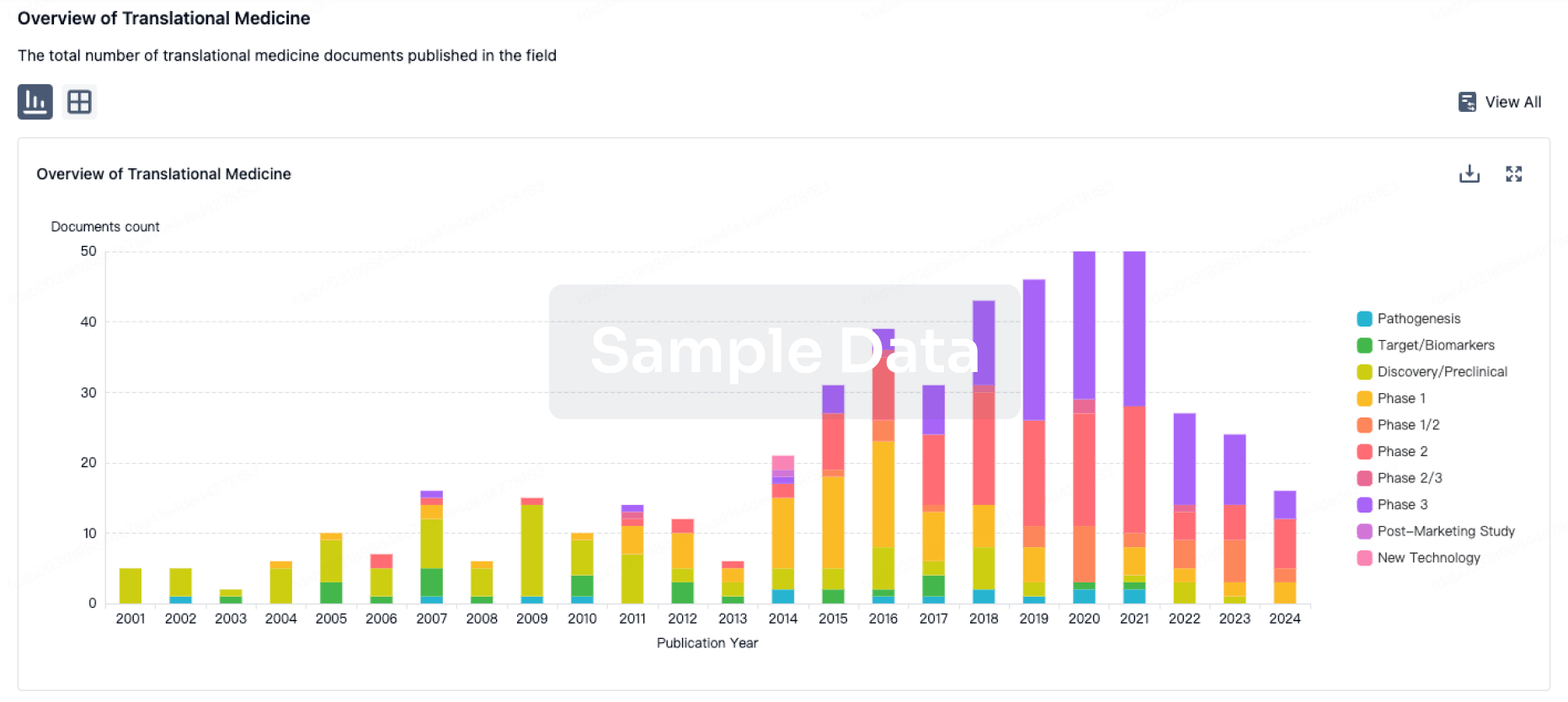
100 Translational Medicine associated with Al Jedaani Group of Hospitals