Target- |
MechanismStem cell replacements |
Active Org.- |
|
Active Indication- |
|
Drug Highest PhasePending |
First Approval Ctry. / Loc.- |
First Approval Date- |
Bioretina Inc Ankara University Technopolis
The axons of the retinal ganglion cells combine to form the optic nerve. The optic nerve transmits electrical signals to the visual cortex by various synapses. Optic nerve axons are more sensitive to toxins than retina because they are outside the blood retinal barrier. Methanol, various solvents and heavy metals, carbon dioxide, antiarrhythmic, antiepileptic, antibiotics and some vasoactive drugs can cause toxic optic neuropathy. There is a different pathophysiology for each toxin. Methanol is easily accessible alcohol in all types of disinfectants. Methanol is converted into formaldehyde and formic acid while metabolized in the liver. Formaldehyde disrupts ATP synthesis by blocking mitochondrial function and oxidative phosphorylation. Formic acid causes demyelination as a result of metabolic acidosis. Neuroinflammation occurs when denatured proteins block axoplasmic flow. All these processes can lead to apoptosis and permanent vision loss. Sildenafil is a vasoactive drug used in erectile dysfunction. Sildenafil decreases optic nerve head blood flow. Neuroinflammation develops secondary to the cessation of axoplasmic flow after hypoxia. If hypoxia and neuroinflammatiom persists, apoptosis and permanent vision loss develop. Amiodarone is an ion channel blocker used in the treatment of cardiac arrhythmias. Long-term use may cause disruption of ion channel balance in the optic nerve. This condition leads to asymmetric neuroinflammation and apoptosis.
Wharton's jelly derived mesenchymal stem cells (WJ-MSC) can increase mitochondrial ATP synthesis with paracrine effects and suppress neuroinflammation with immunomodulatory effects. Repetitive electromagnetic stimulation (rEMS) can rearrange ion channel balances and axoplasmic flow. The aim of this prospective phase-3 clinical study is to investigate the effect of WJ-MSC and rEMS combination in the therapy of toxic optic neuropathies. This combination is the first study in the literature for the therapy of toxic optic neuropathies.
Management of Retinitis Pigmentosa by Wharton's Jelly Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Preliminary Clinical Results
The aim of this study is to determine if umbilical cord Wharton's jelly derived mesenchymal stem cells implanted in sub-tenon space have beneficial effects on visual functions in retinitis pigmentosa patients by reactivating the degenerated photoreceptors in dormant phase.
Bioretina, Ankara University Technopolis
Purpose To investigate whether the natural progression rate of retinitis pigmentosa (RP) can be decreased with subtenon umbilical cord Wharton's jelly derived mesenchymal stemcell (WJ-MSC) application alone or combination with retinal electromagnetic stimulation (rEMS).
Material and methods The study included prospective analysis of 130 eyes of 80 retinitis pigmentosa patients with a 36-month follow-up duration. Patients constitute 4 groups with similar demographic characteristics. The subtenon WJ-MSC only group consisted of 34 eyes of 32 RP patients as Group1; The rEMS only group consisted of 32 eyes of 16 RP patients as Group2; The combined management group consisted of 32 eyes of 16 RP patients who received combined WJ-MSC and rEMS as Group3; The natural course (control) group consisted of 32 eyes of 16 RP patients who did not receive any treatment were classified as Group4. Fundus autofluorescence surface area (FAF-field), horizontal and vertical ellipsoid zone width (EZW), fundus perimetry deviation index (FPDI), full field electroretinography magnitude (ERG-m) and best corrected visual acuity (BCVA) changes were compared within and between groups after 36 month follow up period.
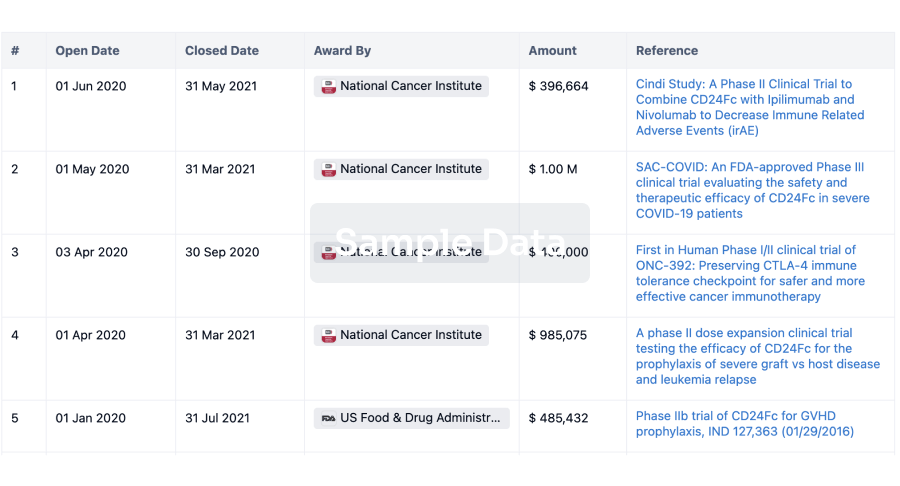
100 Clinical Results associated with Ankara Universitesi Teknokent
0 Patents (Medical) associated with Ankara Universitesi Teknokent
100 Deals associated with Ankara Universitesi Teknokent
100 Translational Medicine associated with Ankara Universitesi Teknokent