Request Demo
Last update 23 Jan 2025
Lipid peroxidase
Last update 23 Jan 2025
Basic Info
Synonyms- |
Introduction- |
Related
2
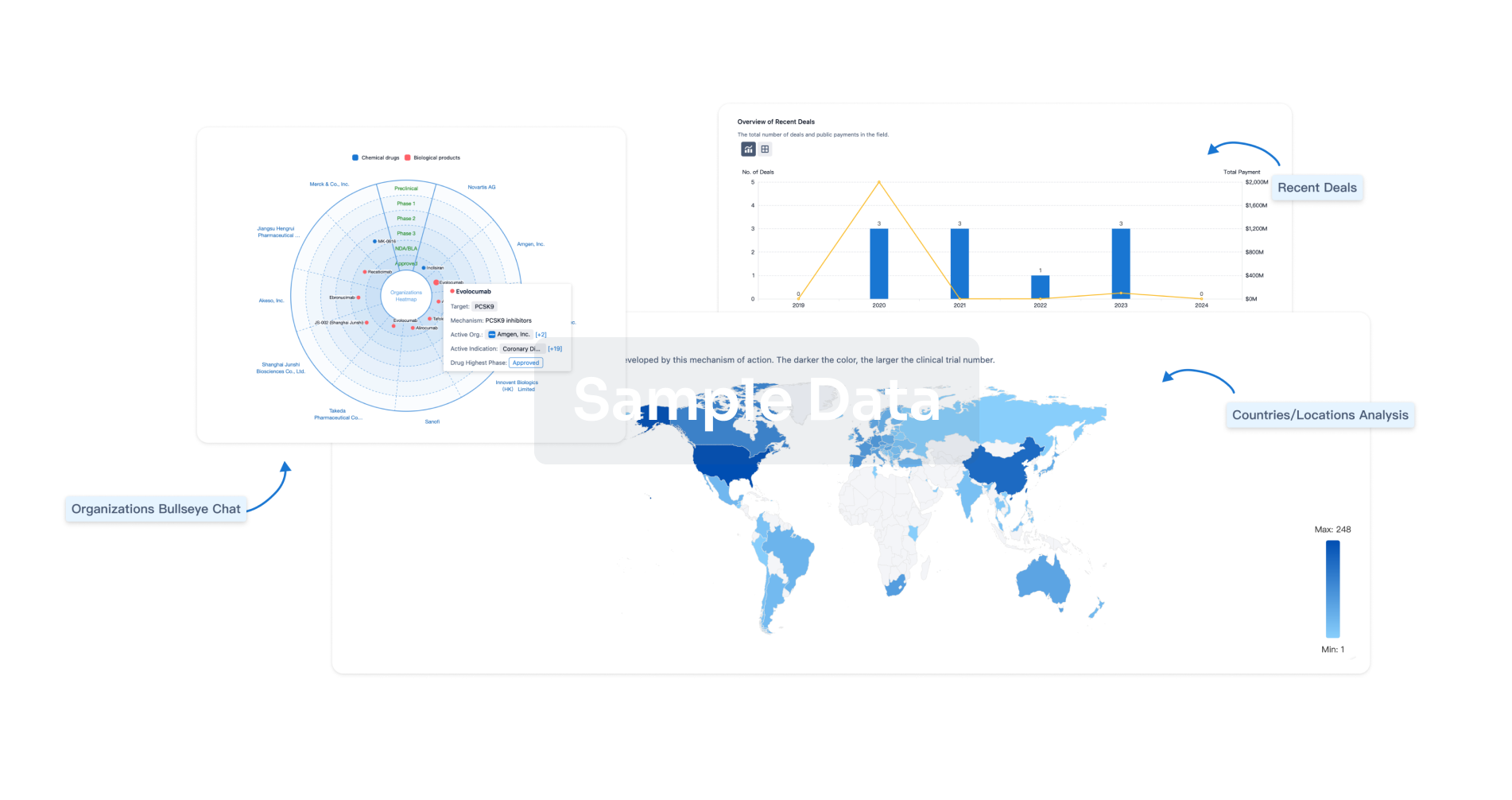
Drugs associated with Lipid peroxidaseTarget |
Mechanism Lipid peroxidase inhibitors [+1] |
Active Org. |
Originator Org. |
Active Indication |
Inactive Indication- |
Drug Highest PhasePreclinical |
First Approval Ctry. / Loc.- |
First Approval Date20 Jan 1800 |
Target |
Mechanism Lipid peroxidase inhibitors |
Active Org.- |
Originator Org. |
Active Indication- |
Inactive Indication- |
Drug Highest PhasePending |
First Approval Ctry. / Loc.- |
First Approval Date20 Jan 1800 |
100 Clinical Results associated with Lipid peroxidase
Login to view more data
100 Translational Medicine associated with Lipid peroxidase
Login to view more data
0 Patents (Medical) associated with Lipid peroxidase
Login to view more data
175
Literatures (Medical) associated with Lipid peroxidase01 Jan 2025·International Journal of Cell Biology
Radioprotective Effects of Vitamin C, Cimetidine, and Famotidine on Lipid Peroxidase and Hepatic Glutathione Levels in Mouse Liver
Article
Author: Hajimazdarany, Shima ; Khanchoupan, Milad ; Najibi, Reza ; Gholami, Mana ; Yusofvand, Reza ; Ahmadi, Ali Asghar
01 Nov 2024·Drug and Chemical Toxicology
Unraveling the neuroprotective mechanisms of naltrexone against aluminum-induced neurotoxicity
Article
Author: Baydar, Terken ; Demirel, Göksun ; Sanajou, Sonia ; Erkekoğlu, Pinar ; Şahin, Gönül ; Yirün, Anil ; Arca Çakır, Deniz
02 Oct 2024·Journal of Microencapsulation
Nanoparticles encapsulated in
Abelmoschus esculentus
polysaccharide-based pellets as colon targeting approach
Article
Author: Arora, Akshita ; Sharma, Anshul ; Singh, Rajveer ; Singh, Amrinder ; Sharma, Nitin ; Singh, Shamsher ; Kakkar, Dipti
Analysis
Perform a panoramic analysis of this field.
login
or
AI Agents Built for Biopharma Breakthroughs
Accelerate discovery. Empower decisions. Transform outcomes.
Get started for free today!
Accelerate Strategic R&D decision making with Synapse, PatSnap’s AI-powered Connected Innovation Intelligence Platform Built for Life Sciences Professionals.
Start your data trial now!
Synapse data is also accessible to external entities via APIs or data packages. Empower better decisions with the latest in pharmaceutical intelligence.
Bio
Bio Sequences Search & Analysis
Sign up for free
Chemical
Chemical Structures Search & Analysis
Sign up for free
