A Comprehensive Review of Clofazimine's R&D Innovations and Drug Target Mechanism
Clofazimine's R&D Progress
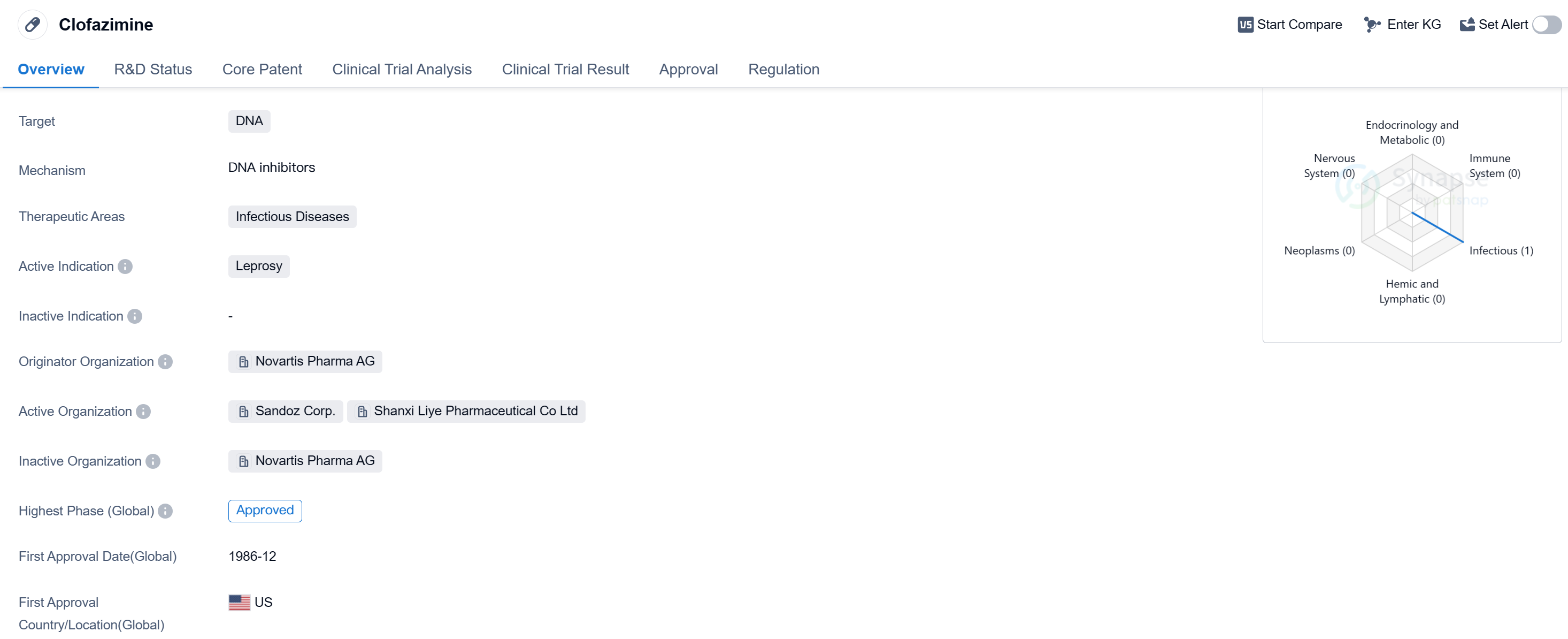
Clofazimine is a small molecule drug that targets DNA and is primarily used in the treatment of infectious diseases. Its active indication is leprosy, a chronic infectious disease caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium leprae. The drug was developed by Novartis Pharma AG, a renowned pharmaceutical company.
Clofazimine has been approved for use in multiple countries, including the United States, where it received its first approval in December 1986. It is classified as an orphan drug, indicating that it is used to treat rare diseases or conditions that affect a small number of people. This designation often provides certain incentives to pharmaceutical companies, such as extended market exclusivity and financial support for research and development.
As a small molecule drug, clofazimine is designed to interact with specific targets in the DNA of the bacteria, inhibiting their growth and replication. By targeting the DNA, it disrupts the essential processes required for the survival of the bacteria, ultimately leading to their elimination from the body.
Leprosy, the active indication for clofazimine, is a chronic infectious disease that primarily affects the skin, nerves, and mucous membranes. It is caused by the slow-growing bacteria Mycobacterium leprae and can lead to severe deformities and disabilities if left untreated. Clofazimine, along with other antibiotics, is used in the multidrug therapy recommended by the World Health Organization for the treatment of leprosy.
The approval of clofazimine in multiple countries, including the United States and China. Its long history of use since its first approval in 1986 demonstrates its established position in the field of infectious diseases.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Clofazimine: DNA inhibitors
DNA inhibitors are substances that interfere with the replication or transcription of DNA, thereby inhibiting the growth and proliferation of cells. From a biomedical perspective, DNA inhibitors are often used in cancer treatment as chemotherapy drugs. They work by targeting rapidly dividing cancer cells and preventing them from replicating their DNA, ultimately leading to cell death. DNA inhibitors can also be used in research settings to study DNA replication and transcription processes. By inhibiting these processes, scientists can gain insights into the mechanisms behind DNA replication and gene expression. Overall, DNA inhibitors play a crucial role in both cancer therapy and scientific research related to DNA biology.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Clofazimine
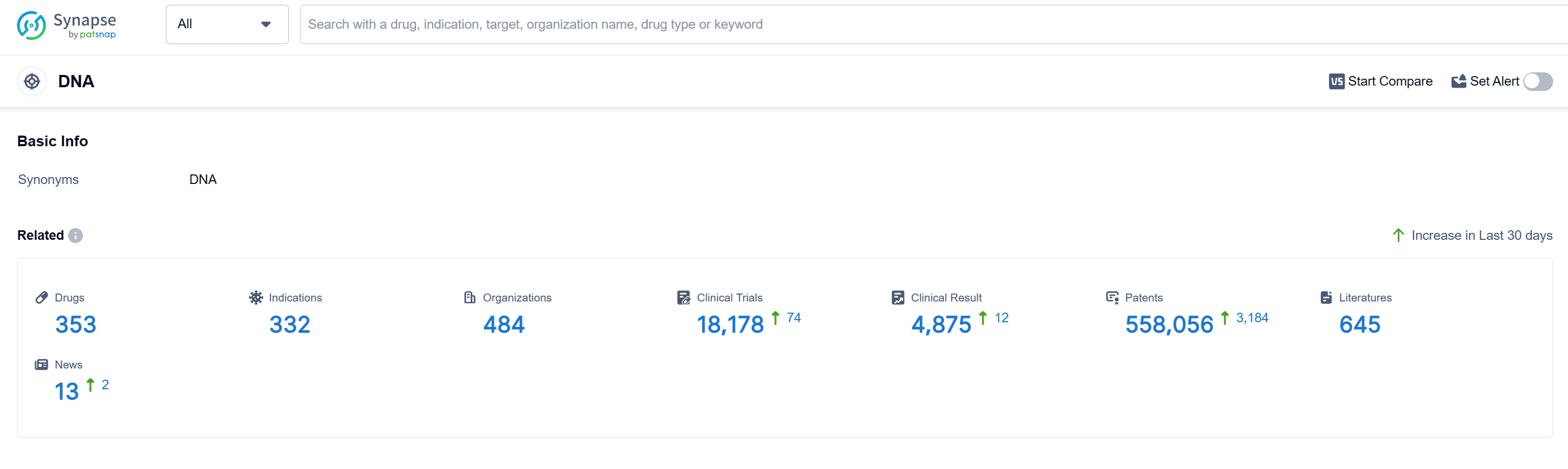
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 13 Sep 2023, there are a total of 353 DNA drugs worldwide, from 484 organizations, covering 332 indications, and conducting 18178 clinical trials.
The analysis of the current competitive landscape and future development of the target DNA reveals that Pfizer Inc., Novartis AG, Baxter International, Inc., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and Johnson & Johnson are the companies growing fastest under the current target. Lymphoma, Ovarian Cancer, and Breast Cancer are the indications with the highest number of approved drugs. Small molecule drugs, Monoclonal antibodies, and Antibody drug conjugates are the drug types progressing most rapidly. China, the United States, Japan, and the European Union are the countries/locations developing fastest under the current target DNA. The progress in China, with a high number of approved drugs, indicates its significant contribution to the R&D progress of the target DNA. Overall, the target DNA presents a competitive landscape with promising future development potential.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, clofazimine is a small molecule drug developed by Novartis Pharma AG that targets DNA and is primarily used in the treatment of leprosy. Its approval in multiple countries, including the United States, and its orphan drug status emphasize its importance in addressing rare infectious diseases. With its ability to disrupt the DNA of bacteria, clofazimine plays a crucial role in the multidrug therapy for leprosy, contributing to the elimination of the bacteria and the prevention of severe complications.