A Comprehensive Review of dobutamine hydrochloride's R&D Innovations and Drug Target Mechanism
Dobutamine hydrochloride's R&D Progress
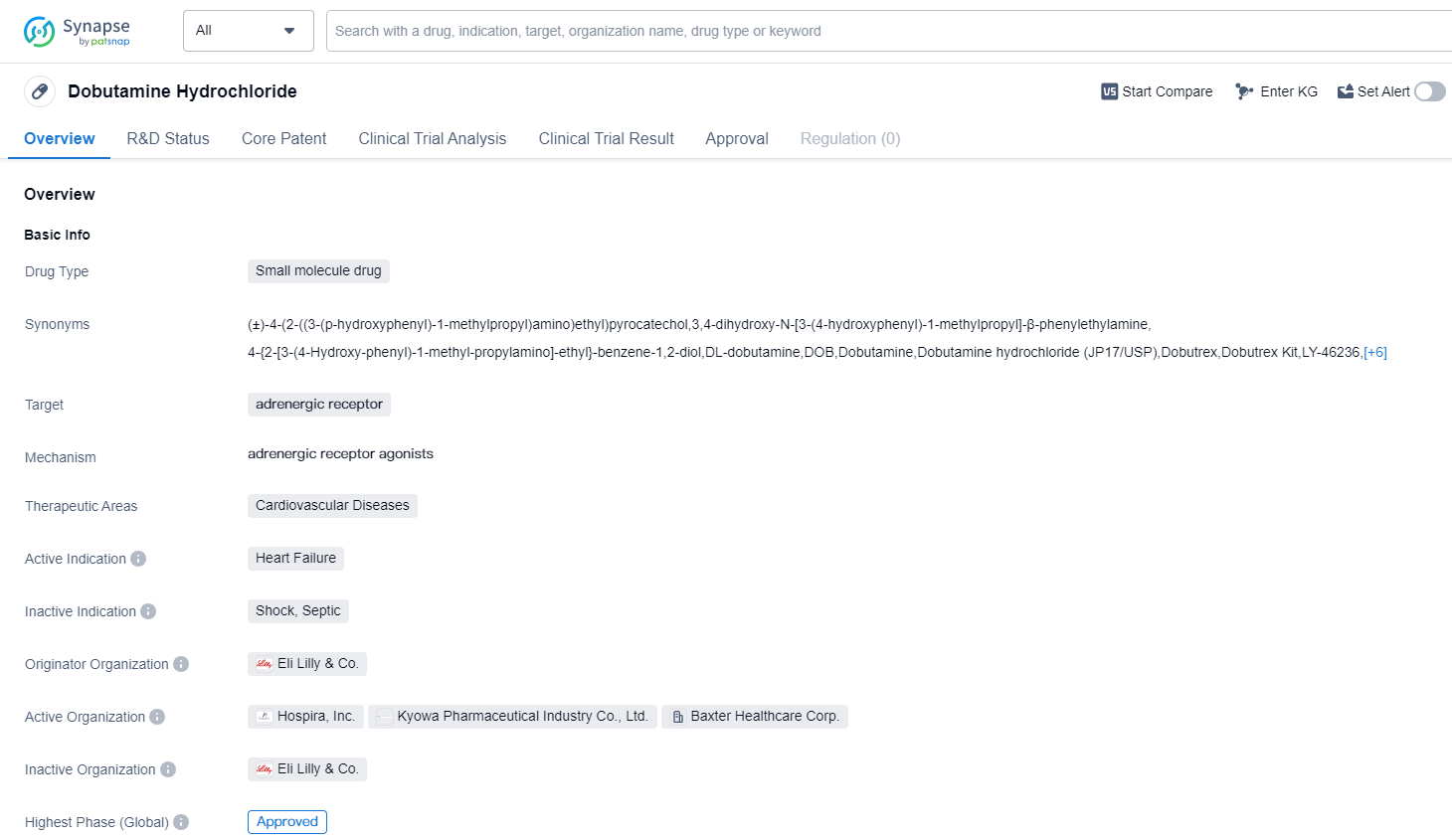
Dobutamine Hydrochloride is a small molecule drug that targets the adrenergic receptor and is primarily used in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases, specifically heart failure. It was first approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in July 1978 and has since been approved in other countries as well.
The drug is developed by Eli Lilly & Co., a renowned pharmaceutical company. As a small molecule drug, Dobutamine Hydrochloride is composed of relatively low molecular weight and is able to penetrate cell membranes easily. This characteristic allows it to interact with adrenergic receptors, which are involved in the regulation of the cardiovascular system.
Dobutamine Hydrochloride is primarily indicated for heart failure, a condition characterized by the heart's inability to pump blood effectively. By targeting the adrenergic receptor, the drug stimulates the heart muscle, increasing its contractility and improving cardiac output. This mechanism of action helps to alleviate symptoms associated with heart failure, such as shortness of breath and fatigue.
The highest R&D phase of this drug is approved. Since its initial approval in 1978, Dobutamine Hydrochloride has been widely used in the management of heart failure. It has become an essential component of the treatment regimen for patients with this condition, providing symptomatic relief and improving overall cardiac function.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for dobutamine hydrochloride: Adrenergic receptor agonists
Adrenergic receptor agonists are a class of drugs that activate adrenergic receptors in the body. Adrenergic receptors are a type of receptor found on the surface of cells that bind to and respond to the neurotransmitters norepinephrine and epinephrine (also known as adrenaline). These receptors are part of the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the "fight or flight" response.
When adrenergic receptor agonists bind to these receptors, they mimic the effects of norepinephrine and epinephrine, leading to various physiological responses. These responses can include increased heart rate, increased blood pressure, dilation of airways, and increased blood flow to certain organs.
Adrenergic receptor agonists are used in the treatment of various medical conditions. For example, they can be used to treat asthma by dilating the airways and relieving bronchospasms. They can also be used to treat hypotension (low blood pressure) by increasing blood pressure. Additionally, adrenergic receptor agonists are used in ophthalmology to dilate the pupils during eye examinations.
It's important to note that adrenergic receptor agonists should be used under medical supervision, as they can have side effects and interact with other medications. The specific type of adrenergic receptor agonist used will depend on the medical condition being treated and the desired physiological response.
Drug Target R&D Trends for dobutamine hydrochloride
Adrenergic receptors play a crucial role in the human body by responding to the neurotransmitters adrenaline and noradrenaline. These receptors are found in various tissues and organs, including the heart, blood vessels, lungs, and brain. Activation of adrenergic receptors leads to a wide range of physiological responses, such as increased heart rate, blood pressure, and bronchodilation. These receptors also play a role in regulating smooth muscle contraction, glucose metabolism, and neurotransmitter release. Understanding the function of adrenergic receptors is essential in the development of drugs targeting conditions like hypertension, asthma, and cardiovascular diseases.
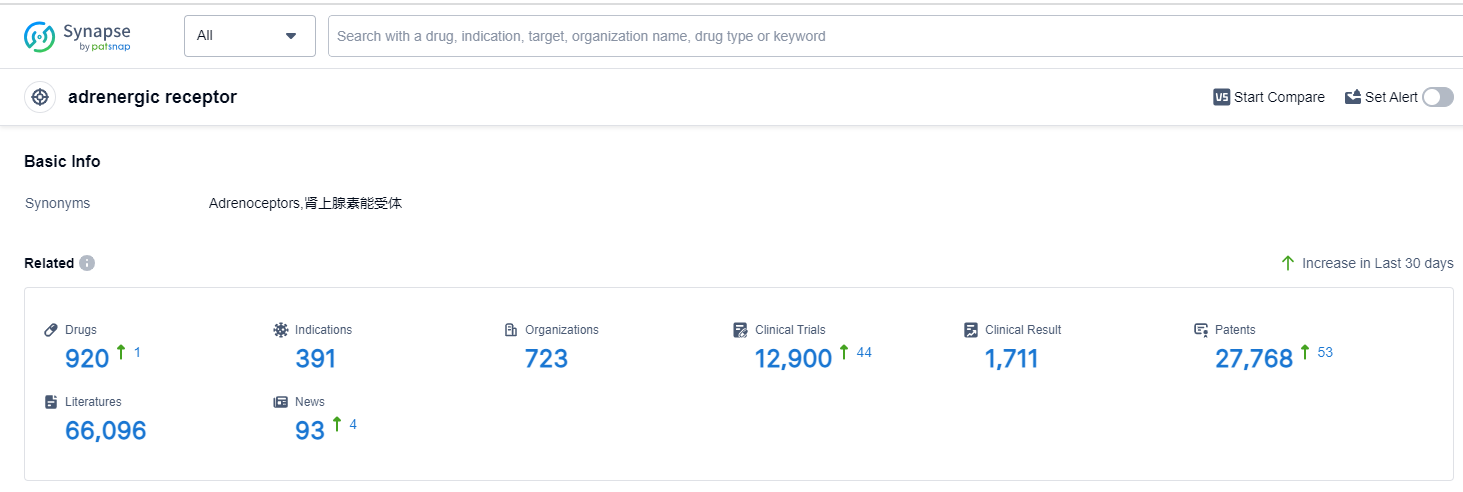
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 14 Sep 2023, there are a total of 920 adrenergic receptor drugs worldwide, from 723 organizations, covering 391 indications, and conducting 12900 clinical trials.
The analysis of the target adrenergic receptor reveals a competitive landscape with multiple companies actively involved in research and development. Novartis AG, GSK Plc, AstraZeneca PLC, Pfizer Inc., and Sanofi are the leading companies with a strong presence in different phases of development. Drugs targeting the adrenergic receptor have been approved for various indications, including hypertension, asthma, common cold, and pulmonary diseases. Small molecule drugs dominate the drug types, indicating intense competition and ongoing research. China, the United States, and Japan are the leading countries in terms of drug development, with significant contributions from other countries as well. The target adrenergic receptor presents a promising area for future development and therapeutic interventions in various diseases.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Dobutamine Hydrochloride is a small molecule drug developed by Eli Lilly & Co. It targets the adrenergic receptor and is primarily indicated for the treatment of heart failure. With its approval in multiple countries, including the United States and China, the drug has proven its safety and efficacy in clinical trials. Since its first approval in 1978, Dobutamine Hydrochloride has played a crucial role in managing heart failure and improving the quality of life for patients suffering from this condition.