A Comprehensive Review of dermatan sulfate's R&D Innovations and Drug Target Mechanism
Dermatan sulfate's R&D Progress
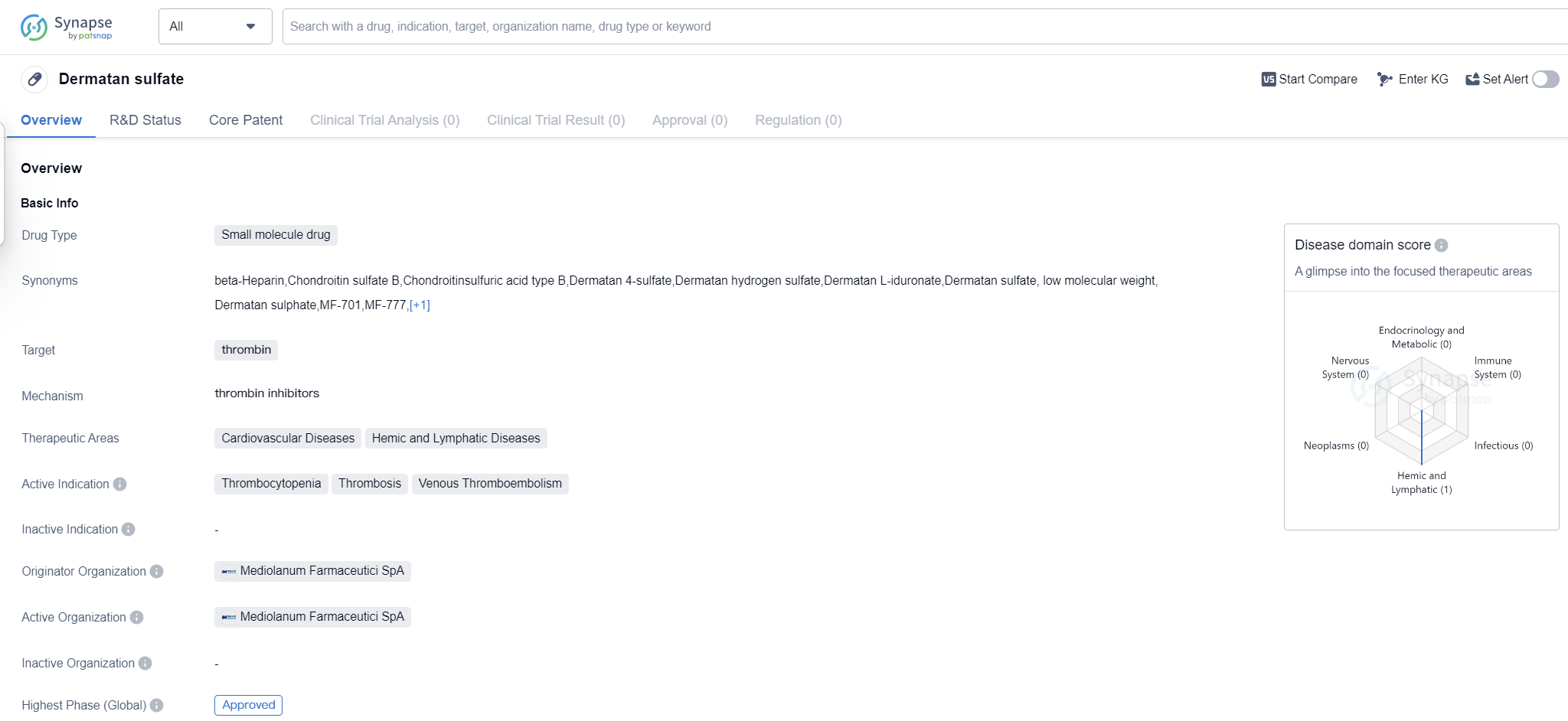
Dermatan sulfate is a small molecule drug that primarily targets thrombin, a key enzyme involved in blood clotting. It is used in the treatment of various cardiovascular diseases and hemic and lymphatic diseases. The drug has been approved for use in patients suffering from thrombocytopenia, thrombosis, and venous thromboembolism.
The originator organization of Dermatan sulfate is Mediolanum Farmaceutici SpA, an Italian pharmaceutical company. The drug received its first approval in July 1998 in Italy, making it available for use in the country. It is important to note that Dermatan sulfate has reached the highest phase of development, indicating that it has successfully completed clinical trials and has been approved for commercial use.
Dermatan sulfate's approval for use in the treatment of thrombocytopenia, thrombosis, and venous thromboembolism highlights its potential in managing these conditions. Thrombocytopenia refers to a low platelet count, which can lead to excessive bleeding or bruising. Dermatan sulfate may help increase platelet levels and improve blood clotting in patients with this condition.
Thrombosis, on the other hand, refers to the formation of blood clots within blood vessels, obstructing blood flow. Dermatan sulfate's ability to target thrombin, an enzyme involved in clot formation, suggests that it may help prevent or dissolve blood clots, reducing the risk of thrombosis-related complications.
Venous thromboembolism encompasses conditions such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE), where blood clots form in the veins and can potentially travel to the lungs. As a small molecule drug, Dermatan sulfate likely acts by directly interacting with thrombin, inhibiting its activity and preventing excessive clot formation. This mechanism of action makes it a promising therapeutic option for patients with cardiovascular and hemic and lymphatic diseases.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for dermatan sulfate: Thrombin inhibitors
Thrombin inhibitors are a type of medication that specifically target and inhibit the activity of thrombin, which is an enzyme involved in the blood clotting process. Thrombin plays a crucial role in converting fibrinogen to fibrin, the main component of blood clots. By inhibiting thrombin, these medications prevent the formation of blood clots or help dissolve existing clots.
From a biomedical perspective, thrombin inhibitors are commonly used in the treatment and prevention of various conditions related to abnormal blood clotting. They are particularly beneficial for individuals at high risk of developing blood clots, such as those with atrial fibrillation, deep vein thrombosis, or pulmonary embolism. Thrombin inhibitors can also be used during certain medical procedures, such as cardiac surgeries or angioplasty, to prevent clot formation.
There are different types of thrombin inhibitors, including direct thrombin inhibitors and indirect thrombin inhibitors. Direct thrombin inhibitors directly bind to thrombin and block its activity, while indirect thrombin inhibitors work by targeting other molecules involved in the clotting cascade, ultimately leading to reduced thrombin production.
Examples of thrombin inhibitors include medications like dabigatran, argatroban, and heparin. These drugs are typically prescribed by healthcare professionals and require careful monitoring to ensure appropriate dosing and minimize the risk of bleeding complications, which is a potential side effect of these medications.
Drug Target R&D Trends for dermatan sulfate
Thrombin is a crucial enzyme in the human body that plays a vital role in the blood clotting process, known as coagulation. It is produced from its precursor, prothrombin, and is activated in response to injury or damage to blood vessels. Thrombin acts as a catalyst in the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin, forming a mesh-like structure that helps in the formation of blood clots to prevent excessive bleeding. Additionally, thrombin also activates other factors involved in the coagulation cascade, amplifying the clotting response. Its precise regulation is essential to maintain the delicate balance between clot formation and prevention of unwanted clotting within the body.
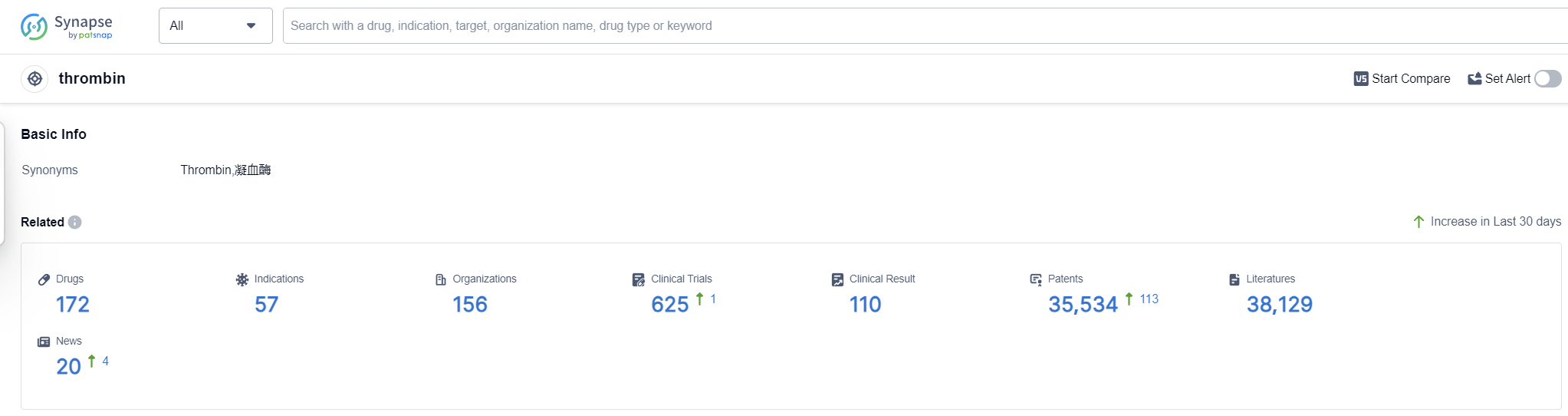
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 13 Sep 2023, there are a total of 172 thrombin drugs worldwide, from 156 organizations, covering 57 indications, and conducting 625 clinical trials.
The analysis of the current competitive landscape and future development of target thrombin reveals several key findings. Grifols SA, Hualan Biological Engineering, Inc., and Shaanxi Coal & Chemical Industry Group Co., Ltd. are the companies with the highest stage of development under this target. Hemorrhage, hemophilia B, thrombosis, and venous thromboembolism are the most common indications for drugs targeting thrombin. Non-recombinant coagulation factors, small molecule drugs, and biosimilars are the most rapidly progressing drug types. China, the United States, and the European Union are the countries/locations with the highest development under this target. China's progress in particular highlights its growing presence in the pharmaceutical industry. Overall, the analysis suggests a competitive landscape with a focus on bleeding disorders and blood clotting management.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Dermatan sulfate is a small molecule drug developed by Mediolanum Farmaceutici SpA. It targets thrombin and has been approved for use in the treatment of thrombocytopenia, thrombosis, and venous thromboembolism. Its approval in Italy in 1998 signifies its successful completion of clinical trials and its availability for patients in need. Dermatan sulfate's ability to inhibit thrombin suggests its potential in managing various cardiovascular and blood-related conditions.