Advances in Clinical Research on Cyclin-dependent Kinase Inhibitor
CDKs or cyclin-dependent kinase,are a group of enzymes that play a crucial role in regulating the cell cycle in the human body. They work in conjunction with cyclins, which are proteins that activate CDKs at specific stages of the cell cycle. CDKs control the progression of the cell cycle by phosphorylating target proteins, thereby initiating various cellular processes such as DNA replication, cell division, and cell differentiation. Dysregulation of CDK activity has been implicated in numerous diseases, including cancer, making them attractive targets for drug development. Inhibitors of CDKs have shown promise in clinical trials as potential therapeutic agents for cancer treatment.
According to the different functions of CDKs, they can be divided into two main categories:
One type of CDKs participates in cell cycle regulation and inhibits proliferation, including mainly CDK1, CDK2, CDK4, CDK6, etc.; the other type of CDKs participates in transcription regulation, mainly including CDK7, CDK8, CDK9, CDK10, CDK11, etc.
In cancer cells, changes in CDKs activity can be caused by overexpression or excessive activation of cyclin, inhibition of CDKI activity, and persistent activation of upstream mitotic signals, thus participating in the development of tumors. Since the activity of CDKs is necessary for cell division, and there is often an increase in CDKs activity in cancer cells. In clinical practice, CDKs inhibitors have become important drugs for treating cancers and other diseases.
Over the past decade, there has been significant progress in drug discovery in the field of CDKs inhibitors. The CDKs inhibitors on the market are all CDK4/6 inhibitors, namely Palbociclib, Ribociclib, Abemaciclib, and Trilaciclib, among which Palbociclib and Abemaciclib have been marketed in China.
CDKs Competitive Landscape
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 11 Oct 2023, there are a total of 28 CDKs drugs worldwide, from 34 organizations, covering 22 indications, and conducting 31 clinical trials.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or login directly if you have freemium accounts, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs , indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target.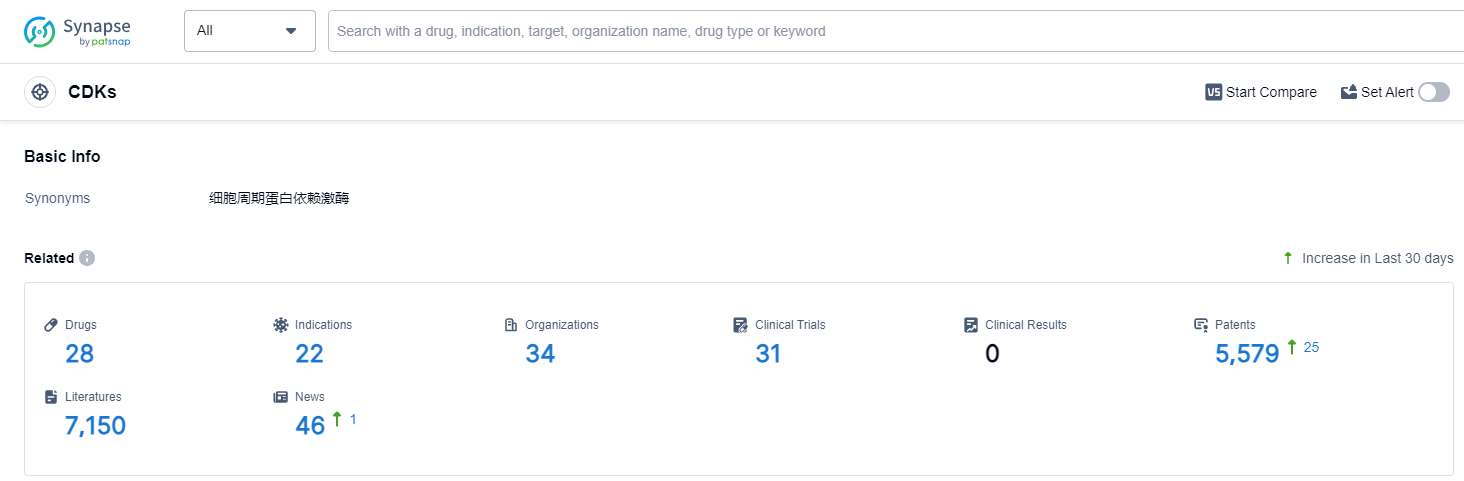
Based on the analysis of the provided data, the current competitive landscape for target CDKs shows that Ocuphire Pharma, Inc., Processa Pharmaceuticals, Inc., and Shanghai Junshi Biosciences Co., Ltd. are leading in R&D progress. Indications such as solid tumors, breast cancer, and neoplasms have the highest number of drugs in development. Small molecule drugs are progressing rapidly, indicating their significance in the development of target CDKs. The United States and China are the main countries driving the development, with China showing some progress. Further research and analysis are required to fully understand the competitive landscape and future development of target CDKs in the pharmaceutical industry.
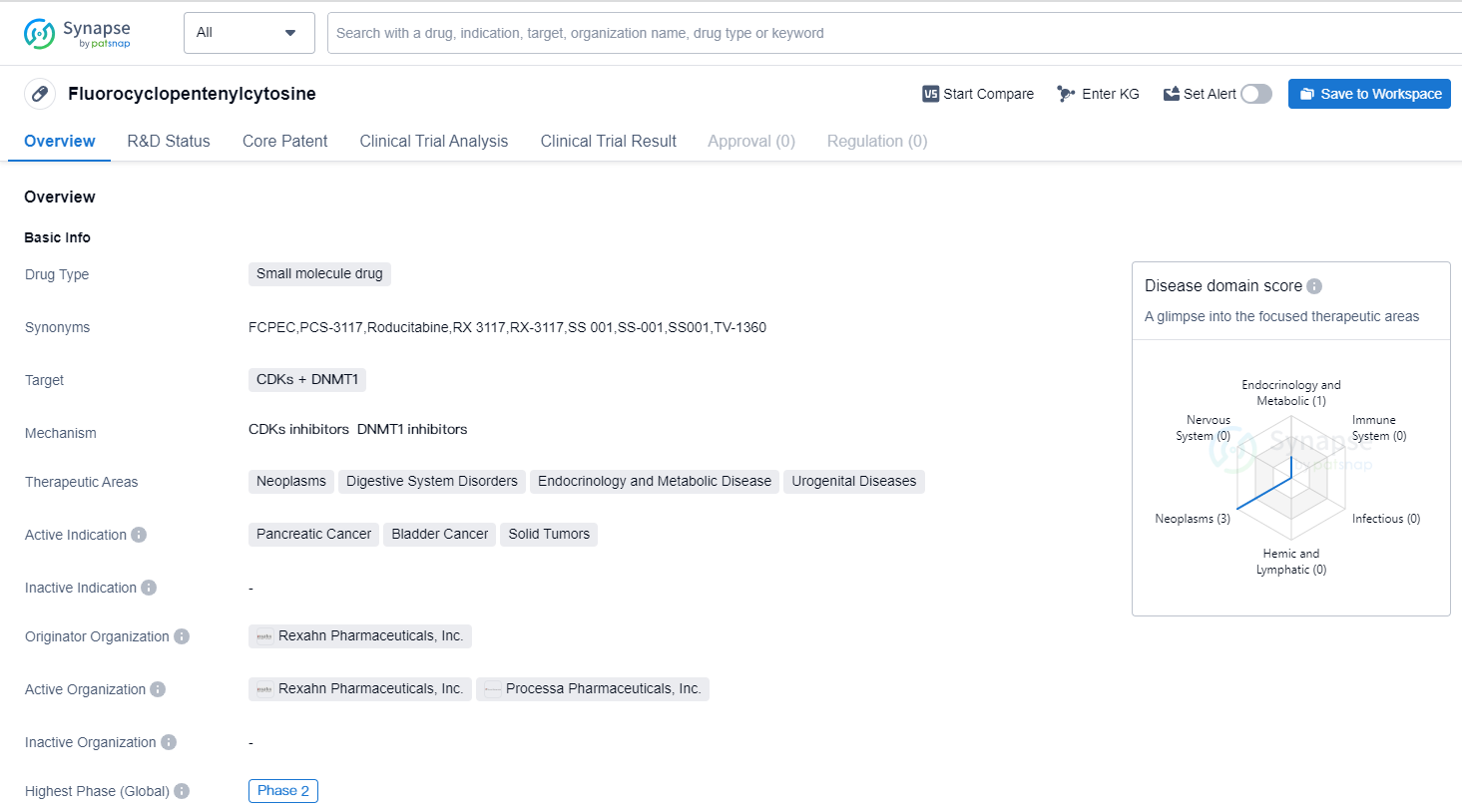
RX-3117 (fluorocyclopentenyl cytosine): a novel specific antimetabolite for selective cancer treatment
Fluorocyclopentenyl cytosine is a small molecule drug that is being developed by Rexahn Pharmaceuticals, Inc. It is designed to target CDKs (cyclin-dependent kinases) and DNMT1 (DNA methyltransferase 1). The drug is currently in Phase 2, which is the highest phase of clinical development.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
The therapeutic areas that Fluorocyclopentenylcytosine aims to address include neoplasms (abnormal growth of cells), digestive system disorders, endocrinology and metabolic diseases, and urogenital diseases. The drug's active indications are pancreatic cancer, bladder cancer, and solid tumors.
As a small molecule drug, Fluorocyclopentenylcytosine is a chemical compound with a relatively low molecular weight. This type of drug is typically orally administered and can easily penetrate cell membranes, allowing it to reach its target within the body.
CDKs are a group of enzymes that play a crucial role in regulating the cell cycle, while DNMT1 is an enzyme involved in DNA methylation, a process that can affect gene expression. By targeting both CDKs and DNMT1, Fluorocyclopentenylcytosine aims to disrupt the abnormal cell growth seen in neoplasms and potentially inhibit the progression of cancer.
Pancreatic cancer, bladder cancer, and solid tumors are all serious medical conditions with limited treatment options. The development of Fluorocyclopentenylcytosine offers hope for patients suffering from these diseases, as it may provide a new therapeutic approach.
Rexahn Pharmaceuticals, Inc. is the originator organization behind Fluorocyclopentenylcytosine. As the developer of the drug, Rexahn Pharmaceuticals is responsible for conducting clinical trials, obtaining regulatory approvals, and ultimately bringing the drug to market if it proves to be safe and effective.
In summary, Fluorocyclopentenylcytosine is a small molecule drug being developed by Rexahn Pharmaceuticals, Inc. It targets CDKs and DNMT1 and aims to treat neoplasms, digestive system disorders, endocrinology and metabolic diseases, and urogenital diseases. The drug is currently in Phase 2 of clinical development and shows promise as a potential treatment for pancreatic cancer, bladder cancer, and solid tumors.
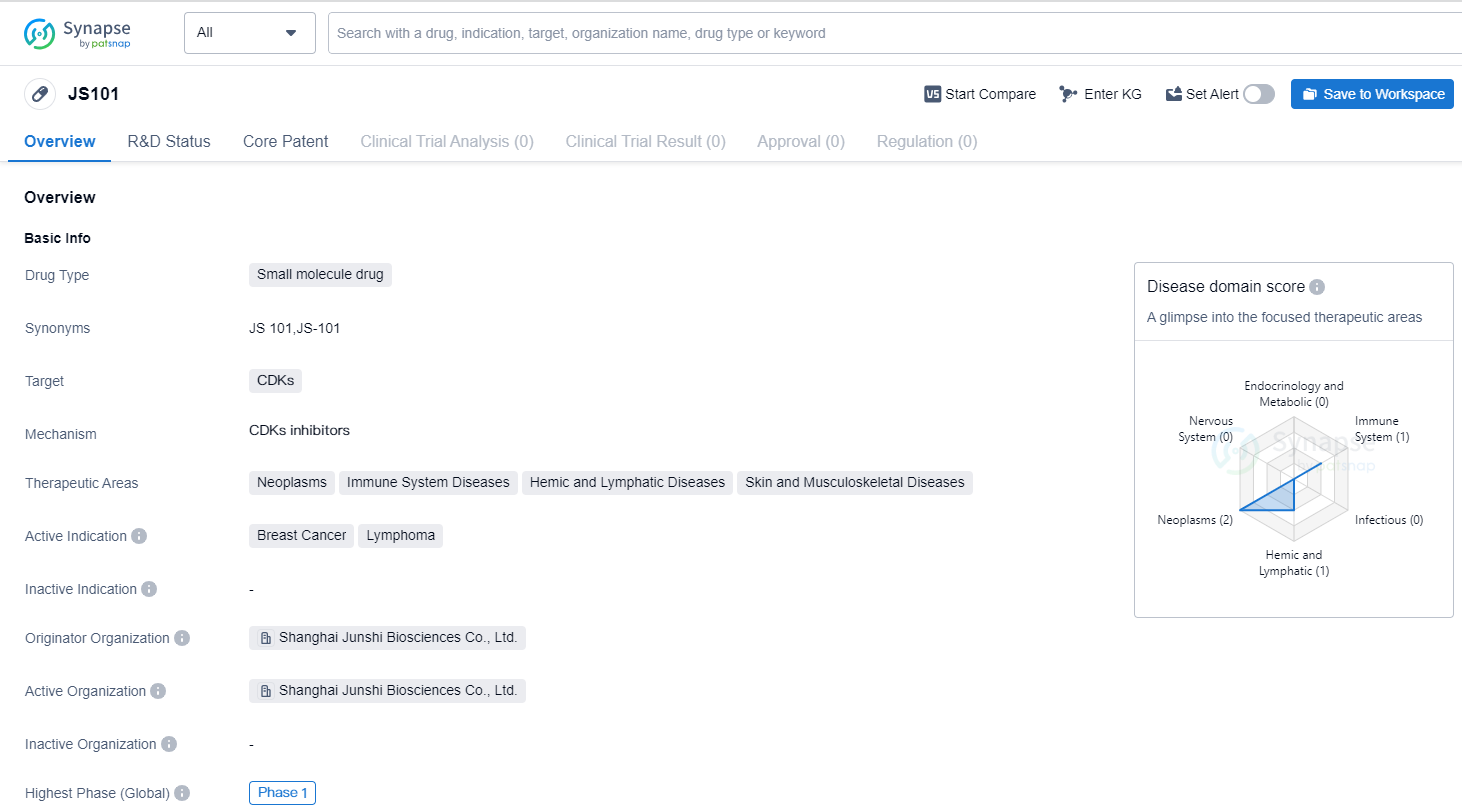
A chemical drug called JS101 that inhibits the function of cyclin-dependent kinases
JS101 is a small molecule drug developed by Shanghai Junshi Biosciences Co., Ltd. It belongs to the therapeutic area of biomedicine and specifically targets CDKs (Cyclin-Dependent Kinases). CDKs are enzymes that play a crucial role in regulating the cell cycle and are often dysregulated in various diseases, including cancer.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
The drug has shown potential in treating neoplasms, immune system diseases, hemic and lymphatic diseases, as well as skin and musculoskeletal diseases. However, its active indication is primarily focused on breast cancer and lymphoma. Breast cancer is a prevalent form of cancer that affects both men and women, while lymphoma is a type of cancer that affects the lymphatic system.
Currently, JS101 is in the highest phase of clinical development, which is Phase 1. Phase 1 trials are conducted to evaluate the safety, dosage, and potential side effects of a drug in a small group of healthy volunteers or patients. This phase is crucial in determining the drug's tolerability and establishing the appropriate dosage for further testing.
It is important to note that the highest phase mentioned refers to both global and China-specific development. This suggests that JS101 is still in the early stages of clinical trial globally. This information indicates that further research and development are required before the drug can progress to later stages of clinical trials and potentially receive regulatory approval.
In summary, JS101 is a small molecule drug developed by Shanghai Junshi Biosciences Co., Ltd. It targets CDKs and shows potential in treating various diseases, with a specific focus on breast cancer and lymphoma. Currently, the drug is in Phase 1 of clinical development, indicating that it is still in the early stages of testing. Further research and development are needed to determine its efficacy, safety, and potential for regulatory approval.