Analysis on the Clinical Research Progress of cholesterol drug
Cholesterol, also known as cholesterin, is a derivative of polycyclic hydrocarbon, widely present in animal bodies, especially abundant in brain and neural tissues. Cholesterol has multiple physiological functions. It not only participates in the formation of cell membranes, but also serves as the raw material for synthesizing bile acids, vitamin D, and steroid hormones.
Cholesterol is a waxy substance present in the blood. The body needs cholesterol to build healthy cells, but having too much cholesterol might increase your risk of heart disease.
High cholesterol can lead to fatty deposits in your blood vessels. Over time, these deposits grow, limiting the flow of blood through your arteries. These deposits can break suddenly and form a clot that causes a heart attack or stroke. High cholesterol can be genetic but is often preventable and treatable, caused mainly by unhealthy lifestyle habits. A healthy diet, regular exercise, and sometimes medication can help reduce high cholesterol.
HMG-CoA Reductase is the rate-limiting enzyme in the biosynthesis of cholesterol in the body, catalyzing the substrate HMG-CoA to produce mevalonic acid. This is the rate-limiting step in the in vivo synthesis of cholesterol. HMG-CoA reductase is an important target of lipid-regulating drugs.
Inhibitors of HMG-CoA reductase have similar structural fragments to the substrate HMG-CoA. The affinity of inhibitors for HMG-CoA reductase is greater than that of the substrate. They can inhibit HMG-CoA reductase to produce mevalonic acid, which reduces the synthesis and content of cholesterol in the body, helping to reduce cholesterol, especially low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol is a leading cause of atherosclerosis. Lowering it can slow the progression of atherosclerotic disease, thereby preventing and treating cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases.
HMG-CoA Reductase Competitive Landscape
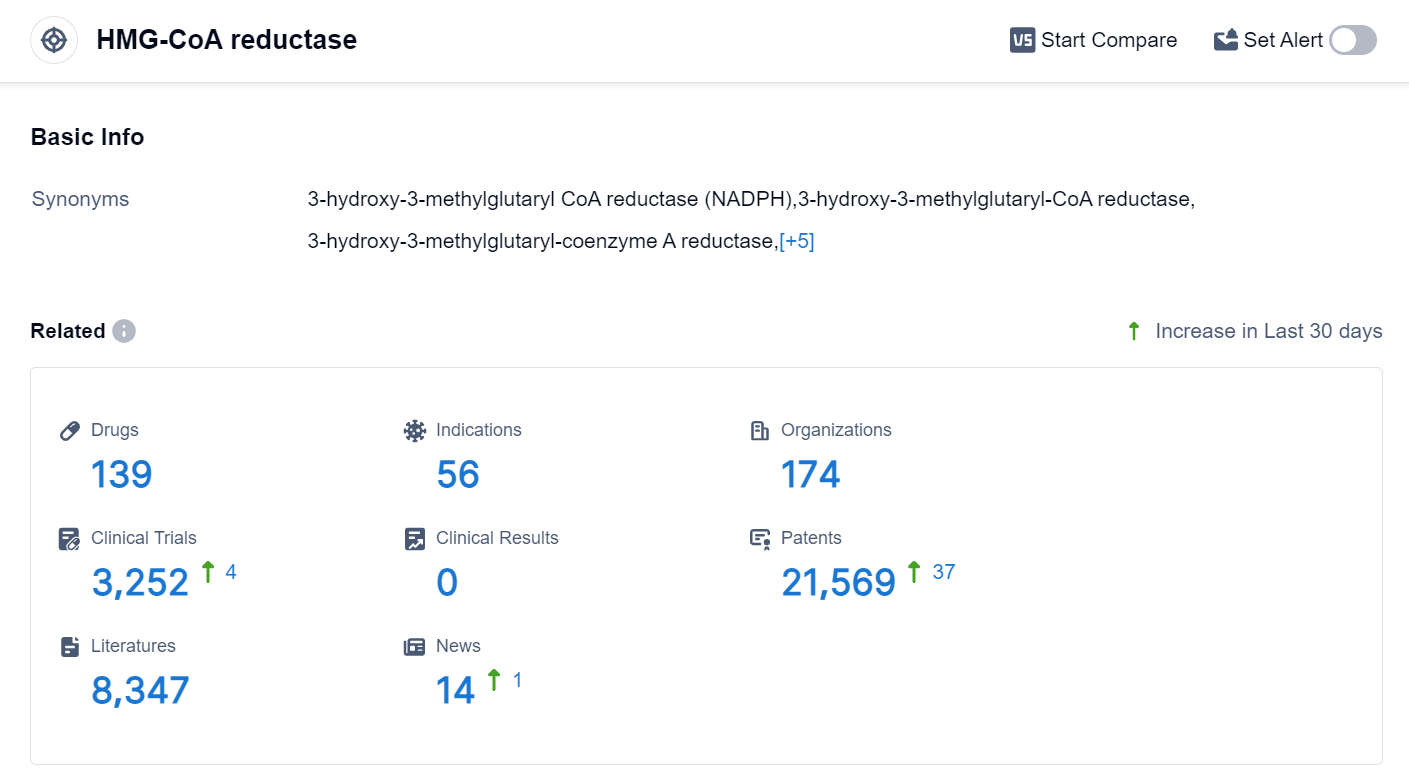
According to the data provided by Patsnap Synapse-Global Drug Intelligence Database: the following figure shows that as of 25 Sep 2023, there are a total of 139 HMG-CoA reductase drugs worldwide, from 174 organizations, covering 56 indications, and conducting 3252 clinical trials.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or login directly if you have freemium accounts, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs , indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target.
The analysis of the target HMG-CoA reductase reveals a competitive landscape with multiple companies making progress in their research and development efforts. Merck & Co., Inc., Hanmi Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and Organon & Co. have shown significant growth with multiple approved drugs. The most common indications for drugs targeting HMG-CoA reductase are hyperlipidemias, dyslipidemias, and hypertension. Small molecule drugs dominate the drug type analysis, indicating their effectiveness and widespread use. South Korea, the United States, and the European Union are leading in terms of the number of approved drugs, with China also making progress in this field. Overall, the target HMG-CoA reductase presents a competitive landscape with promising future development potential.
The globally approved HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor on the market: Simvastatin
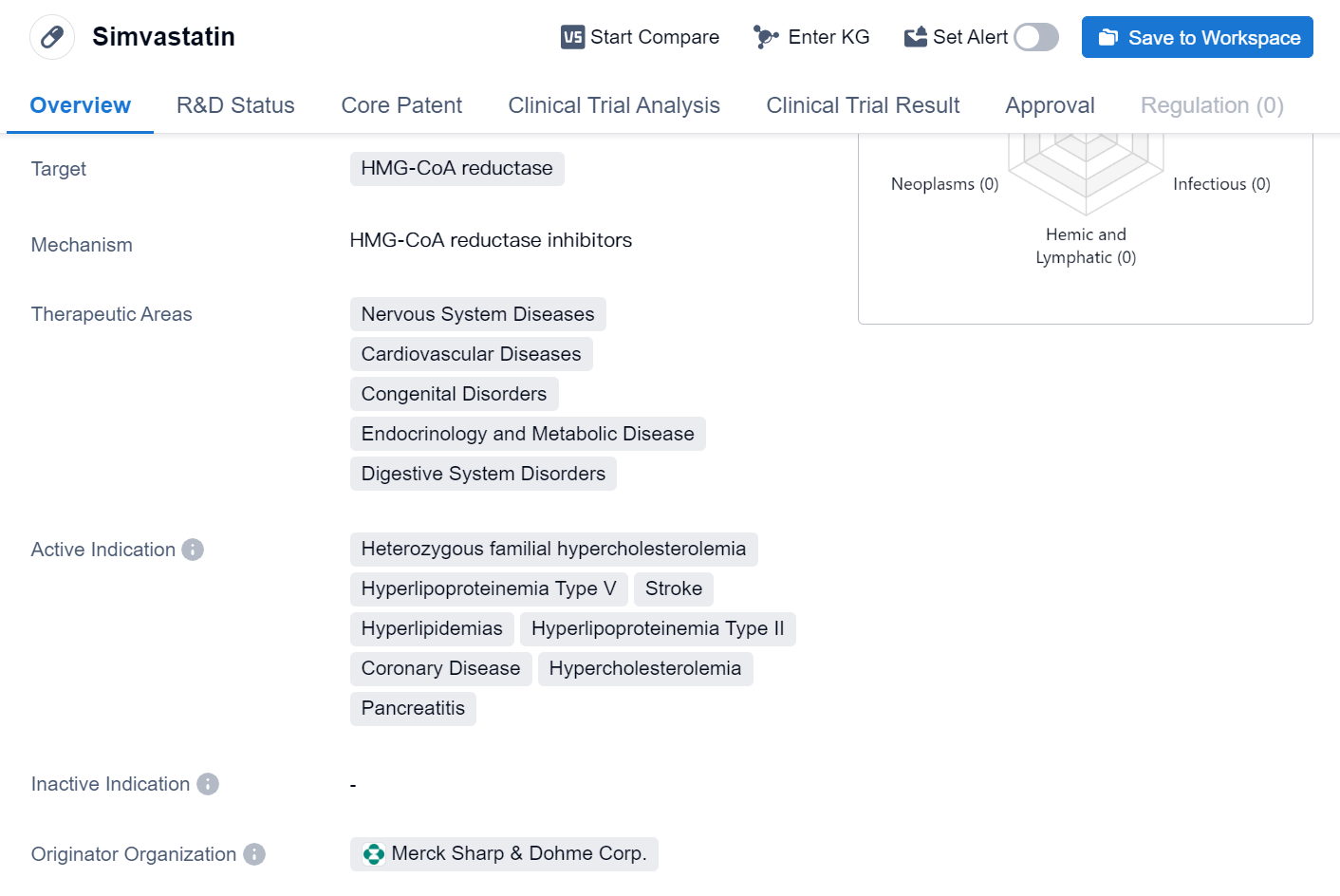
Simvastatin is a small molecule drug that belongs to the class of statins. It primarily targets HMG-CoA reductase, an enzyme involved in cholesterol synthesis. This drug has been approved for various therapeutic areas, including Nervous System Diseases, Cardiovascular Diseases, Congenital Disorders, Endocrinology and Metabolic Disease, and Digestive System Disorders.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Simvastatin is indicated for the treatment of several conditions, including Heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia, Hyperlipoproteinemia Type V, Stroke, Hyperlipidemias, Hyperlipoproteinemia Type II, Coronary Disease, Hypercholesterolemia, and Pancreatitis. These indications highlight the drug's effectiveness in managing cholesterol levels and reducing the risk of cardiovascular events.
The originator organization of Simvastatin is Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. This pharmaceutical company played a crucial role in the development and commercialization of the drug. Simvastatin has achieved the highest phase of approval globally.
Simvastatin was first approved globally in January 1988. Since then, it has been widely used in clinical practice and has become a cornerstone in the management of hyperlipidemia and related disorders. The drug's long history of use and approval demonstrates its established position in the pharmaceutical market.
In summary, Simvastatin is a small molecule drug that targets HMG-CoA reductase and is approved for various therapeutic areas, including Nervous System Diseases, Cardiovascular Diseases, Congenital Disorders, Endocrinology and Metabolic Disease, and Digestive System Disorders. It is indicated for the treatment of conditions such as hyperlipidemia, hypercholesterolemia, and coronary disease. Developed by Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., Simvastatin has achieved the highest phase of approval globally and in China. Its first approval dates back to January 1988, highlighting its long-standing presence in the pharmaceutical market.