Analysis on the Clinical Research Progress of MAO-B inhibitors
Monoamine oxidase-B (MAO-B) is an enzyme found in the human body that plays a crucial role in the metabolism of neurotransmitters such as dopamine. It specifically breaks down excess dopamine, preventing its accumulation and maintaining a balance in the brain. By regulating dopamine levels, MAO-B helps to control various neurological functions, including mood, cognition, and movement. Dysfunction or inhibition of MAO-B has been linked to neurodegenerative disorders like Parkinson's disease, as well as psychiatric conditions such as depression and anxiety. Understanding the role of MAO-B is essential for developing therapeutic interventions that target this enzyme to treat these disorders effectively.
MAO-B Competitive Landscape
According to the data provided by Patsnap Synapse-Global Drug Intelligence Database: the following figure shows that as of 20 Sep 2023, there are a total of 54 MAO-B drugs worldwide, from 57 organizations, covering 42 indications, and conducting 244 clinical trials.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or login directly if you have freemium accounts, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs , indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target.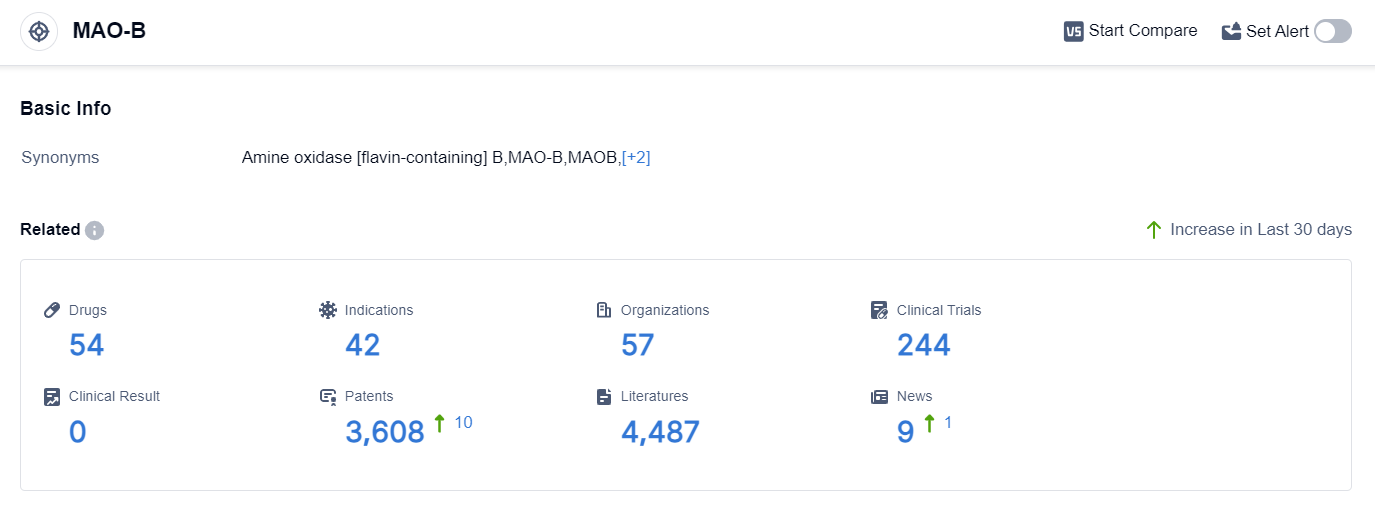
The analysis of the current competitive landscape of target MAO-B reveals that Viatris Inc., Newron Pharmaceuticals SpA, Zambon Company SpA, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., and FP Pharmaceutical Corporation are the companies growing fastest.
Parkinson Disease is the most targeted indication, followed by Depressive Disorder, Major, and Alzheimer Disease. Small molecule drugs are progressing rapidly, indicating intense competition.
The United States, Japan, and the European Union are leading in the development of drugs targeting MAO-B, with China also making progress. The future development of target MAO-B is promising, with ongoing research and development efforts by various companies and countries.
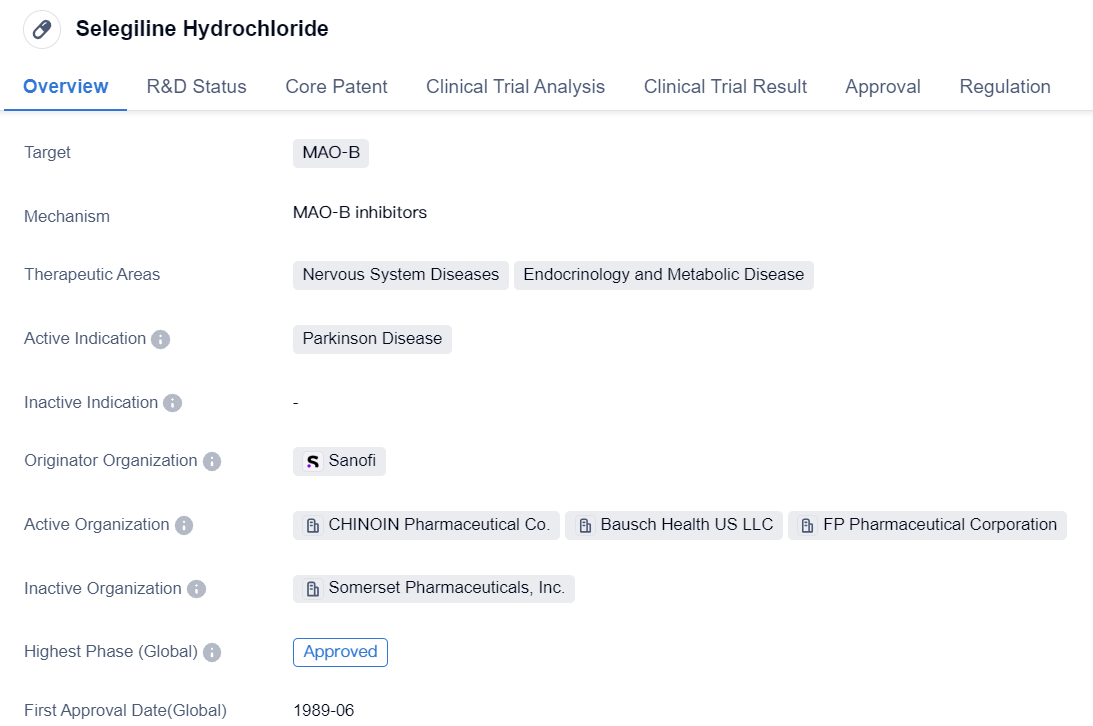
First Generation of Monoamine Oxidase B (MAO-B) Inhibitors: Selegiline Hydrochloride
Selegiline Hydrochloride is a small molecule drug that primarily targets MAO-B. It is used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease, a nervous system disorder characterized by tremors, stiffness, and difficulty with movement. The drug is also indicated for certain endocrinology and metabolic diseases.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
The drug was first approved for use in the United States in June 1989, making it a well-established treatment option for Parkinson's disease. It is worth noting that Selegiline Hydrochloride has received orphan drug status, indicating that it is used to treat rare diseases or conditions.
The originator organization of Selegiline Hydrochloride is Sanofi, a multinational pharmaceutical company. Sanofi has played a significant role in the development and commercialization of this drug.
Selegiline Hydrochloride has reached the highest phase of development, with global approval. This means that it has successfully undergone clinical trials and met the necessary regulatory requirements for market authorization. The drug has also received approval in China, further expanding its availability to patients.
As a small molecule drug targeting MAO-B, Selegiline Hydrochloride works by inhibiting the activity of this enzyme. By doing so, it helps to increase the levels of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, such as dopamine, which are essential for proper nerve cell communication. This mechanism of action is particularly beneficial for individuals with Parkinson's disease, as the condition is associated with a deficiency of dopamine.
In summary, Selegiline Hydrochloride is a small molecule drug developed by Sanofi. It is primarily used for the treatment of Parkinson's disease and has received global and Chinese approval. The drug targets the enzyme MAO-B and has been granted orphan drug status. Its approval in 1989 in the United States signifies its long-standing presence in the market as an effective treatment option for Parkinson's disease.
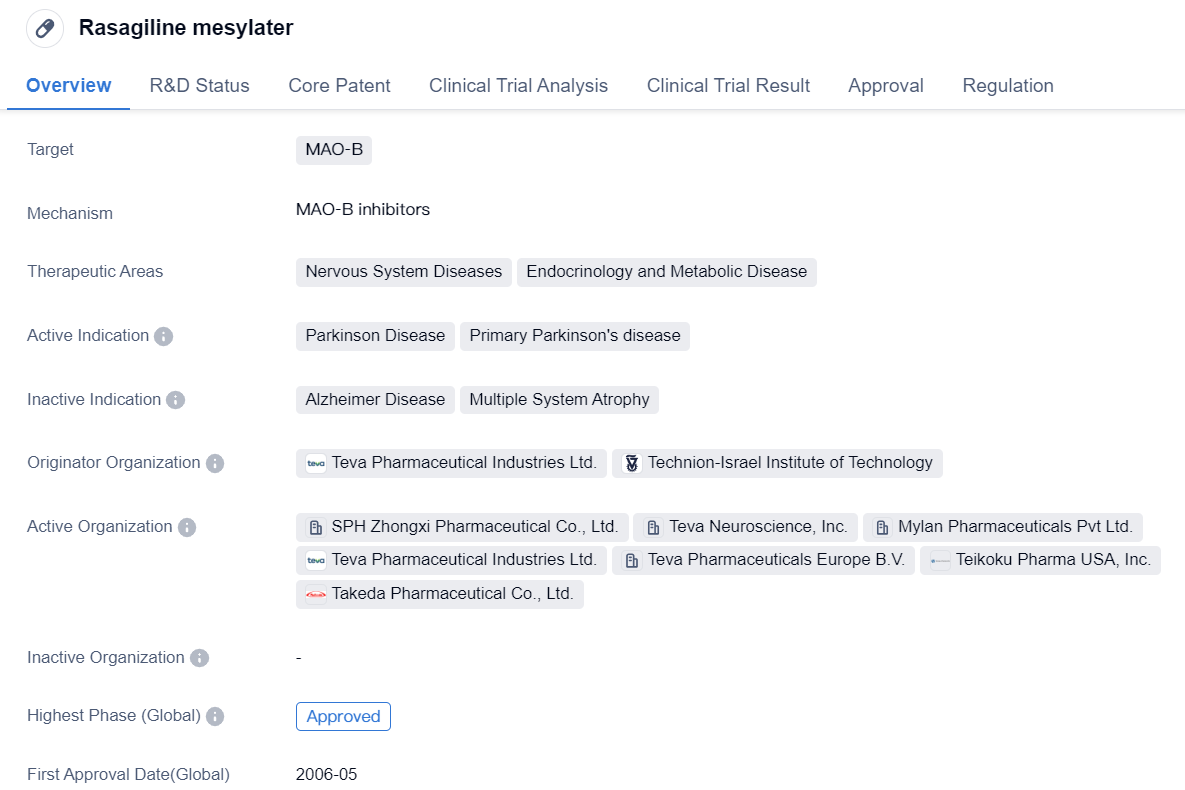
Second-generation MAO-B inhibitors: Rasagiline mesylate
Rasagiline mesylate is a small molecule drug that primarily targets MAO-B. It is used in the treatment of nervous system diseases and endocrinology and metabolic diseases. Specifically, it is indicated for the management of Parkinson's disease, particularly primary Parkinson's disease.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
The drug was developed by Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. in collaboration with the Technion-Israel Institute of Technology. It received its first approval in the United States in May 2006, making it available for use in patients. The approval process for Rasagiline mesylate involved priority review, indicating that it was considered a high-priority drug due to its potential therapeutic benefits.
Rasagiline mesylate has successfully completed the highest phase of clinical trials, both globally and in China, leading to its approval in these regions. This suggests that the drug has demonstrated its safety and efficacy in treating Parkinson's disease, meeting the regulatory requirements set by the respective authorities.
As a small molecule drug, Rasagiline mesylate is designed to interact with the MAO-B enzyme, which plays a role in the breakdown of certain neurotransmitters in the brain. By inhibiting MAO-B, the drug helps to increase the levels of these neurotransmitters, thereby improving the symptoms associated with Parkinson's disease.
The approval of Rasagiline mesylate represents a significant milestone in the treatment of Parkinson's disease, providing patients with an additional therapeutic option. The drug's success in clinical trials and subsequent approval highlights its potential to address the unmet medical needs of individuals suffering from this debilitating neurological disorder.
In summary, Rasagiline mesylate is a small molecule drug that targets MAO-B and is approved for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Developed by Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. and the Technion-Israel Institute of Technology, it has successfully completed clinical trials and received regulatory approval in the United States and China. Its approval signifies its potential to improve the lives of patients with Parkinson's disease, offering a new treatment option in the field of biomedicine.