Analysis on the Research Progress of D2 Receptor Agonist
The D2 receptor is a type of dopamine receptor found in the human body. It plays a crucial role in various physiological and neurological processes. The D2 receptor is a postsynaptic receptor that is highly expressed in the striatum. Activation of D2R can lead to signal pathways related to cell differentiation, growth, metabolism, and apoptosis. D2R also plays an important role in dopaminergic neurotransmission and motor control.
As a G-protein coupled receptor, the D2 receptor is involved in the regulation of dopamine neurotransmission, which affects mood, motivation, and reward. Dysfunction of the D2 receptor has been implicated in several psychiatric disorders, including schizophrenia and addiction. Additionally, the D2 receptor is a target for antipsychotic medications, which work by blocking its activity to alleviate symptoms associated with psychosis. Understanding the role of the D2 receptor is essential for developing therapeutic interventions for psychiatric and neurological conditions.
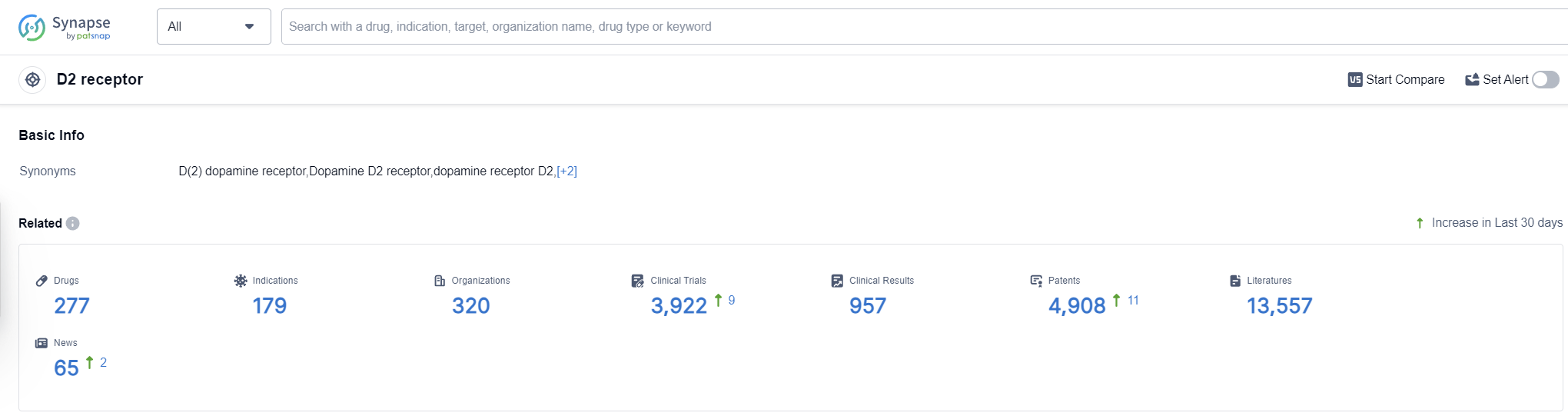
D2 receptor Competitive Landscape
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 14 Oct 2023, there are a total of 277 D2 receptor drugs worldwide, from 320 organizations, covering 179 indications, and conducting 3922 clinical trials.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or login directly if you have freemium accounts, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs , indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target.
The analysis of the target D2 receptor reveals a competitive landscape with multiple companies making progress in the development of drugs. Johnson & Johnson, Mitsubishi Chemical Group Corp., and Novartis AG have shown the highest stage of development, with multiple approved drugs. The most common indications for approved drugs are schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, bipolar I disorder, and Parkinson's disease.
Small molecule drugs dominate the development pipeline, indicating intense competition around innovative drugs. Synthetic peptides and fusion proteins also show some progress. The United States, Japan, China, and the European Union are the leading countries/locations in the development of drugs targeting the D2 receptor, with China showing significant progress.
Overall, the target D2 receptor presents opportunities for further research and development, particularly in indications such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and Parkinson's disease. The competitive landscape is dynamic, with companies and countries actively contributing to the advancement of drugs targeting the D2 receptor.
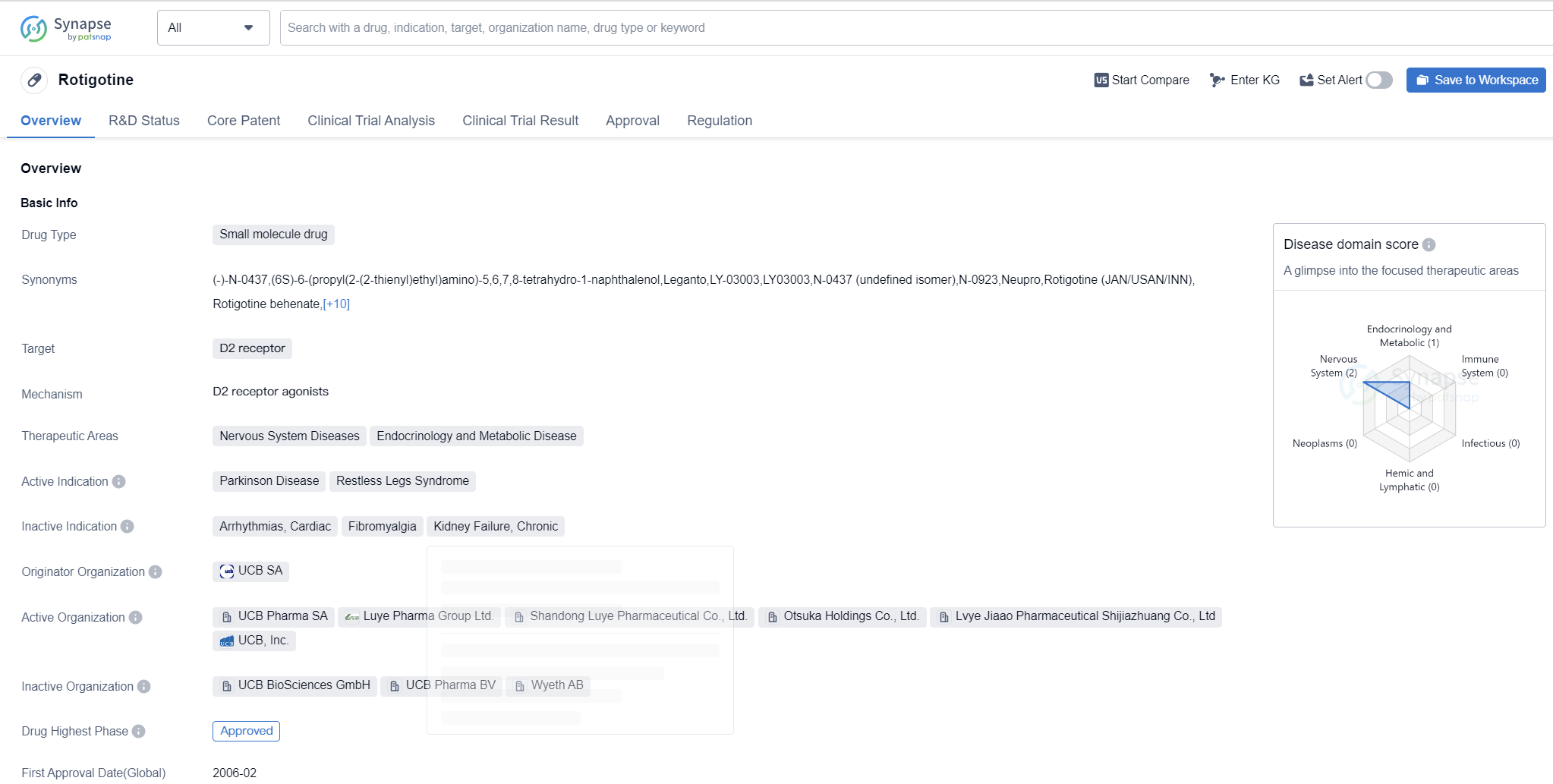
The world's only transdermal patch for Parkinson's: Rotigotine
Rotigotine is a small molecule drug that targets the D2 receptor. It is primarily used in the treatment of nervous system diseases and endocrinology and metabolic diseases. The drug has been approved for the treatment of Parkinson's disease and restless legs syndrome.
Rotigotine was first approved in the European Union in February 2006. It is developed by UCB SA, a pharmaceutical company specializing in the research and development of innovative medicines. The drug has also received approval in China.
The approval of Rotigotine in both the European Union and China indicates its efficacy and safety in treating Parkinson's disease and restless legs syndrome. The drug's mechanism of action involves targeting the D2 receptor, which is involved in the regulation of movement and mood.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
The therapeutic areas of nervous system diseases and endocrinology and metabolic diseases encompass a wide range of conditions, including neurological disorders and hormonal imbalances. Rotigotine's approval in these therapeutic areas suggests its potential to address various medical needs within these fields.
The fact that Rotigotine has reached the highest phase of development, which is approved, indicates that it has successfully undergone rigorous clinical trials and met the necessary regulatory requirements. The drug's approval status also suggests that it has demonstrated significant efficacy and safety in treating Parkinson's disease and restless legs syndrome.
The priority review designation further highlights the importance and potential impact of Rotigotine in the pharmaceutical industry. This designation is typically granted to drugs that address unmet medical needs or provide significant advancements in treatment options.
In summary, Rotigotine is a small molecule drug that targets the D2 receptor and is approved for the treatment of Parkinson's disease and restless legs syndrome. Developed by UCB SA, the drug has received approval in both the European Union and China. Its approval status and priority review designation indicate its efficacy and potential impact in the field of biomedicine.
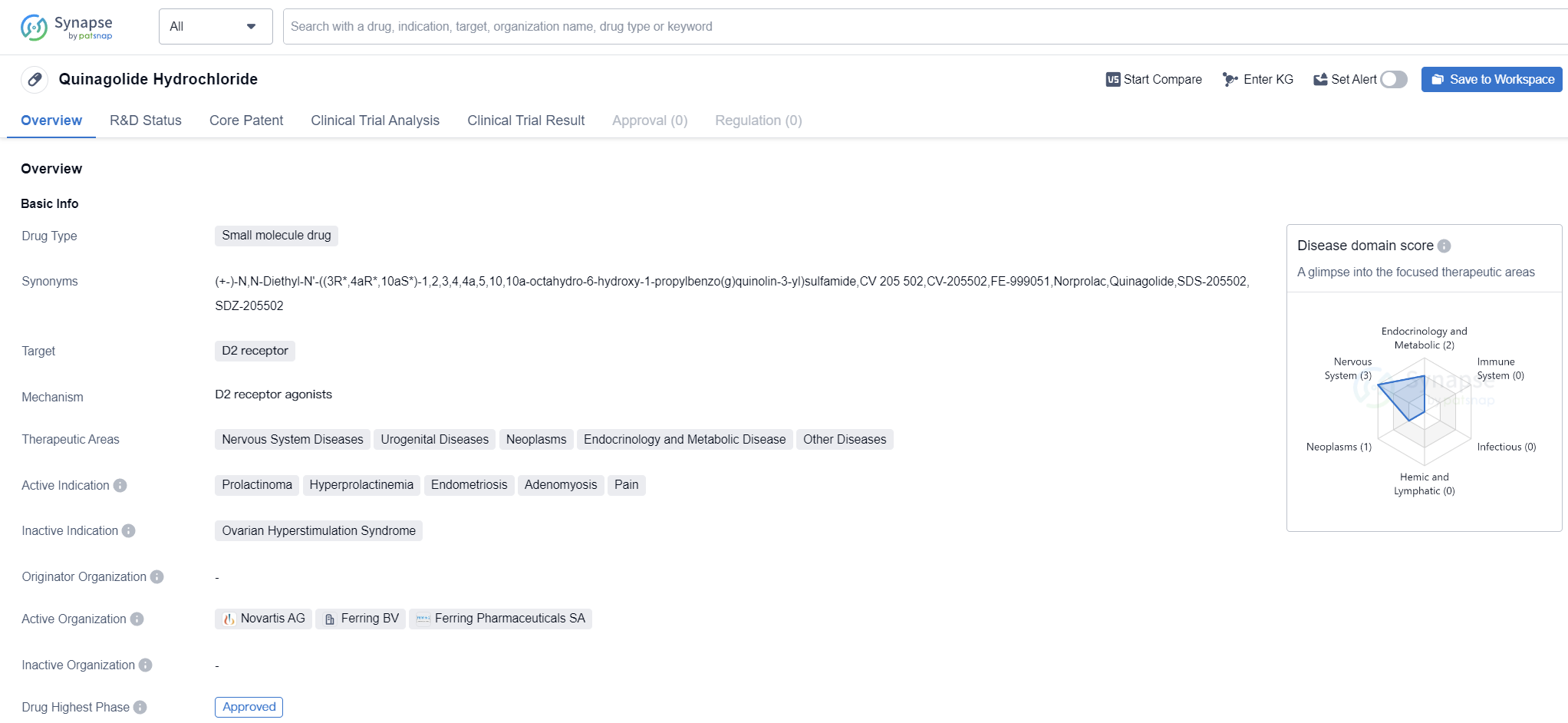
Quinagolide Hydrochloride
Quinagolide Hydrochloride is a small molecule drug that primarily targets the D2 receptor. It has been approved for use in the treatment of various diseases related to the nervous system, urogenital system, neoplasms, endocrinology, metabolic diseases, and other conditions. The drug has shown efficacy in treating specific indications such as prolactinoma, hyperprolactinemia, endometriosis, adenomyosis, and pain.
Quinagolide Hydrochloride received its first global approval in September 1997 in South Africa. Since then, it has been used in clinical settings to address the aforementioned conditions. As a small molecule drug, it is designed to interact with the D2 receptor, which plays a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Prolactinoma, a condition characterized by the overproduction of prolactin hormone, can lead to infertility, menstrual irregularities, and other complications. Quinagolide Hydrochloride has been found to effectively reduce prolactin levels, thereby alleviating the symptoms associated with this condition.
Hyperprolactinemia, a condition characterized by abnormally high levels of prolactin hormone, can also be effectively managed with Quinagolide Hydrochloride. By targeting the D2 receptor, the drug helps regulate prolactin secretion, restoring hormonal balance and improving patient outcomes.
Endometriosis and adenomyosis are conditions that affect the female reproductive system, causing pain, inflammation, and fertility issues. Quinagolide Hydrochloride has shown promise in managing these conditions by reducing pain and inflammation, improving quality of life, and potentially preserving fertility.
Additionally, Quinagolide Hydrochloride has demonstrated potential in the treatment of various neoplasms, endocrinology, metabolic diseases, and other conditions. However, further research and clinical trials are needed to fully understand its efficacy and safety profile in these areas.
Overall, Quinagolide Hydrochloride is an approved small molecule drug that targets the D2 receptor. It has shown effectiveness in treating various conditions related to the nervous system, urogenital system, neoplasms, endocrinology, metabolic diseases, and other diseases. Its approval in South Africa in 1997 marked an important milestone in the pharmaceutical industry, providing healthcare professionals with a valuable tool in managing specific indications such as prolactinoma, hyperprolactinemia, endometriosis, adenomyosis, and pain.