CDK7 inhibitor - potential treatment strategy for multiple tumors
CDK7 is a member of the cell cycle-dependent kinase (CDK) family, and a subunit of the multiprotein basal transcription factor TFIIH. It is a major regulator of cell cycle progression and gene transcription and has now become a potential hot target in cancer drug research. During the cell cycle, CDK7 forms a cell cycle kinase (CAK) after binding with cyclin H and activating subunit MAT1, and controls cells, especially cancer cells' cell cycle, by activating other kinases in the family (such as CDK1/2/4/6). CDK7 also participates in the formation of the multiprotein basal transcription factor TFIIH, playing a key role in transcription and regulation of the cell cycle, and is associated with various types of tumors driven by genes with abnormal transcription control (such as MYC and ESR1 activation) and/or abnormal cell cycle control (such as changes in RB1, CCNE1, CDKN2A).
Research indicates that the growth and proliferation of various tumor cells are highly dependent on CDK7, including triple-negative breast cancer, recurrent or refractory ovarian cancer, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, and blood tumors. Therefore, CDK7 inhibitors are expected to become a potential treatment for these tumors. At present, no CDK7 inhibitors have been approved for marketing globally, and the enormous clinical demand remains unmet.
CDK7 Competitive Landscape
According to the data provided by Patsnap Synapse-Global Drug Intelligence Database: the following figure shows that as of 10 Sep 2023, there are a total of 29 CDK7 drugs worldwide, from 37 organizations, covering 52 indications, and conducting 47 clinical trials.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or login directly if you have freemium accounts, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs , indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target.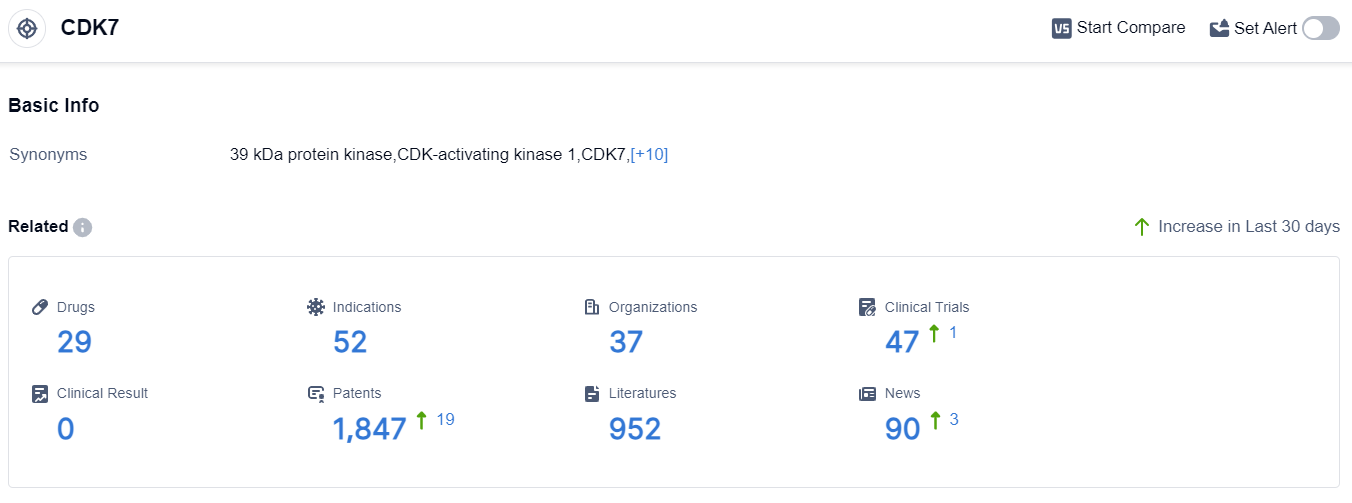
The analysis of the target CDK7 reveals a competitive landscape with multiple companies and institutions actively involved in R&D. The highest stage of development is Phase 2, indicating progress towards clinical trials.
Indications such as breast cancer, small cell lung cancer, and ovarian cancer show potential for CDK7 inhibitors. Small molecule drugs dominate the drug types, indicating intense competition.
The United States, United Kingdom, and China are leading in terms of R&D progress, with other countries also contributing to the development of CDK7 inhibitors. Overall, the target CDK7 presents a promising opportunity for the pharmaceutical industry, with potential for innovative treatments in various indications.
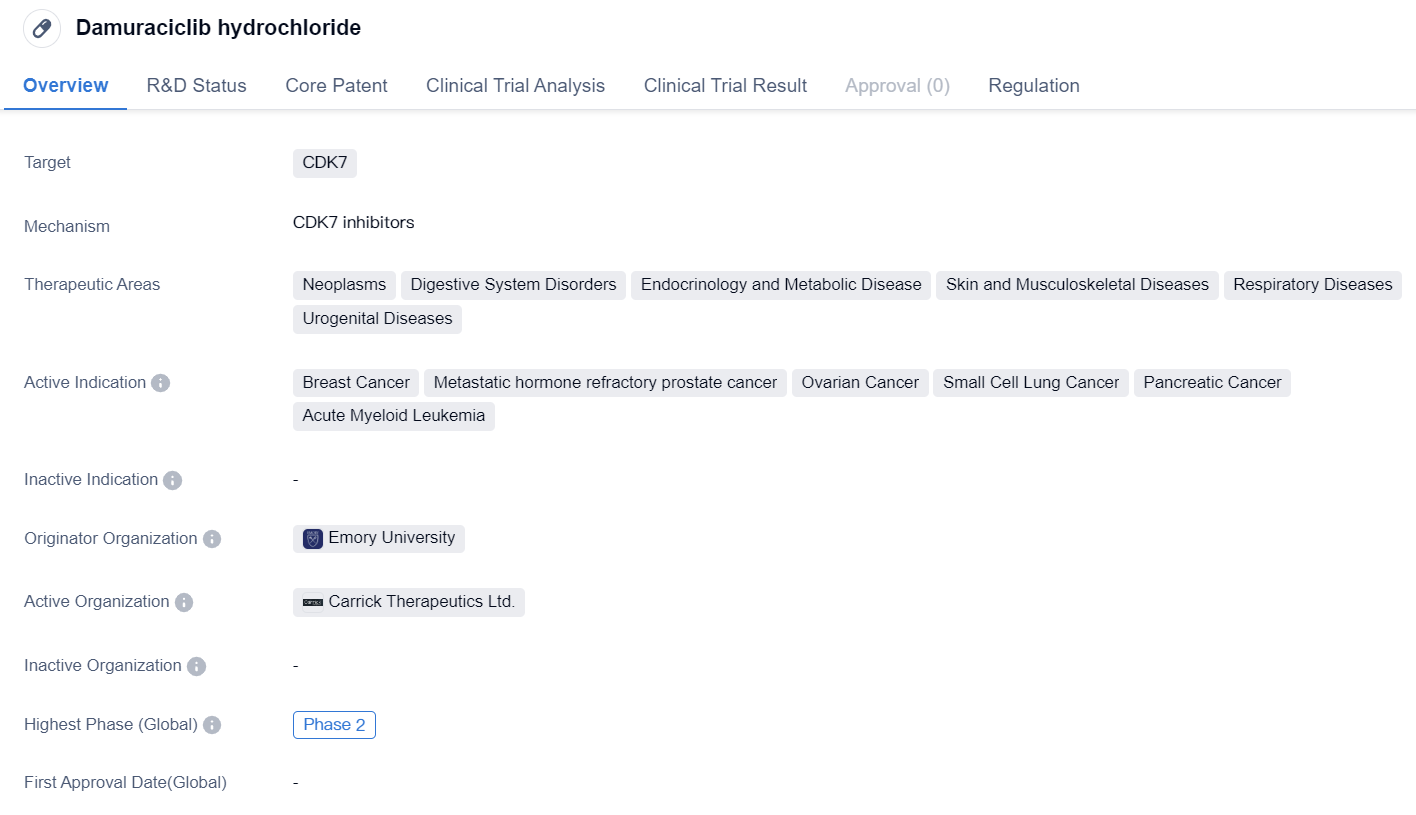
CDK7 Inhibitor Entering Clinical Phase II:Damuraciclib hydrochloride
Damuraciclib hydrochloride is a small molecule drug that targets CDK7, a protein involved in cell cycle regulation. It has shown potential therapeutic benefits in various therapeutic areas including neoplasms, digestive system disorders, endocrinology and metabolic disease, skin and musculoskeletal diseases, respiratory diseases, and urogenital diseases. The drug has been specifically indicated for the treatment of breast cancer, metastatic hormone refractory prostate cancer, ovarian cancer, small cell lung cancer, pancreatic cancer, and acute myeloid leukemia.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
The originator organization of Damuraciclib hydrochloride is Emory University, indicating that it was developed by researchers affiliated with this institution. Currently, the drug has reached Phase 2 of clinical development. This suggests that it has already undergone initial testing for safety and efficacy in a relatively small group of patients and has shown promising results.
In terms of regulation, Damuraciclib hydrochloride has been granted Fast Track designation. This regulatory status is typically given to drugs that address unmet medical needs and have the potential to significantly improve patient outcomes. Fast Track designation expedites the development and review process of the drug, allowing it to reach the market more quickly.
Based on the available information, Damuraciclib hydrochloride appears to be a promising drug candidate in the field of biomedicine. Its specific targeting of CDK7 and its potential therapeutic benefits in various diseases make it an attractive option for further development. The fact that it has reached Phase 2 of clinical development indicates that it has already shown promising results in early testing. The Fast Track designation further highlights the potential significance of this drug in addressing unmet medical needs. However, it is important to note that further research and clinical trials are necessary to fully evaluate the safety and efficacy of Damuraciclib hydrochloride before it can be approved for widespread use.
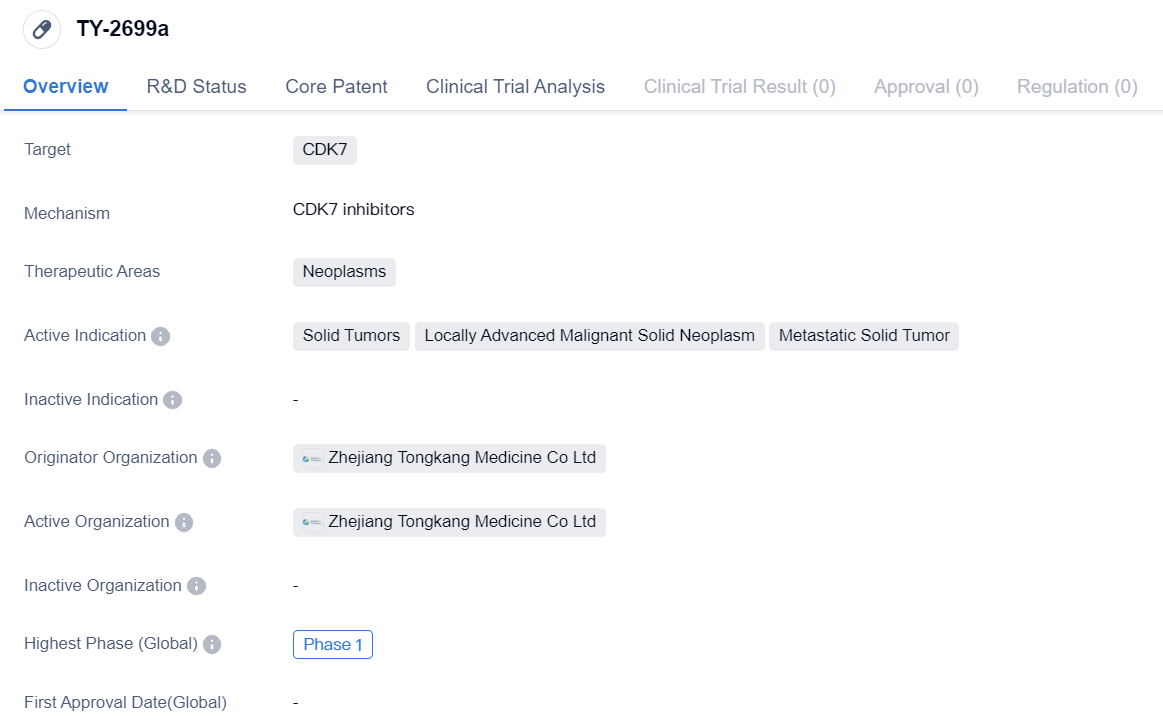
CDK7 Inhibitor Entering into Phase I Clinical Trials:TY-2699a
TY-2699a is a small molecule drug that falls under the therapeutic area of neoplasms. It specifically targets CDK7, a protein involved in cell cycle regulation. The drug is primarily intended for the treatment of solid tumors, including locally advanced malignant solid neoplasms and metastatic solid tumors.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
The originator organization of TY-2699a is Zhejiang Tongkang Medicine Co Ltd, a pharmaceutical company based in China. As of the latest available information, the drug has reached Phase 1 of clinical development, both globally and in China.
Phase 1 is the initial stage of clinical trials, where the drug is tested on a small group of healthy volunteers or patients to evaluate its safety, dosage, and potential side effects. This phase aims to determine the drug's pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, as well as its tolerability in humans.
TY-2699a's specific mechanism of action and potential efficacy in treating neoplasms are not provided in the given information. However, as a CDK7 inhibitor, it is likely that the drug works by inhibiting the activity of CDK7, which plays a crucial role in cell division and proliferation. By targeting CDK7, TY-2699a may disrupt the abnormal growth and division of cancer cells, potentially leading to tumor regression or inhibition of tumor growth.
Since TY-2699a is still in Phase 1, it is important to note that further clinical trials and regulatory approvals are required before the drug can be made available to patients. The information provided does not include any data on the drug's efficacy, safety profile, or potential side effects. Therefore, it is necessary to await the results of future clinical trials to determine the drug's potential as a treatment option for solid tumors.
In summary, TY-2699a is a small molecule drug developed by Zhejiang Tongkang Medicine Co Ltd, targeting CDK7 in the therapeutic area of neoplasms. It is currently in Phase 1 of clinical development, with a focus on treating solid tumors, including locally advanced malignant solid neoplasms and metastatic solid tumors. Further research and clinical trials are needed to assess the drug's efficacy, safety, and potential as a treatment option for patients with solid tumors.