Deciphera announces positive top line results from pivotal Phase 3 trial of vimseltinib in treatment of Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumors
Recently, Deciphera Pharmaceutical announced the positive top-line results of its investigational drug vimseltinib in the pivotal Phase 3 MOTION trial for patients with Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumor (TGCT). The analysis showed that the trial met its primary endpoint, with a statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvement in the Objective Response Rate (ORR) in patients treated with vimseltinib.
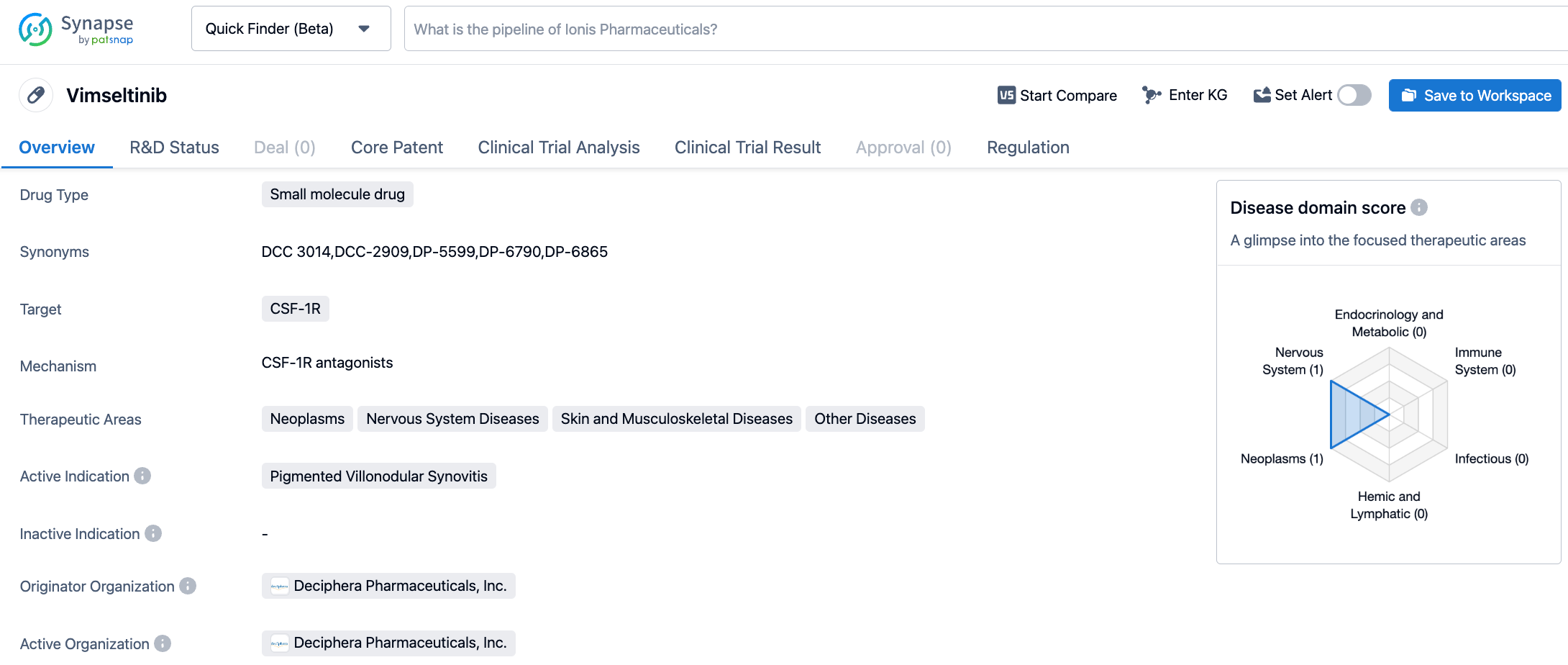
Vimseltinib (DCC-3014) is a potent, highly selective, orally administered CSF-1R kinase inhibitor developed by Deciphera Pharmaceutical. It works by utilizing the unique features of the switch control region activated by kinase conformation to selectively and effectively inhibit CSF-1R, for the treatment of conditions such as Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumor (Phase 3), Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis (Phase 3), and Solid Tumors (Phase 2). Preclinical studies showed that vimseltinib persistently inhibited CSF-1R activity both in vitro and in vivo, depleted macrophages and other cells dependent on CSF-1R, and led to the inhibition of tumor growth and bone degradation in mouse cancer models. In a Phase I clinical study, vimseltinib demonstrated its ability to modulate biomarkers of CSF-1R inhibition and reduce tumor burden in TGCT patients.
The pivotal Phase 3 MOTION trial is a two-part, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study designed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of vimseltinib in patients with TGCT who have not previously received anti-CSF1/CSF1R therapy and cannot undergo surgery. The analysis showed that the study met its primary endpoint in the intent-to-treat (ITT) population, with results from a blinded, independent radiology review (IRR) using RECIST 1.1 showing statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvements in ORR at week 25 compared to placebo. In the ITT population, the ORR in the vimseltinib group at week 25 was 40% (95% CI: 29%-51%), compared to 0% (95% CI: 0%-9%) in the placebo group, with a difference in response of 40% (95% CI: 29%-51%, p<0.0001).
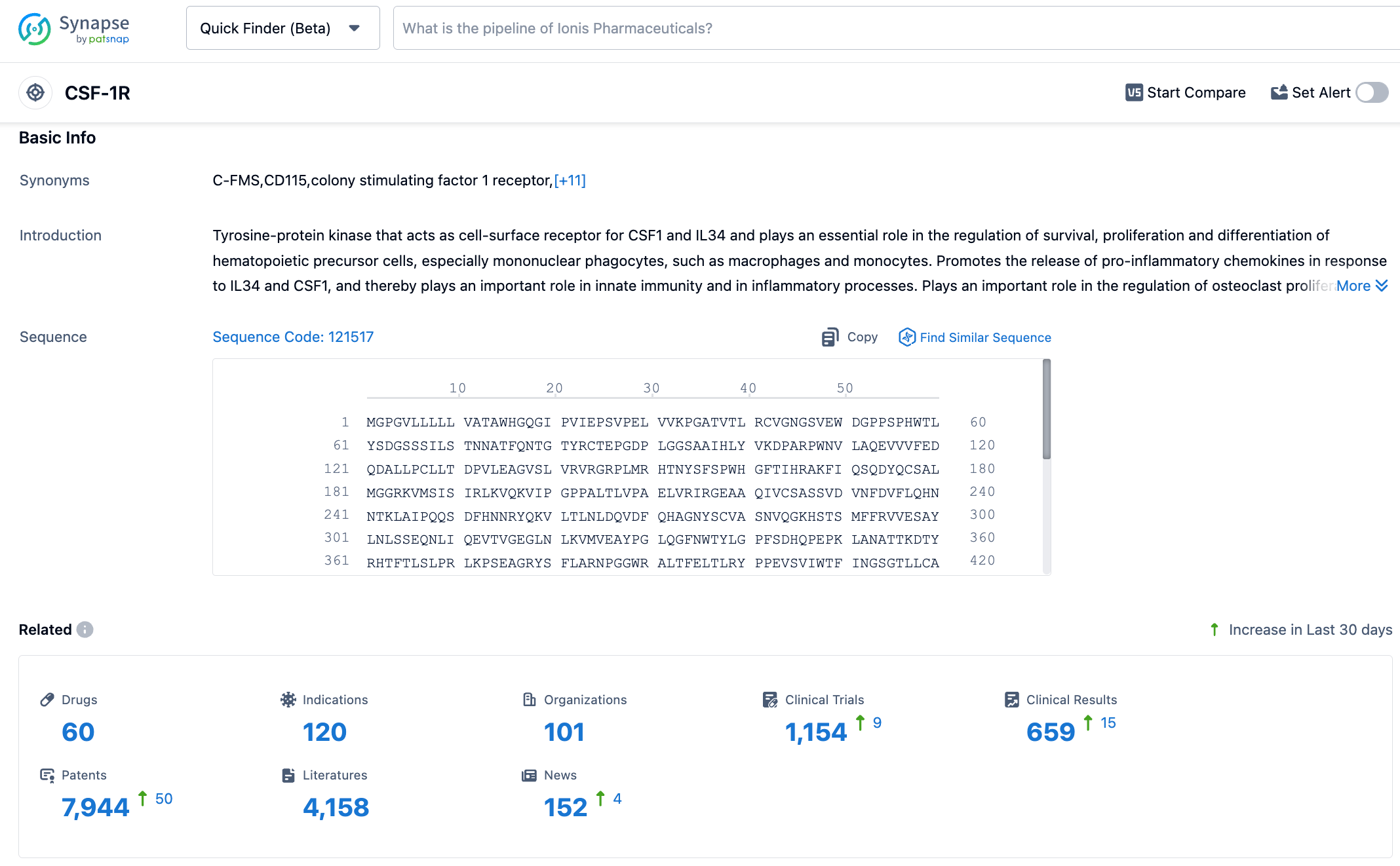
According to information disclosed by the Synapse database, as of November 1, 2023, there were 60 investigational drugs targeting CSF-1R, with 120 indications covered, being studied by 101 institutions, and with 1152 related clinical trials and as many as 7941 patents. CSF-1R is a receptor for the cytokine CSF-1 and is an important member of the receptor tyrosine kinase family, which is closely related to the development and progression of inflammation. In the tumor microenvironment (TME), CSF-1R and its ligand CSF-1 signaling can induce the differentiation and survival of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), thereby promoting tumor cell growth. We look forward to the early market approval of vimseltinib.