Decoding ajmaline: A Comprehensive Study of its R&D Trends and Mechanism on Drug Target
Ajmaline's R&D Progress
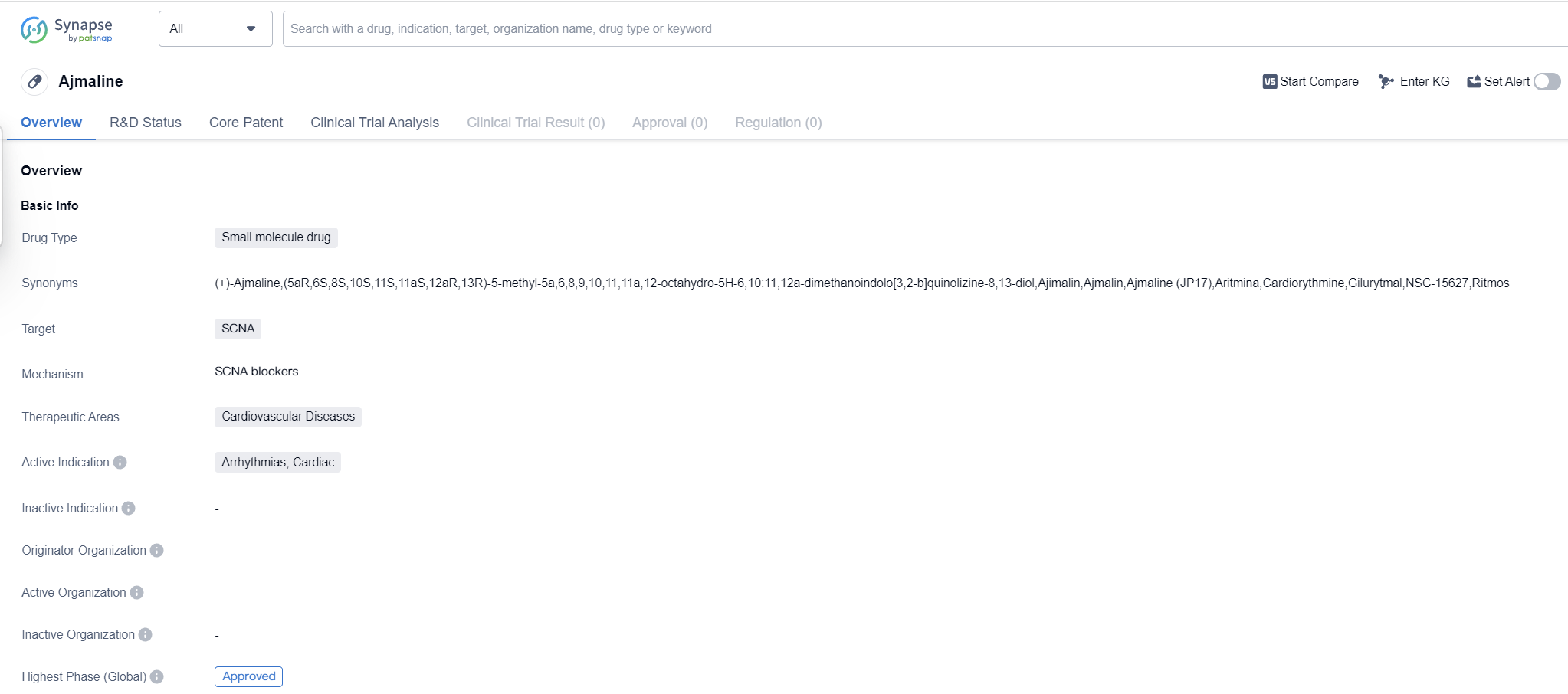
Ajmaline is a small molecule drug that targets the SCNA protein. It is primarily used in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases, specifically arrhythmias and cardiac conditions. The highest R&D phase of this drug is approved.
Ajmaline is classified as a small molecule drug, indicating that it is composed of low molecular weight compounds. Small molecule drugs are typically orally administered and can easily penetrate cell membranes, allowing for efficient distribution throughout the body.
The drug specifically targets the SCNA protein, which is involved in the regulation of sodium channels in the heart. By targeting SCNA, Ajmaline aims to modulate the activity of sodium channels, which play a crucial role in the generation and propagation of electrical signals in cardiac cells. This modulation can help in the management of arrhythmias and other cardiac conditions.
Therapeutically, Ajmaline is primarily used in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. It is particularly effective in managing arrhythmias, which are abnormal heart rhythms that can lead to serious complications if left untreated. By regulating sodium channels, Ajmaline helps restore normal electrical activity in the heart, thereby reducing the occurrence of arrhythmias.
The drug has successfully completed all phases of development and has received approval for global use. This indicates that it has undergone rigorous testing and has demonstrated safety and efficacy in clinical trials. Approval allows Ajmaline to be marketed and prescribed for the treatment of arrhythmias and other cardiac conditions worldwide.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for ajmaline: SCNA blockers
SCNA blockers are a type of drug that target and block sodium channels in the body. Sodium channels play a crucial role in the transmission of electrical signals in cells, including nerve cells. By blocking these channels, SCNA blockers can affect the function of the nervous system.
From a biomedical perspective, SCNA blockers are often used in the treatment of various conditions related to abnormal electrical signaling in the body. For example, they may be used to manage certain types of epilepsy or neuropathic pain. By blocking sodium channels, these drugs can help reduce the excessive or abnormal electrical activity in the nerves, leading to a decrease in symptoms.
It's important to note that SCNA blockers can have side effects, as they can also affect normal electrical signaling in the body. Therefore, their use should be carefully monitored and prescribed by healthcare professionals.
Drug Target R&D Trends for ajmaline
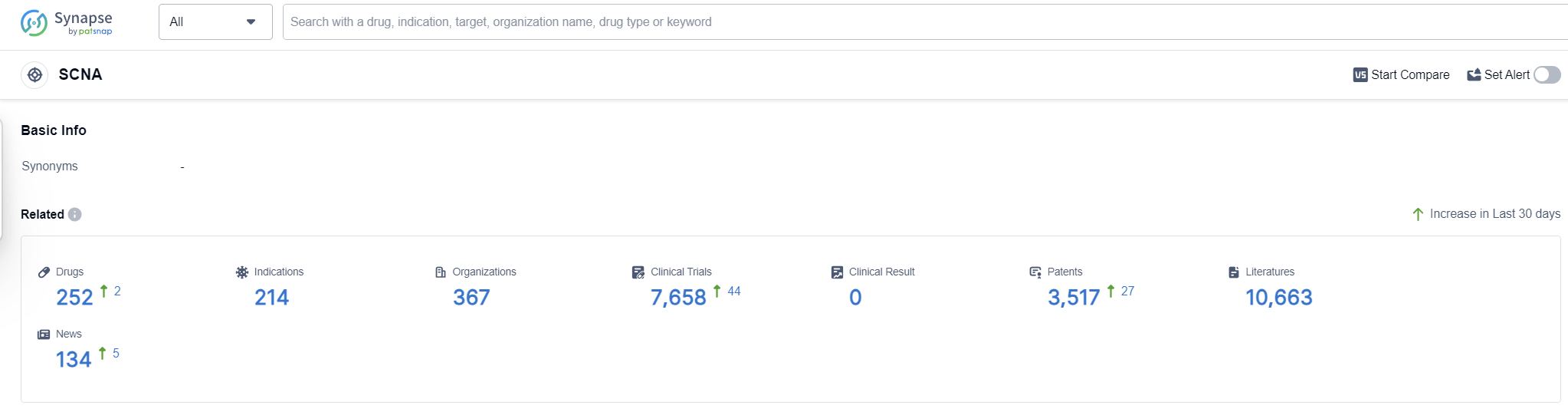
SCNAs, or Sodium Channel Navs, play a crucial role in the human body by facilitating the movement of sodium ions across cell membranes. These channels are responsible for generating and propagating electrical signals in various tissues, including the brain, heart, and muscles. By controlling the flow of sodium ions, SCNAs regulate the excitability and function of cells, enabling processes such as nerve transmission, muscle contraction, and cardiac rhythm. Dysregulation or mutations in SCNAs can lead to various disorders, including epilepsy, cardiac arrhythmias, and muscle disorders. Understanding the role of SCNAs is essential for developing targeted therapies and drugs to treat these conditions.
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 13 Sep 2023, there are a total of 252 SCNA drugs worldwide, from 367 organizations, covering 214 indications, and conducting 7658 clinical trials.
Overall, the analysis suggests a competitive landscape with diverse drug development efforts for the target SCNA. The future development of SCNA drugs is expected to focus on expanding indications, exploring innovative drug types, and further progress in countries like China.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Ajmaline is a small molecule drug that targets the SCNA protein and is used in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases, specifically arrhythmias and cardiac conditions. It has reached the highest phase of development, which is approval for global use. Ajmaline's mechanism of action involves modulating sodium channels to restore normal electrical activity in the heart. Its approval signifies its safety and efficacy in clinical trials, allowing for its widespread use in managing arrhythmias and other cardiac conditions.