Decoding cyclizine hydrochloride: A Comprehensive Study of its R&D Trends and Mechanism on Drug Target
Cyclizine hydrochloride's R&D Progress
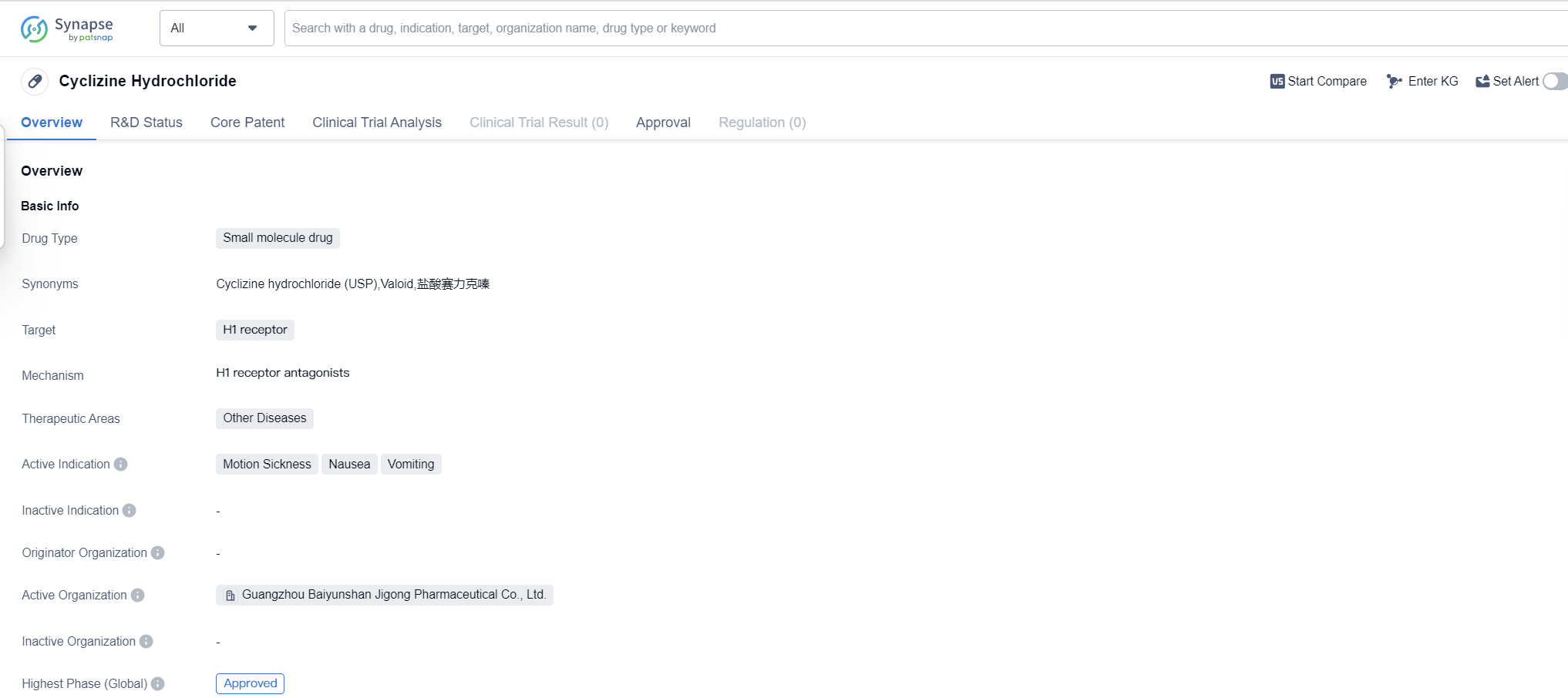
Cyclizine Hydrochloride is a small molecule drug that primarily targets the H1 receptor. It is used in the treatment of various conditions related to motion sickness, nausea, and vomiting. The drug has been approved for use in multiple countries, including the United States, and has been available since its first approval in 1953.
Cyclizine Hydrochloride belongs to the therapeutic area of other diseases, indicating its versatility in treating a range of conditions beyond its primary indications. As a small molecule drug, it is designed to interact with specific receptors in the body to produce the desired therapeutic effects.
The drug's primary target, the H1 receptor, is involved in various physiological processes, including the regulation of allergic responses and the transmission of signals related to motion sickness. By binding to this receptor, Cyclizine Hydrochloride can effectively alleviate symptoms associated with motion sickness, such as dizziness, nausea, and vomiting.
Cyclizine Hydrochloride has undergone rigorous testing and clinical trials to establish its safety and efficacy. It has reached the highest phase of development which is approved globally. The drug's approval in the United States in 1953 marked its initial entry into the pharmaceutical market.
Since its approval, Cyclizine Hydrochloride has been widely used to manage motion sickness and related symptoms. Its effectiveness in alleviating nausea and vomiting has made it a valuable treatment option for individuals experiencing these symptoms due to various causes.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for cyclizine hydrochloride: H1 receptor antagonists
H1 receptor antagonists, also known as H1 antihistamines, are a class of drugs that block the action of histamine at the H1 receptors. Histamine is a chemical released by the immune system during allergic reactions, causing symptoms such as itching, sneezing, and runny nose. By blocking the H1 receptors, H1 receptor antagonists help alleviate these allergy symptoms.
From a biomedical perspective, H1 receptor antagonists are commonly used to treat allergic conditions, including hay fever, allergic rhinitis, and urticaria. They work by binding to the H1 receptors on target cells, preventing histamine from binding and exerting its effects. This blocks the allergic response and reduces symptoms like itching, nasal congestion, and watery eyes.
H1 receptor antagonists can be further classified into two generations. First-generation H1 antihistamines, such as diphenhydramine and chlorpheniramine, have a sedating effect and can cause drowsiness. Second-generation H1 antihistamines, including cetirizine and loratadine, are less likely to cause sedation and are preferred for long-term use.
It's important to note that while H1 receptor antagonists are effective in managing allergy symptoms, they do not treat the underlying cause of allergies. They provide symptomatic relief by blocking the effects of histamine, but they do not alter the immune response or prevent future allergic reactions.
Drug Target R&D Trends for cyclizine hydrochloride
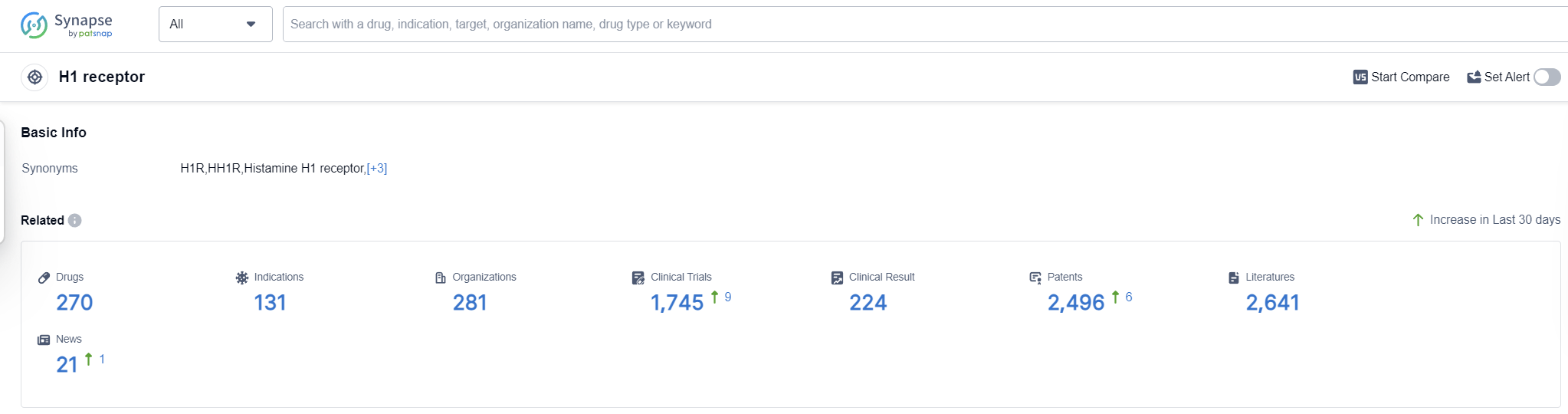
The H1 receptor, also known as the histamine H1 receptor, plays a crucial role in the human body. It is primarily found in smooth muscle cells, endothelial cells, and nerve cells. Activation of the H1 receptor by histamine leads to various physiological responses, including vasodilation, increased vascular permeability, bronchoconstriction, and stimulation of sensory nerve endings. These responses are involved in allergic reactions, inflammation, and immune responses. Antagonists of the H1 receptor, commonly known as antihistamines, are widely used to treat allergies, hay fever, and other conditions associated with excessive histamine release. Understanding the role of the H1 receptor is essential for developing effective treatments for allergic and inflammatory disorders.
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 16 Sep 2023, there are a total of 270 H1 receptor drugs worldwide, from 281 organizations, covering 131 indications, and conducting 1745 clinical trials.
Overall, the target H1 receptor presents opportunities for further research and development, particularly in addressing indications such as urticaria, pruritus, hypersensitivity, and conjunctivitis, allergic. The competitive landscape and future development of the target H1 receptor will continue to evolve as companies, drug types, and countries/locations invest in research and development efforts.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Cyclizine Hydrochloride is a small molecule drug that targets the H1 receptor. It is primarily used to treat motion sickness, nausea, and vomiting. The drug has been approved for use in multiple countries, including the United States, and has been available since its first approval in 1953. Its therapeutic versatility and established safety and efficacy make it a valuable option for individuals experiencing these symptoms.