Deep Scientific Insights on choline alfoscerate's R&D Progress, Mechanism of Action, and Drug Target
Choline alfoscerate's R&D Progress
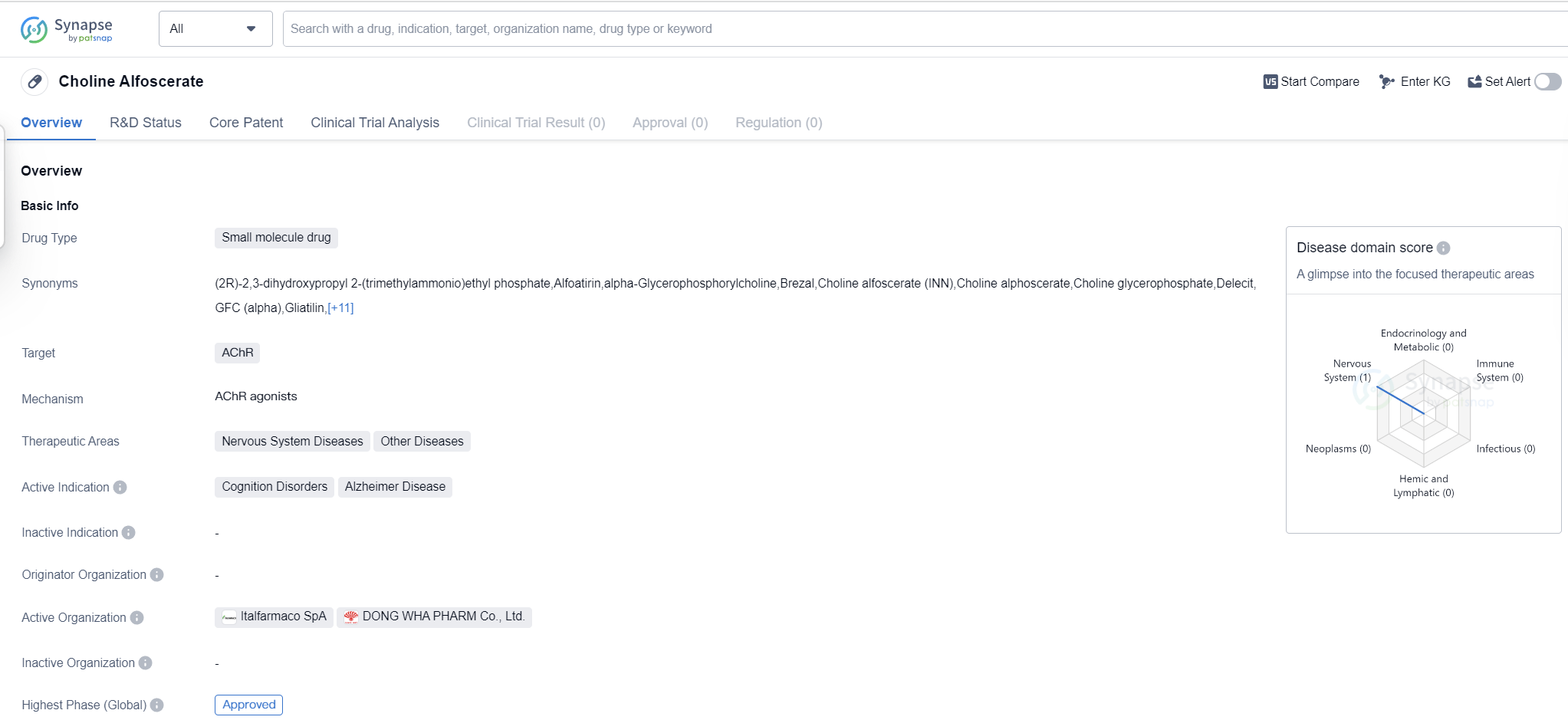
Choline Alfoscerate is a small molecule drug that targets the AChR (acetylcholine receptor). It is primarily used in the treatment of nervous system diseases and other diseases. The drug is specifically indicated for cognition disorders and Alzheimer's disease.
The highest R&D phase of this drug is approved. This means that it has successfully completed all necessary clinical trials and has been deemed safe and effective for use in patients. The drug was first approved globally in April 1996, with Italy being the country/location of the initial approval.
The approval of Choline Alfoscerate in 1996 highlights its long-standing presence in the pharmaceutical market. It has been used for over two decades to address cognitive disorders and Alzheimer's disease. This suggests that the drug has demonstrated consistent efficacy and safety profiles over an extended period.
As a small molecule drug, Choline Alfoscerate is likely to have a well-defined chemical structure, making it easier to manufacture and administer. This can contribute to its widespread availability and accessibility for patients in need.
The drug's specific targeting of the AChR indicates its mechanism of action. By interacting with this receptor, Choline Alfoscerate may enhance acetylcholine signaling in the brain, which is crucial for cognitive function. This mechanism of action aligns with its approved indications for cognition disorders and Alzheimer's disease, both of which involve impaired cognitive abilities.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for choline alfoscerate: AChR agonists
AChR agonists are substances that activate or stimulate the acetylcholine receptors (AChR) in the body. Acetylcholine receptors are proteins found on the surface of cells, particularly in the nervous system, and they play a crucial role in transmitting signals between nerve cells and muscle cells.
From a biomedical perspective, AChR agonists can have therapeutic applications in various conditions where enhancing cholinergic signaling is beneficial. For example, in the treatment of myasthenia gravis, an autoimmune disorder characterized by muscle weakness, AChR agonists can help improve muscle function by increasing the activation of acetylcholine receptors and enhancing neuromuscular transmission.
AChR agonists can also be used in research settings to study the function of acetylcholine receptors and their role in different physiological processes. By selectively activating these receptors, scientists can gain insights into the mechanisms underlying neurotransmission and muscle contraction.
Overall, AChR agonists are substances that interact with acetylcholine receptors to produce a stimulatory effect, and their use can have therapeutic and research applications in the field of biomedicine.
Drug Target R&D Trends for choline alfoscerate
The acetylcholine receptor (AChR) plays a crucial role in the human body as it is responsible for mediating the effects of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter involved in various physiological processes. AChR is a transmembrane protein found on the surface of cells, particularly in the nervous system, skeletal muscles, and other tissues. It functions as a ligand-gated ion channel, allowing the passage of ions across the cell membrane upon binding with acetylcholine. This receptor is essential for muscle contraction, nerve signal transmission, and cognitive functions. Dysregulation or dysfunction of AChR can lead to various disorders, including myasthenia gravis and Alzheimer's disease.
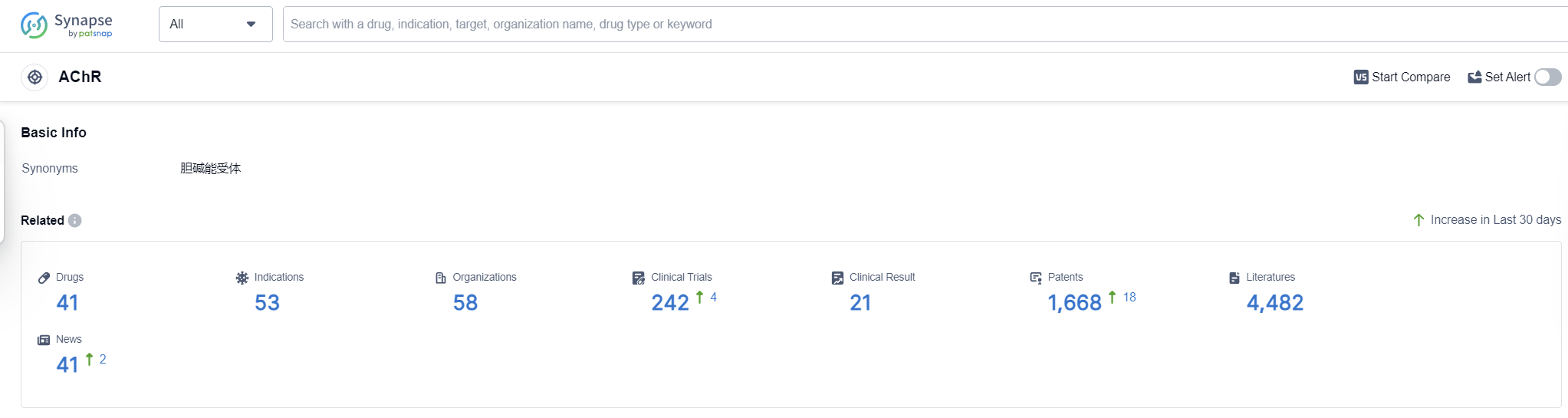
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 16 Sep 2023, there are a total of 41 AChR drugs worldwide, from 58 organizations, covering 53 indications, and conducting 242 clinical trials.
The analysis of the target AChR reveals a competitive landscape with multiple companies making significant progress in the development of drugs. The indications for these drugs cover a wide range of medical conditions, highlighting the potential therapeutic applications of drugs targeting AChR. Small molecule drugs are the most rapidly progressing drug type, indicating their potential as innovative therapies. The presence of biosimilars suggests intense competition around the innovative drugs. The United States, Japan, China, and the European Union are the leading countries/locations in the development of drugs targeting AChR, with China showing notable progress. Overall, the target AChR presents a promising opportunity for pharmaceutical companies and signifies the potential for future advancements in the treatment of various medical conditions.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
Overall, Choline Alfoscerate is an approved small molecule drug that targets the AChR and is primarily used in the treatment of nervous system diseases. Its active indications include cognition disorders and Alzheimer's disease. With its first approval dating back to 1996 in Italy, the drug has established a long history of use in addressing cognitive impairments.