Decoding Dextromethorphan polistirex: A Comprehensive Study of its R&D Trends and Mechanism on Drug Target
Dextromethorphan polistirex's R&D Progress
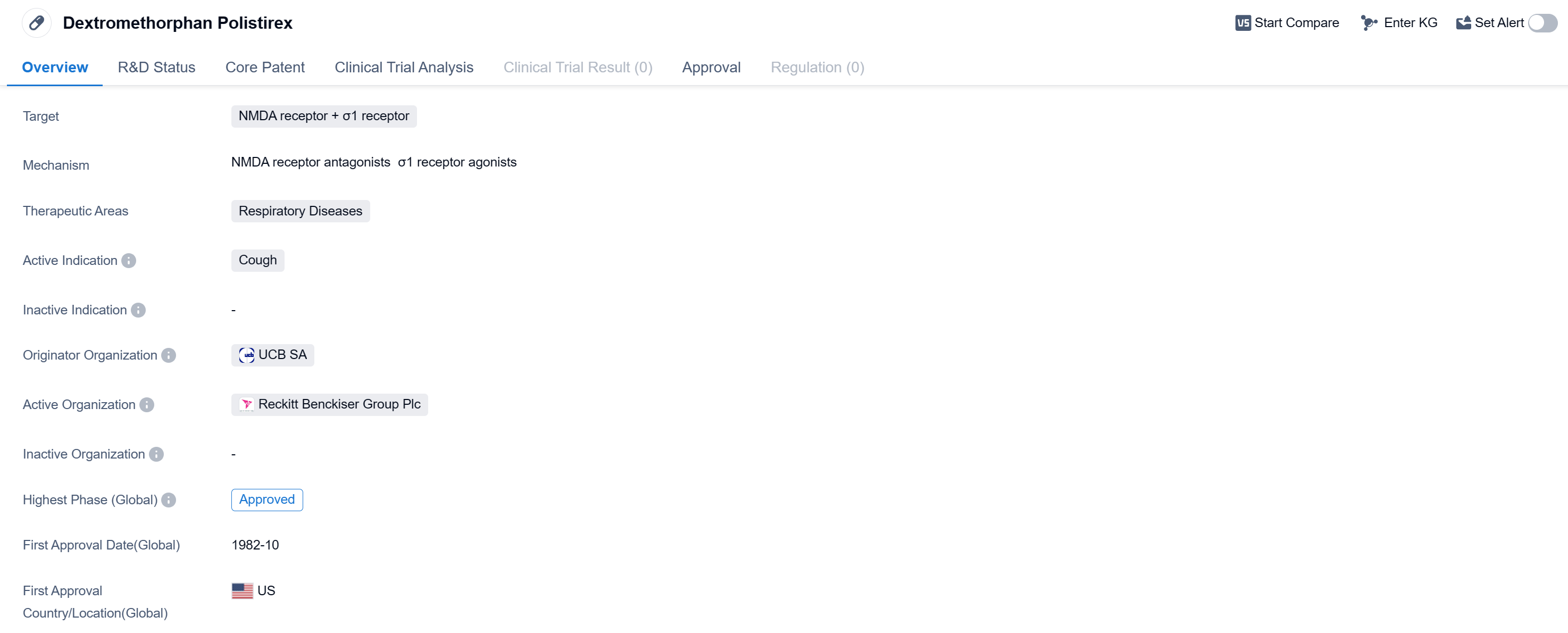
Dextromethorphan Polistirex is a small molecule drug that targets the NMDA receptor and σ1 receptor. It is primarily used in the treatment of respiratory diseases, specifically for the relief of cough symptoms. The drug was first approved in the United States in October 1982 and has since gained global approval.
Dextromethorphan Polistirex is an active ingredient that acts as a cough suppressant by affecting the signals in the brain that trigger the cough reflex. By targeting the NMDA receptor and σ1 receptor, it helps to reduce the urge to cough, providing relief to patients suffering from respiratory conditions.
The drug is classified as a small molecule drug, which means it has a low molecular weight and can easily penetrate cell membranes. This characteristic allows for efficient absorption and distribution within the body, enhancing its therapeutic effects.
UCB SA is the originator organization of Dextromethorphan Polistirex.
Since its first approval in 1982, Dextromethorphan Polistirex has been widely used in the treatment of cough associated with respiratory diseases. Its effectiveness in suppressing cough symptoms has made it a popular choice among healthcare professionals and patients alike.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Dextromethorphan polistirex: NMDA receptor antagonists and σ1 receptor agonists
NMDA receptor antagonists are a class of drugs that block or inhibit the activity of the NMDA receptor, which is a type of receptor found in the brain and spinal cord. The NMDA receptor is involved in the transmission of signals between nerve cells and plays a crucial role in processes such as learning, memory, and pain perception. By antagonizing or blocking the NMDA receptor, these drugs can modulate the activity of glutamate, a neurotransmitter that is associated with excitatory signaling in the brain.
From a biomedical perspective, NMDA receptor antagonists are primarily used in the treatment of conditions such as chronic pain, neuropathic pain, and certain psychiatric disorders like major depressive disorder and schizophrenia. By blocking the NMDA receptor, these drugs can help reduce excessive excitatory signaling in the brain, which may contribute to the symptoms of these conditions.
On the other hand, σ1 receptor agonists are drugs that activate or stimulate the activity of the σ1 receptor, which is a protein found in various tissues including the brain. The σ1 receptor is involved in regulating several cellular processes, including calcium signaling, neurotransmitter release, and cell survival.
From a biomedical perspective, σ1 receptor agonists have shown potential therapeutic effects in various conditions such as neurodegenerative diseases, depression, and neuropathic pain. By activating the σ1 receptor, these drugs can modulate cellular processes and potentially exert neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects.
In summary, NMDA receptor antagonists and σ1 receptor agonists are two different classes of drugs that have distinct mechanisms of action and potential therapeutic applications in biomedicine. NMDA receptor antagonists block the NMDA receptor to modulate glutamate signaling, while σ1 receptor agonists activate the σ1 receptor to influence various cellular processes.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Dextromethorphan polistirex
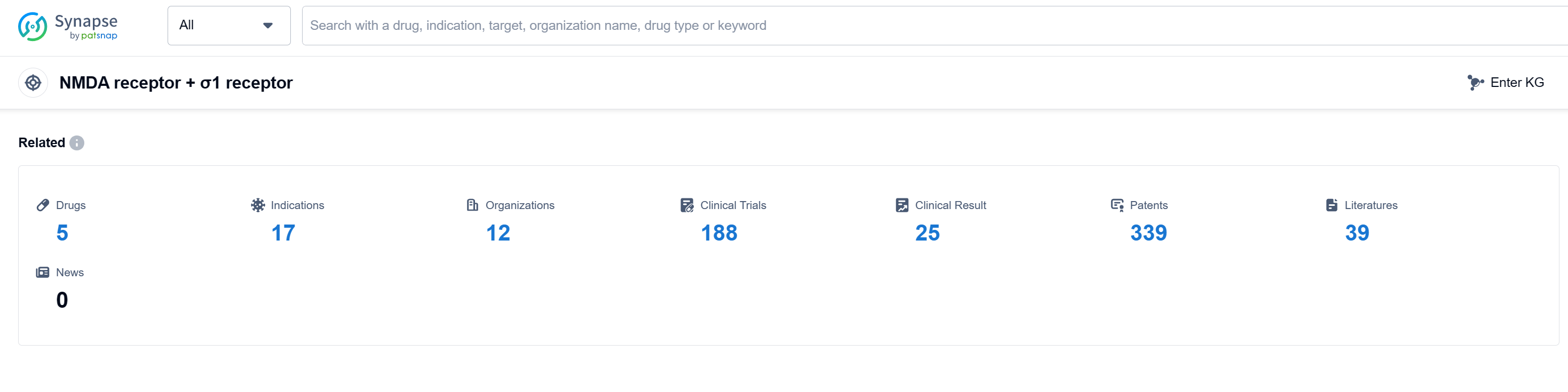
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 12 Sep 2023, there are a total of 5 NMDA receptor + σ1 receptor drugs worldwide, from 12 organizations, covering 17 indications, and conducting 188 clinical trials.
The current competitive landscape of the target NMDA receptor + σ1 receptor is characterized by the presence of multiple companies actively involved in research and development. Axsome Therapeutics, Inc. is leading in terms of development phase, with drugs in the approved, Phase 3, and Phase 2 stages. Indications such as cough, depressive disorder, and dementia due to Parkinson's disease have drugs approved under the target. Small molecule drugs are progressing rapidly, and the United States is the leading country in terms of drug development. Further research is needed to understand the specific progress in China. Overall, the target NMDA receptor + σ1 receptor shows promise for future development in the pharmaceutical industry.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Dextromethorphan Polistirex is a small molecule drug that targets the NMDA receptor and σ1 receptor. It is primarily used for the relief of cough symptoms in patients with respiratory diseases. Developed by UCB SA, the drug has gained global approval and has been in use since 1982. Its efficacy in suppressing cough has made it a valuable treatment option for patients worldwide.