Deep Scientific Insights on Deutetrabenazine's R&D Progress, Mechanism of Action, and Drug Target
Deutetrabenazine's R&D Progress
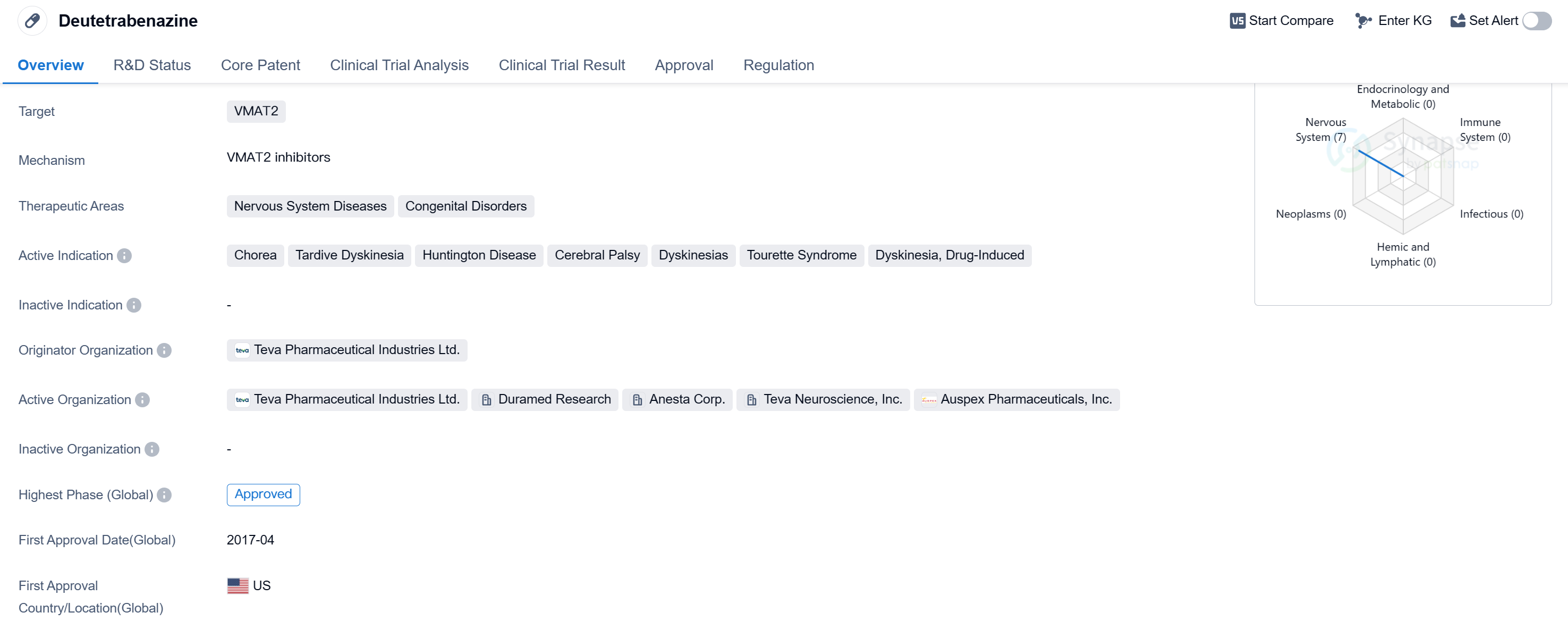
Deutetrabenazine is a small molecule drug that primarily targets the vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2). It is used in the treatment of various nervous system diseases and congenital disorders. The drug has been approved for use in several indications, including chorea, tardive dyskinesia, Huntington's disease, cerebral palsy, dyskinesias, Tourette syndrome, and drug-induced dyskinesia.
Deutetrabenazine was developed by Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., a prominent pharmaceutical organization. It received its first approval in the United States in April 2017, making it available for patients in need. The drug has also obtained approval in China, indicating its global recognition and potential for widespread use.
In terms of regulatory status, deutetrabenazine has undergone priority review, suggesting its significance in addressing unmet medical needs. It has also been classified as an overseas new drug urgently needed in clinical settings, highlighting its potential to address critical healthcare challenges. Additionally, the drug has been granted breakthrough therapy designation, indicating its potential to provide substantial benefits over existing treatments. Furthermore, deutetrabenazine has been designated as an orphan drug, indicating its intended use in the treatment of rare diseases.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Deutetrabenazine: VMAT2 inhibitors
VMAT2 inhibitors are a type of drug that target and inhibit the vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2) protein. From a biomedical perspective, VMAT2 is a protein found in the membranes of synaptic vesicles in neurons. It plays a crucial role in the packaging and transport of neurotransmitters, such as dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine, into these vesicles.
By inhibiting VMAT2, these inhibitors reduce the uptake of neurotransmitters into synaptic vesicles, leading to decreased release of these neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. This ultimately affects the signaling between neurons and can have various effects on the central nervous system.
VMAT2 inhibitors have been primarily studied and used in the treatment of certain neurological and psychiatric disorders, such as Parkinson's disease and schizophrenia. In Parkinson's disease, these inhibitors help to alleviate symptoms by reducing the excessive release of dopamine, which is responsible for the motor symptoms associated with the condition. In schizophrenia, VMAT2 inhibitors can help modulate the levels of neurotransmitters involved in the disease's pathophysiology.
It's important to note that VMAT2 inhibitors should be used under medical supervision due to their potential side effects and interactions with other medications.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Deutetrabenazine
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 13 Sep 2023, there are a total of 27 VMAT2 drugs worldwide, from 61 organizations, covering 22 indications, and conducting 91 clinical trials.
The analysis of the target VMAT2 reveals a competitive landscape with multiple companies actively involved in R&D. Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc. is leading in terms of the highest stage of development, with drugs in various phases. The indications for the approved drugs under this target are diverse, covering a range of diseases and disorders. Small molecule drugs and Diagnostic radiopharmaceuticals are the most rapidly progressing drug types. China is emerging as a key player in the development of drugs under the target VMAT2, with the highest number of approved drugs. Overall, the target VMAT2 shows promising potential for future development and innovation in the pharmaceutical industry.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
Overall, deutetrabenazine is a small molecule drug that targets VMAT2 and has been approved for various indications related to nervous system diseases and congenital disorders. Developed by Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., it has received approvals in both the United States and China. The drug has undergone priority review, breakthrough therapy designation, and has been designated as an orphan drug, emphasizing its potential to address unmet medical needs and provide significant benefits to patients.